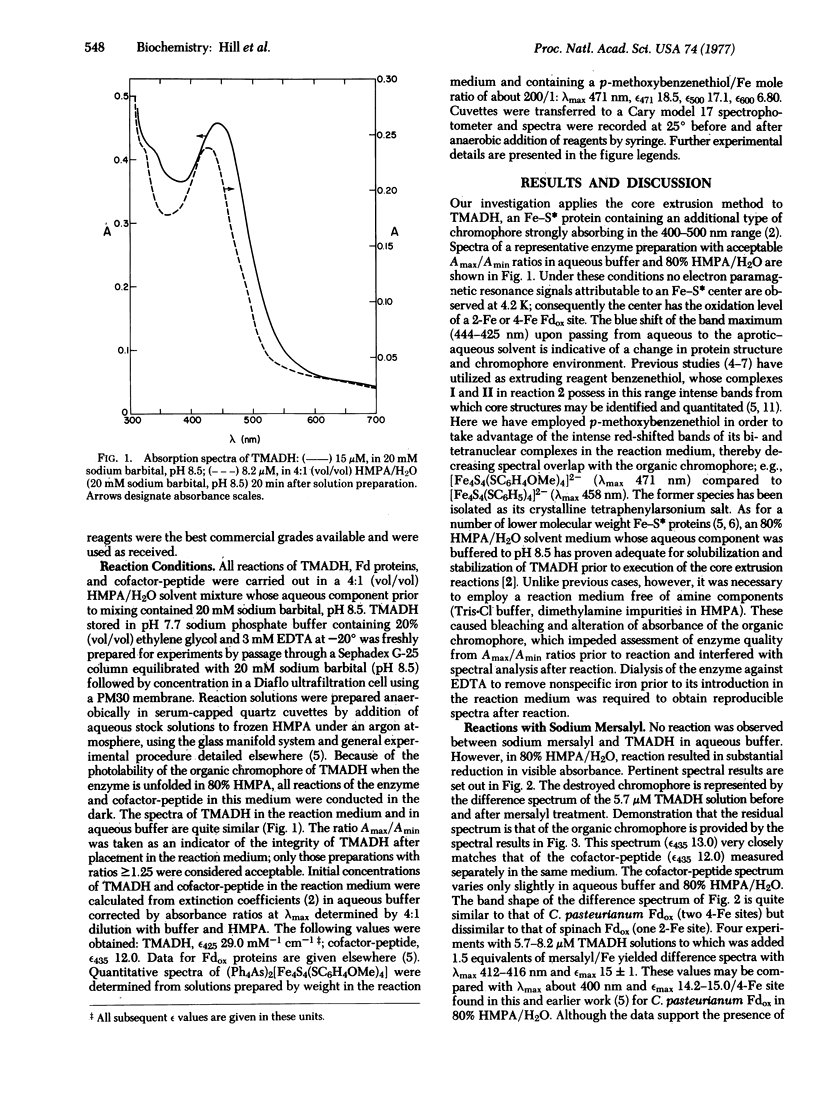
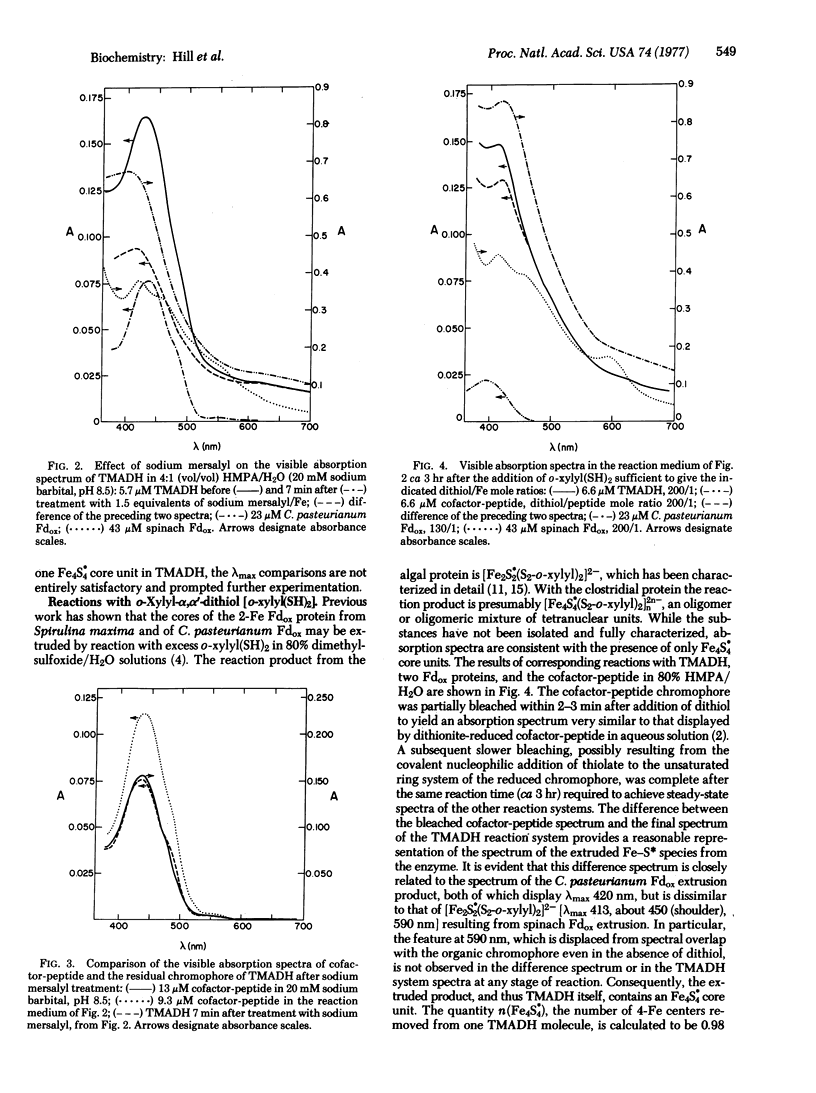
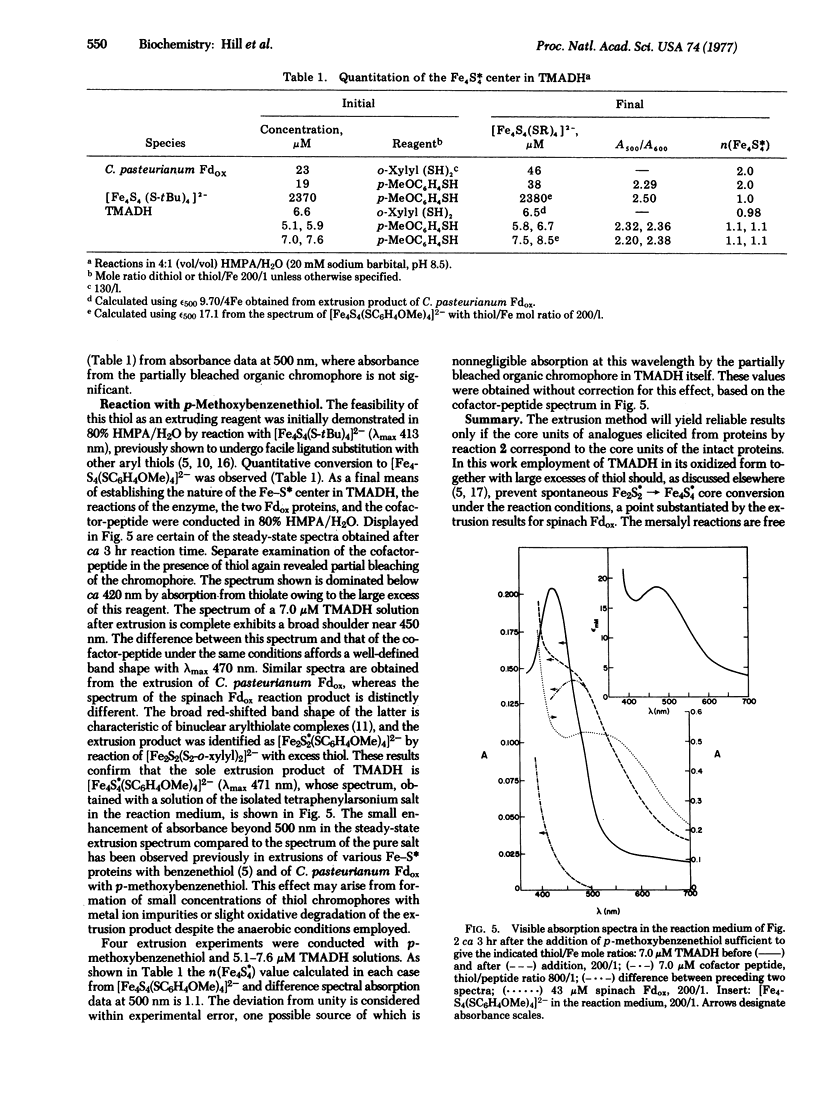
Abstract
Trimethylamine dehydrogenase [trimethylamine:(acceptor) oxidoreductase (demethylating), EC 1.5.99.7] from a facultative methylotroph bacterium has a molecular weight of 147,000 and contains two types of prosthetic groups, one a covalently bound organic chromophore of uncertain structure and the other containing iron and labile sulfur (S*). The structure of the Fe-S* center has been investigated by reactions of the enzyme with sodium mersalyl, o-xylyl-alpha,alpha'-dithiol, and p-methoxybenzenethiol in a 4:1 vol/vol hexamethylphosphoramide/water reaction medium, which destabilizes tertiary structure. Mersalyl treatment results in reduction of visible absorbance consistent with the presence of a 4-Fe center of the ferredoxin type. Reaction with thiols effects partial bleaching of the organic chromophore, as established by separate studies of a detached chromophore peptide, and results in removal (extrusion) of the core unit of the Fe-s* center in the form of the complexes [Fe4S*4(S2-o-xylyl)2]n2n- and [Fe4S*4(SC6H4OMe)4]2-, which were identified by absorption spectra. These results, in conjunction with control extrusion reactions of oxidized ferredoxins from spinach and Clostridium pasteurianum, establish that trimethylamine dehydrogenase contains one Fe4S*4 core unit most probably present as a ferredoxin-type, cysteinate-ligated cluster [Fe4S*4(S-Cys)4].
