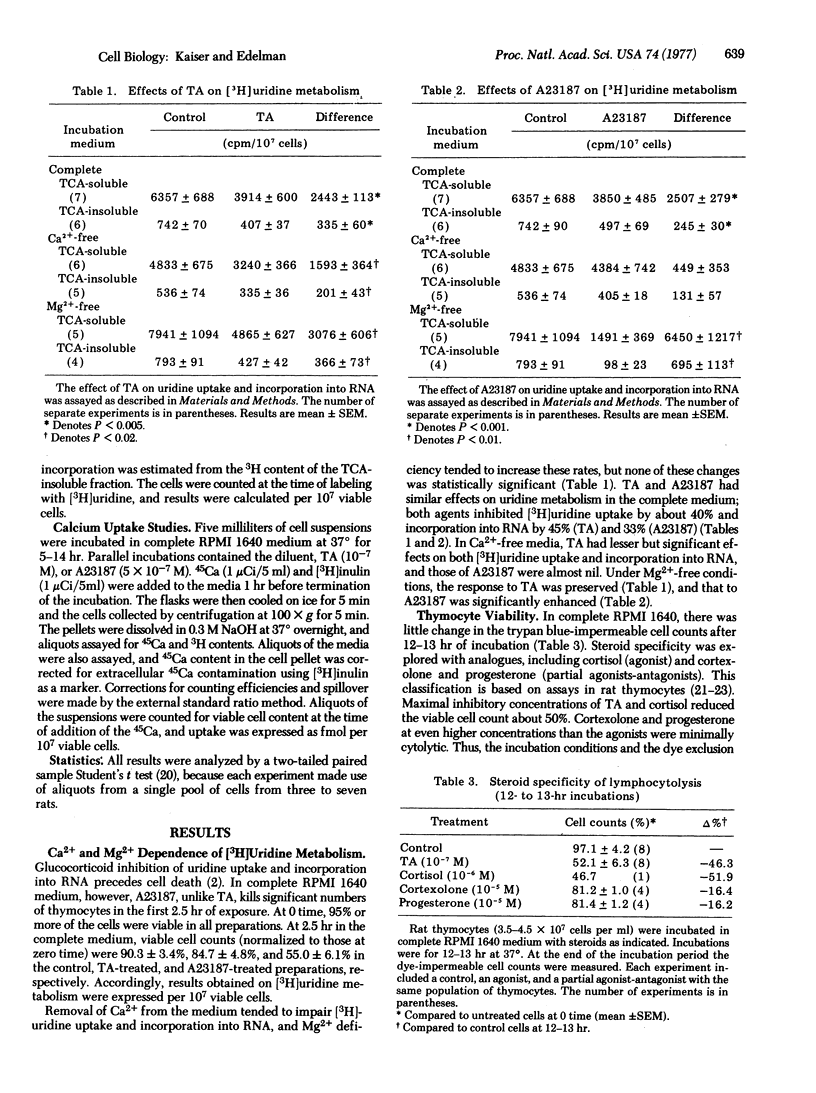
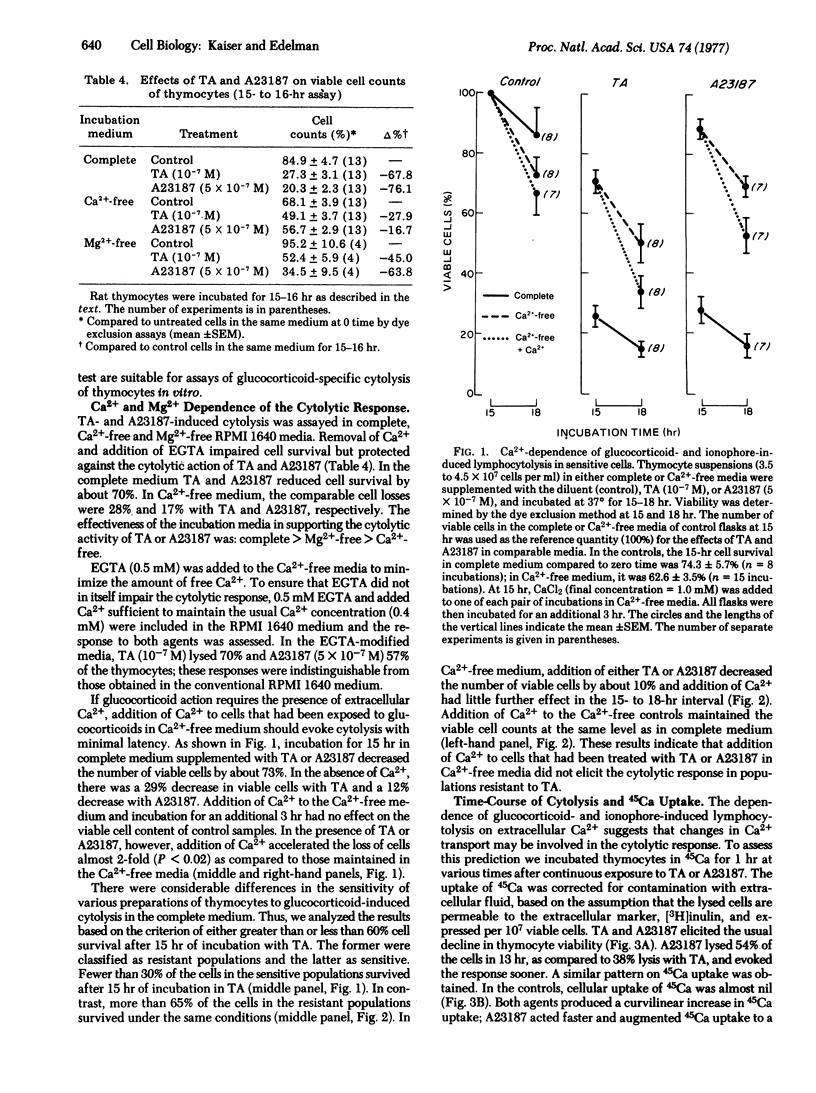
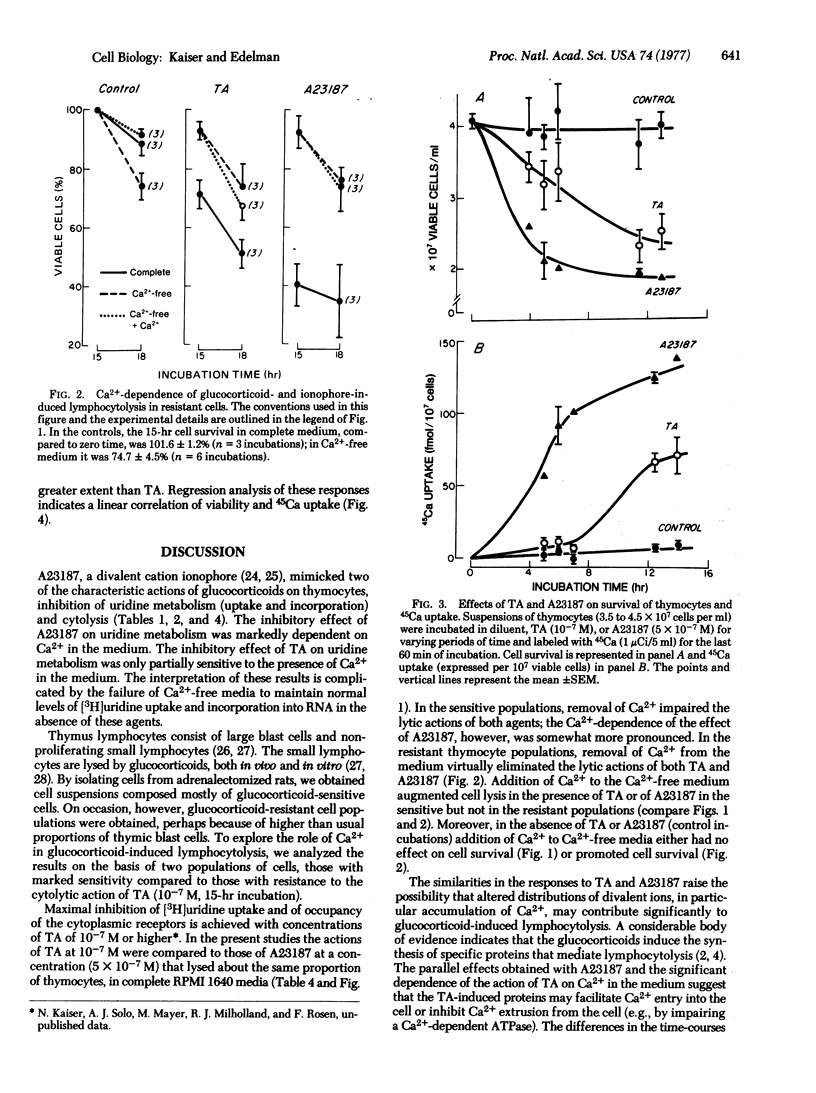
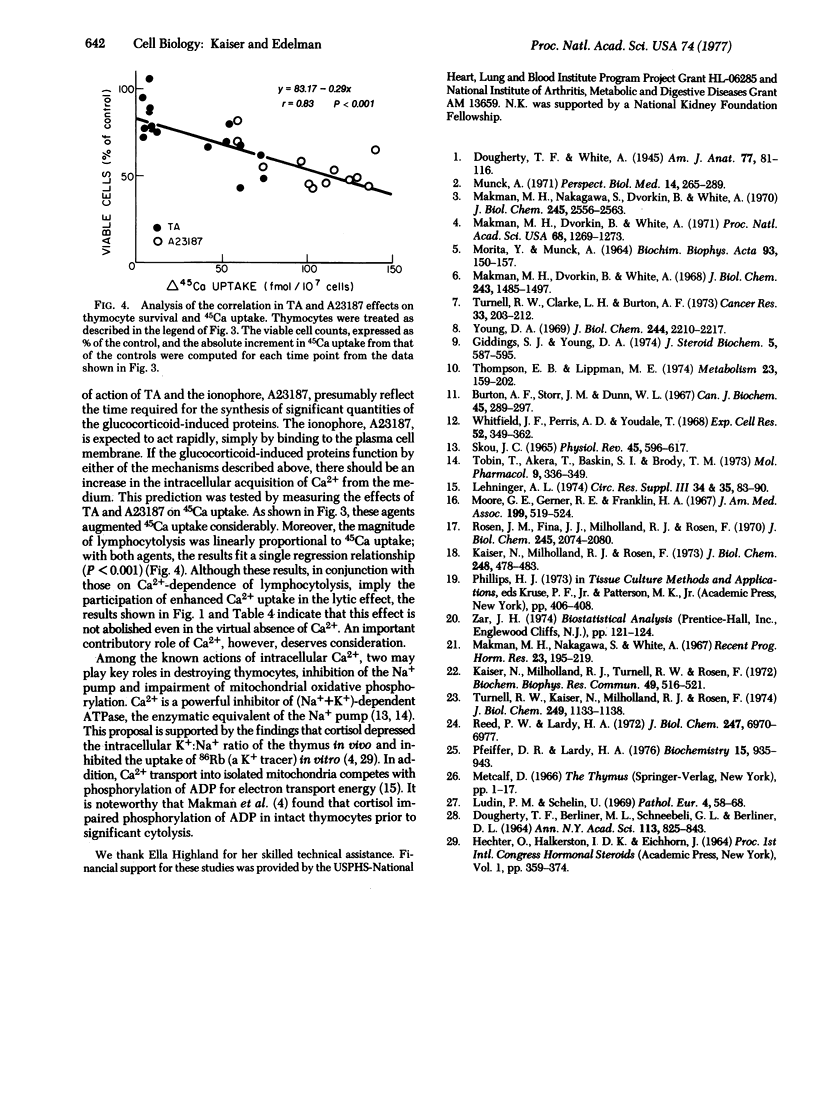
Abstract
A potent glucocorticoid, triamcinolone acetonide (9alpha-fluoro-11beta, 16alpha,17alpha, 21-tetrahydroxypregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione-16,17-acetonide) and a divalent cation ionophore (A23187) had similar effects in vitro on [3H]uridine uptake and on lysis of thymocytes of adrenalectomized rats. Removal of Ca2+ from the medium blunted the cytolytic action of triamcinolone acetonide and virtually eliminated that of A23187. In Ca2+-free media, treatment of the thymocytes for 15 hr with triamcinolone acetonide or A23187 followed by re-introduction of Ca2+ resulted in a rapid decrease in cell survival. Based on the time courses of the responses, triamcinolone acetonide and A23187 evoked proportionate increases in 45Ca uptake and lysis of the thymocytes. These findings implicate enhanced Ca2+ uptake in glucocorticoid-dependent lymphocytolysis.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burton A. F., Storr J. M., Dunn W. L. Cytolytic action of corticosteroids on thymus and lymphoma cells in vitro. Can J Biochem. 1967 Feb;45(2):289–297. doi: 10.1139/o67-032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOUGHERTY T. F., BERLINER M. L., SCHNEEBELI G. L., BERLINER D. L. HORMONAL CONTROL OF LYMPHATIC STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Feb 28;113:825–843. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb40707.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giddings S. J., Young D. A. An in vitro effect of physiological levels of cortisol and related steroids on the structural integrity of the nucleus in rat thymic lymphocytes as measured by resistance to lysis. J Steroid Biochem. 1974 Oct;5(6):587–595. