Abstract
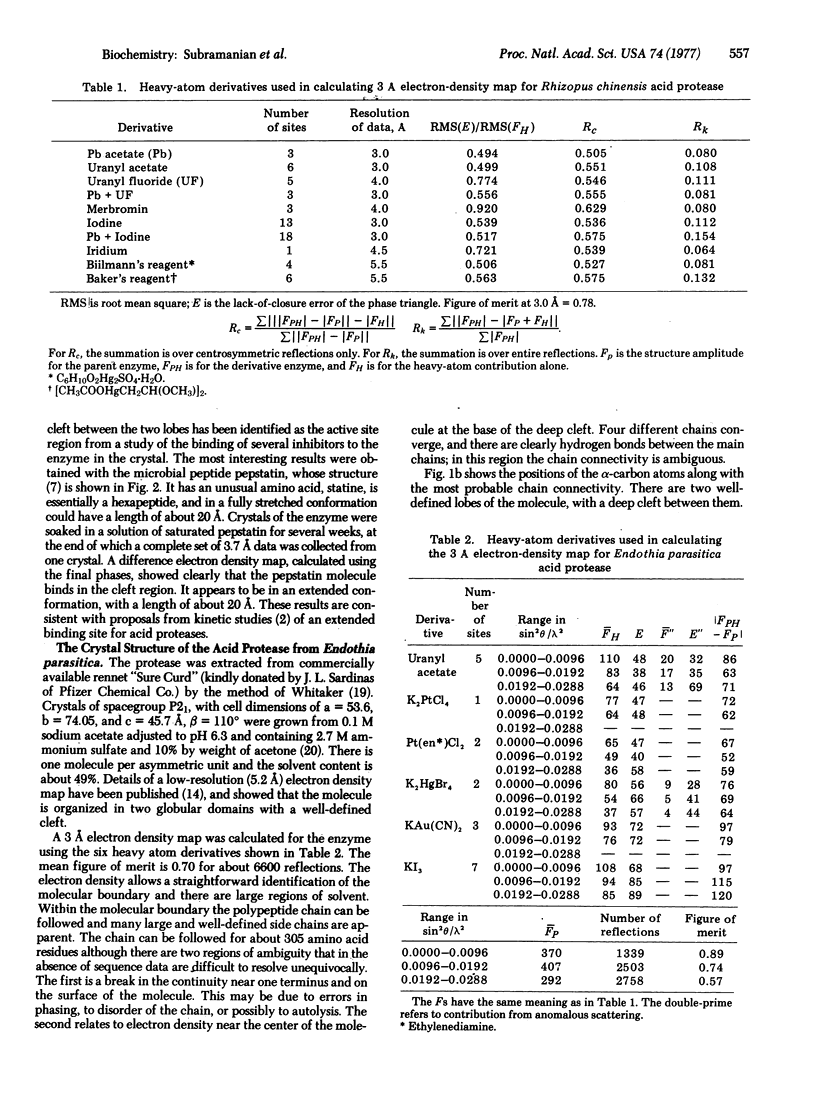
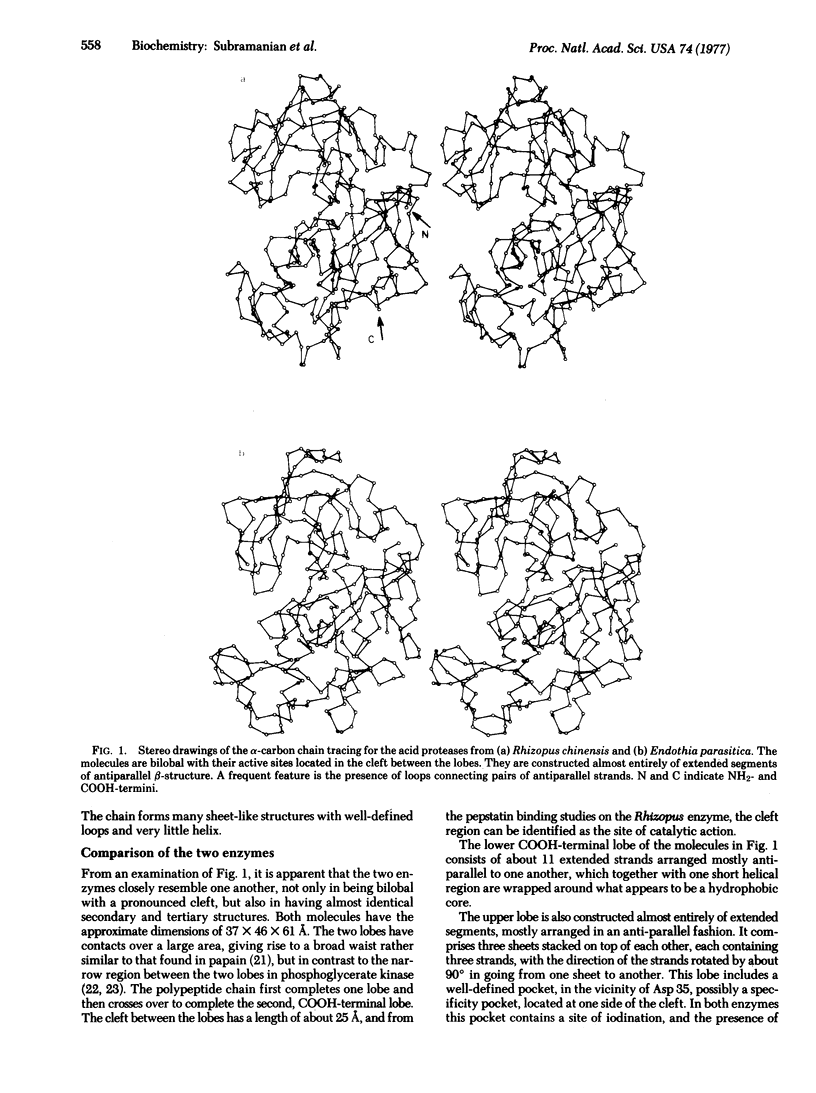
The molecular structures of two fungal acid proteases at 3 A resolution have been compared, and found to have similar secondary and tertiary folding. These enzymes are bilobal and have a pronounced cleft between the two lobes. This cleft has been identified as the active site region from inhibitor binding studies. The results of the comparison are discussed in terms of homology among the acid proteases in general.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aoyagi T., Kunimoto S., Morishima H., Takeuchi T., Umezawa H. Effect of pepstatin on acid proteases. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1971 Oct;24(10):687–694. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.24.687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aoyagi T., Morishima H., Nishizawa R., Kunimoto S., Takeuchi T. Biological activity of pepstatins, pepstanone A and partial peptides on pepsin, cathepsin D and renin. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1972 Dec;25(12):689–694. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.25.689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake C. C., Evans P. R. Structure of horse muscle phosphoglycerate kinase. Some results on the chain conformation, substrate binding and evolution of the molecule from a 3 angstrom Fourier map. J Mol Biol. 1974 Apr 25;84(4):585–601. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90118-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant T. N., Watson H. C., Wendell P. L. Structure of yeast phosphoglycerate kinase. Nature. 1974 Jan 4;247(5435):14–17. doi: 10.1038/247014a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drenth J., Jansonius J. N., Koekoek R., Swen H. M., Wolthers B. G. Structure of papain. Nature. 1968 Jun 8;218(5145):929–932. doi: 10.1038/218929a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fruton J. S. The mechanism of the catalytic action of pepsin and related acid proteinases. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1976;44:1–36. doi: 10.1002/9780470122891.ch1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu I. N., Hofmann T., Nyburg S. C. The crystal structure of penicillopesin at 6 A resolution. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Sep 7;72(1):363–368. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)91002-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins J. A., Blundell T. L., Tickle I. J., Ungaretti L. The low resolution structure analysis of an acid proteinase from Endothia parasitica. J Mol Biol. 1975 Dec 25;99(4):583–590. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80173-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moews P. C., Bunn C. W. An x-ray crystallographic study of the rennin-like enzyme of Endothia parasitica. J Mol Biol. 1970 Dec 14;54(2):395–397. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90439-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen V. B., Foltmann B. Amino-acid sequence of the peptide segment liberated during activation of prochymosin (prorennin). Eur J Biochem. 1975 Jun 16;55(1):95–103. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02141.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajagopalan T. G., Stein W. H., Moore S. The inactivation of pepsin by diazoacetylnorleucine methyl ester. J Biol Chem. 1966 Sep 25;241(18):4295–4297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sepulveda P., Jackson K. W., Tang J. The amino terminal sequences of acid proteases-human pepsin and gastricsin and the protease of Rhizopus chinensis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Apr 21;63(4):1106–1112. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90683-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subramanian E., Swan I. D., Davies D. R. The crystal at 5.5A resolution of an acid-protease from Rhizopus chinensis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Feb 9;68(3):875–880. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)91226-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi K., Chang W. J. Specific chemical modifications of acid proteases in the presence and absence of pepstatin. J Biochem. 1973 Mar;73(3):675–677. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a130129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang J. Specific and irreversible inactivation of pepsin by substrate-like epoxides. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jul 25;246(14):4510–4517. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umezawa H., Aoyagi T., Morishima H., Matsuzaki M., Hamada M. Pepstatin, a new pepsin inhibitor produced by Actinomycetes. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1970 May;23(5):259–262. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.23.259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]