Abstract
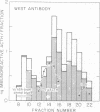
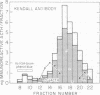
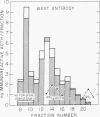
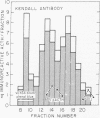
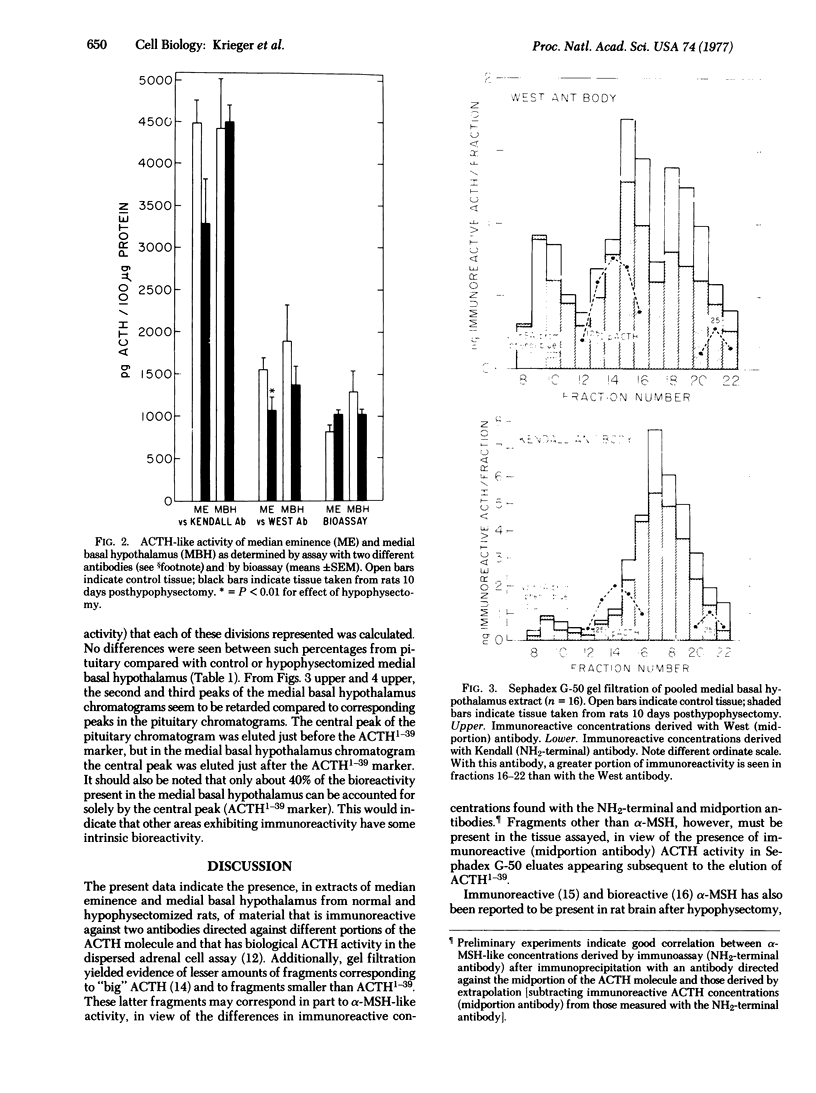
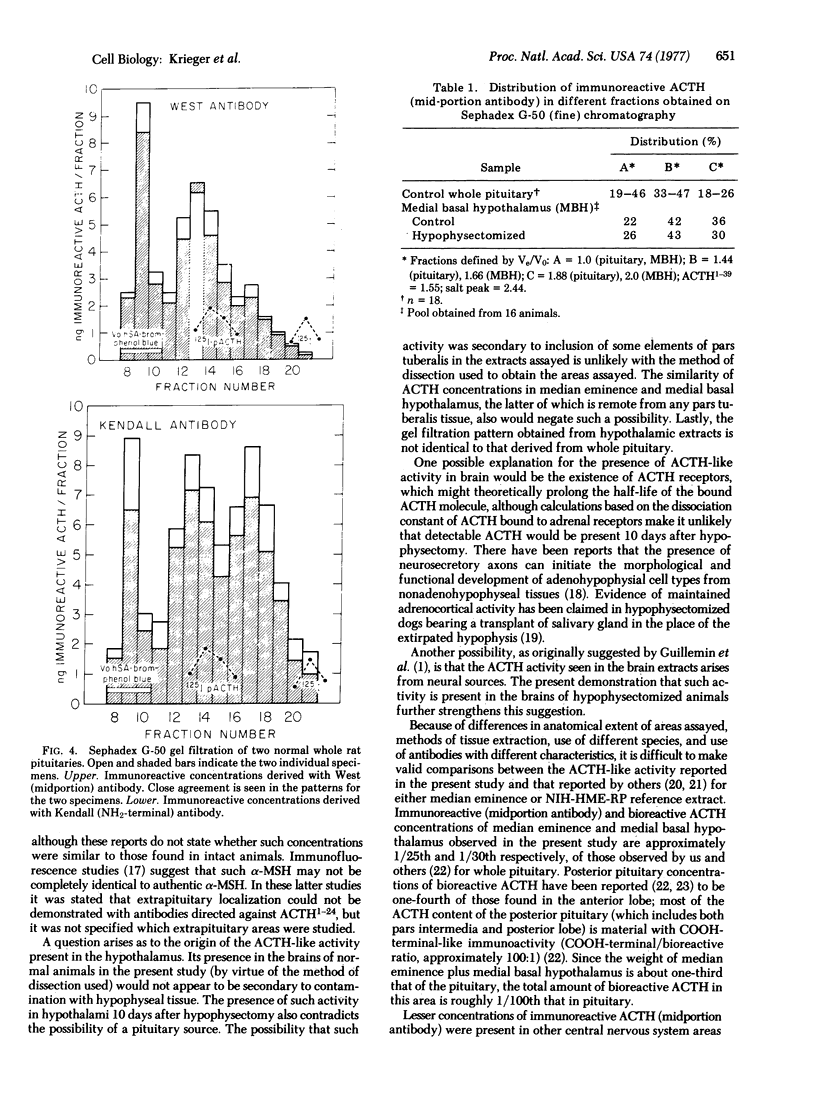
Immunoreactive and bioreactive corticotropin (ACTH-like) activities have been detected in the median eminence and remaining medial basal hypothalamus of both normal and hypophysectomized adult male rats: bioreactive ACTH (pg/100 mug of protein) 1028 in median eminence and 1289 in medial basal hypothalamus; immunoreactive ACTH (midportion ACTH antibody), 1554 in median eminence and 1887 in medial basal hypothalamus. By use of appropriate antibodies and bioassay, it was demonstrated that immunoreactivity was not due solely to alpha-melanotropin, which has previously been reported to be present in the brain of hypophysectomized animals. The Sephadex G-50 gel filtration patterns determined by immunoassay of column eluates obtained from hypothalamic extracts of normal or hypophysectomized animals were similar but were not identical to the pattern derived from whole pituitary. Immunoreactive (midportion ACTH antibody) ACTH concentrations (pg/100 mug of protein) of other central nervous system areas in normal animals were: cerebellum 34.3, cortex 46.3, thalamus 23.8, and hippocampus 116.3. The total amount of bioreactive ACTH present in the median eminence and medial basal hypothalamus is approximately 1% of that present in the pituitary. The present data suggest that such ACTH may have a diencephalic rather than pituitary origin and raise the question of the functional significance of such ACTH.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alvarez-Buylla R., De Alvarez-Buylla E. R. Adrenocortical activity in normal dogs, hypophysectomized dogs and dogs with a transplant of salivary gland in the place of the extirpated hypophysis. Acta Physiol Lat Am. 1970;20(2):93–96. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownstein M., Arimura A., Sato H., Schally A. V., Kizer J. S. The regional distribution of somatostatin in the rat brain. Endocrinology. 1975 Jun;96(6):1456–1461. doi: 10.1210/endo-96-6-1456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox B. M., Opheim K. E., Teschemacher H., Goldstein A. A peptide-like substance from pituitary that acts like morphine. 2. Purification and properties. Life Sci. 1975 Jun 15;16(12):1777–1782. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(75)90272-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUILLEMIN R., SCHALLY A. V., LIPSCOMB H. S., ANDERSEN R. N., LONG J. M. On the presence in hog hypothalamus of 3-corticotropin releasing factor, alpha- and beta-melanocyte stimulating hormones, adrenocorticotropin, lysine-vasopressin and oxytocin. Endocrinology. 1962 Apr;70:471–477. doi: 10.1210/endo-70-4-471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillemin R., Ling N., Burgus R. Endorphines, peptides, d'origine hypothalamique et neurohypophysaire à activité morphinomimétique. Isolement et structure moléculaire de l'alpha-endorphine. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1976 Feb 23;282(8):783–785. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes J., Smith T. W., Kosterlitz H. W., Fothergill L. A., Morgan B. A., Morris H. R. Identification of two related pentapeptides from the brain with potent opiate agonist activity. Nature. 1975 Dec 18;258(5536):577–580. doi: 10.1038/258577a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarus L. H., Ling N., Guillemin R. beta-Lipotropin as a prohormone for the morphinomimetic peptides endorphins and enkephalins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jun;73(6):2156–2159. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.6.2156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liotta A., Krieger D. T. A sensitive bioassay for the determination of human plasma ACTH levels. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1975 Feb;40(2):268–267. doi: 10.1210/jcem-40-2-268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsukura S., West C. D., Ichikawa Y., Jubiz W., Harada G., Tyler F. H. A new phenomenon of usefulness in the radioimmunoassay of plasma adrenocorticotropic hormone. J Lab Clin Med. 1971 Mar;77(3):490–500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moriarty C. M., Moriarty G. C. Bioactive and immunoactive ACTH in the rat pituitary: influence of stress and adrenalectomy. Endocrinology. 1975 Jun;96(6):1419–1425. doi: 10.1210/endo-96-6-1419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez E. M., Piezzi R. S. The effects of adenohypophysectomy on the hypothalamic-hypophysial neurosecrtory systm and the adrenal gland of the toad Bufo arenarum Hensel. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1967;80(1):93–107. doi: 10.1007/BF00331479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHALLY A. V., LIPSCOMB H. S., LONG J. M., DEAR W. E., GUILLEMIN R. Chromatography and hormonal activities of dog hypothalamus. Endocrinology. 1962 Apr;70:478–480. doi: 10.1210/endo-70-4-478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott A. P., Lowry P. J., Ratcliffe J. G., Rees L. H., Landon J. Corticotrophin-like peptides in the rat pituitary. J Endocrinol. 1974 Jun;61(3):355–367. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0610355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takebe K., Yasuda N., Greer M. A. A sensitive and simple in vitro assay for corticotropin-releasing substances utilizing ACTH release from cultured anterior pituitary cells. Endocrinology. 1975 Nov;97(5):1248–1255. doi: 10.1210/endo-97-5-1248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terenius L., Gispen W. H., De Wied D. ACTH-like peptides and opiate receptors in the rat brain: structure-activity studies. Eur J Pharmacol. 1975 Sep-Oct;33(2):395–399. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(75)90185-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yalow R. S., Berson S. A. Characteristics of "big ACTH" in human plasma and pituitary extracts. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1973 Mar;36(3):415–423. doi: 10.1210/jcem-36-3-415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]