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aparicio P. J., Knaff D. B., Malkin R. The role of an iron-sulfur center and siroheme in spinach nitrite reductase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Jul;169(1):102–107. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90321-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Averill B. A., Herskovitz T., Holm R. H., Ibers J. A. Synthetic analogs of the active sites of iron-sulfur proteins. II. Synthesis and structure of the tetra(mercapto-m 3 -sulfido-iron) clusters, (Fe 4 S 4 (SR) 4 ) 2- . J Am Chem Soc. 1973 May 30;95(11):3523–3534. doi: 10.1021/ja00792a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beinert H., Ackrell B. A., Kearney E. B., Singer T. P. Iron-sulfur components of succinate dehydrogenase: stoichiometry and kinetic behavior in activated preparations. Eur J Biochem. 1975 May;54(1):185–194. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb04128.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colby J., Zatman L. J. Purification and properties of the trimethylamine dehydrogenase of bacterium 4B6. Biochem J. 1974 Dec;143(3):555–567. doi: 10.1042/bj1430555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DePamphilis B. V., Averill B. A., Herskovitz T., Que L., Jr, Holm R. H. Synthetic analogs of the active sites of iron-sulfur proteins. VI. Spectral and redox characteristics of the tetranuclear clusters (Fe4S4(SR)4).2-. J Am Chem Soc. 1974 Jun 26;96(13):4159–4167. doi: 10.1021/ja00820a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erbes D. L., Burris R. H., Orme-Johnson W. H. On the iron-sulfur cluster in hydrogenase from Clostridium pasteurianum W5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):4795–4799. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.4795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard J. B., Lorsbach T., Que L. Iron-sulfur clusters and cysteine distribution in a ferredoxin from Azotobacter vinelandii. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 May 17;70(2):582–588. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)91087-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen L. H. X-ray structural studies of ferredoxin and related electron carriers. Annu Rev Biochem. 1974;43(0):461–507. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.43.070174.002333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOVENBERG W., BUCHANAN B. B., RABINOWITZ J. C. STUDIES ON THE CHEMICAL NATURE OF CLOSTRIDIAL FERREDOXIN. J Biol Chem. 1963 Dec;238:3899–3913. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohnishi T., Lim J., Winter D. B., King T. E. Thermodynamic and EPR characteristics of a HiPIP-type iron-sulfur center in the succinate dehydrogenase of the respiratory chain. J Biol Chem. 1976 Apr 10;251(7):2105–2109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orme-Johnson W. H. Iron-sulfur proteins: structure and function. Annu Rev Biochem. 1973;42(0):159–204. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.42.070173.001111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Que L., Jr, Bobrik M. A., Ibers J. A., Holm R. H. Synthetic analogs of the active sites of iron-sulfur proteins. VII. Ligand substitution reactions of the tetranuclear clusters (Fe4S4(SR)4)2- and the structure of ((CH3)4N)2(Fe4S4(SC6H5)4). J Am Chem Soc. 1974 Jun 26;96(13):4168–4178. doi: 10.1021/ja00820a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Que L., Jr, Holm R. H., Mortenson L. E. Letter: Extrusion of Fe2S2 and Fe4S4 cores from the active sites of ferredoxin proteins. J Am Chem Soc. 1975 Jan 22;97(2):463–464. doi: 10.1021/ja00835a064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel L. M., Davis P. S. Reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate-sulfite reductase of enterobacteria. IV. The Escherichia coli hemoflavoprotein: subunit structure and dissociation into hemoprotein and flavoprotein components. J Biol Chem. 1974 Mar 10;249(5):1587–1598. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steenkamp D. J., Mallinson J. Trimethylamine dehydrogenase from a methylotrophic bacterium. I. Isolation and steady-state kinetics. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 May 13;429(3):705–719. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(76)90319-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steenkamp D. J., Singer T. P. On the presence of a novel covalently bound oxidation-reduction cofactor, iron and labile sulfur in trimethylamine dehydrogenase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Aug 23;71(4):1289–1295. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90794-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van de Bogart M., Beinert H. Micro methods for the quantitative determination of iron and copper in biological material. Anal Biochem. 1967 Aug;20(2):325–334. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(67)90038-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