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(74)90110-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser N., Milholland R. J., Rosen F. Glucocorticoid-binding macromolecules in rat and mouse thymocytes. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jan 25;248(2):478–483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser N., Milholland R. J., Turnell R. W., Rosen F. Cortexolone: binding to glucocorticoid receptors in rat thymocytes and mechanism of its antiglucocorticoid action. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Oct 17;49(2):516–521. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90441-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehninger A. L. Ca2+ transport by mitochondria and its possible role in the cardiac contraction-relaxation cycle. Circ Res. 1974 Sep;35 (Suppl 3):83–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundin P. M., Schelin U. The effect of steroids on the histology and ultrastructure of lymphoid tissue. 3. Thymus in prolonged steroid induced involution. Pathol Eur. 1969;4(1):58–68. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORITA Y., MUNCK A. EFFECT OF GLUCOCORTICOIDS IN VIVO AND IN VITRO ON NET GLUCOSE UPTAKE AND AMINO ACID INCORPORATION BY RAT-THYMUS CELLS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Oct 9;93:150–157. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(64)90269-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makman M. H., Dvorkin B., White A. Evidence for induction by cortisol in vitro of a protein inhibitor of transport and phosphorylation processes in rat thymocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jun;68(6):1269–1273. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.6.1269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makman M. H., Dvorkin B., White A. Influence of cortisol on the utilization of precursors of nucleic acids and protein by lymphoid cells in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1968 Apr 10;243(7):1485–1497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makman M. H., Nakagawa S., Dvorkin B., White A. Inhibitory effects of cortisol and antibiotics on substrate entry and ribonucleic acid synthesis in rat thymocytes in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1970 May 25;245(10):2556–2563. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makman M. H., Nakagawa S., White A. Studies of the mode of action of adrenal steroids on lymphocytes. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1967;23:195–227. doi: 10.1016/b978-1-4831-9826-2.50008-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore G. E., Gerner R. E., Franklin H. A. Culture of normal human leukocytes. JAMA. 1967 Feb 20;199(8):519–524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munck A. Glucocorticoid inhibition of glucose uptake by peripheral tissues: old and new evidence, molecular mechanisms, and physiological significance. Perspect Biol Med. 1971 Winter;14(2):265–269. doi: 10.1353/pbm.1971.0002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeiffer D. R., Lardy H. A. Ionophore A23187: the effect of H+ concentration on complex formation with divalent and monovalent cations and the demonstration of K+ transport in mitochondria mediated by A23187. Biochemistry. 1976 Mar 9;15(5):935–943. doi: 10.1021/bi00650a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed P. W., Lardy H. A. A23187: a divalent cation ionophore. J Biol Chem. 1972 Nov 10;247(21):6970–6977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen J. M., Fina J. R., Milholland J., Rosen F. Inhibition of glucose uptake in lymphosarcoma P1798 by cortisol and its relationship to the biosynthesis of deoxyribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1970 Apr 25;245(8):2074–2080. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SKOU J. C. ENZYMATIC BASIS FOR ACTIVE TRANSPORT OF NA+ AND K+ ACROSS CELL MEMBRANE. Physiol Rev. 1965 Jul;45:596–617. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1965.45.3.596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson E. B., Lippman M. E. Mechanism of action of glucocorticoids. Metabolism. 1974 Feb;23(2):159–202. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(74)90113-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobin T., Akera T., Baskin S. I., Brody T. M. Calcium ion and sodium- and potassium-dependent adenosine triphosphatase: its mechanism of inhibition and identification of the E 1 -P intermediate. Mol Pharmacol. 1973 May;9(3):336–349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turnell R. W., Clarke L. H., Burton A. F. Studies on the mechanism of corticosteroid-induced lymphocytolysis. Cancer Res. 1973 Feb;33(2):203–212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turnell R. W., Kaiser N., Milholland R. J., Rosen F. Glucocorticoid receptors in rat thymocytes. Interactions with the antiglucocorticoid cortexolone and mechanism of its action. J Biol Chem. 1974 Feb 25;249(4):1133–1138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitfield J. F., Perris A. D., Youdale T. Destruction of the nuclear morphology of thymic lymphocytes by the corticosteroid cortisol. Exp Cell Res. 1968 Oct;52(2):349–362. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(68)90476-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young D. A. Glucocorticoid action on rat thymus cells. Interrelationships between carbohydrate, protein, and adenine nucleotide metabolism and cortisol effects on these functions in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1969 Apr 25;244(8):2210–2217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


