Abstract
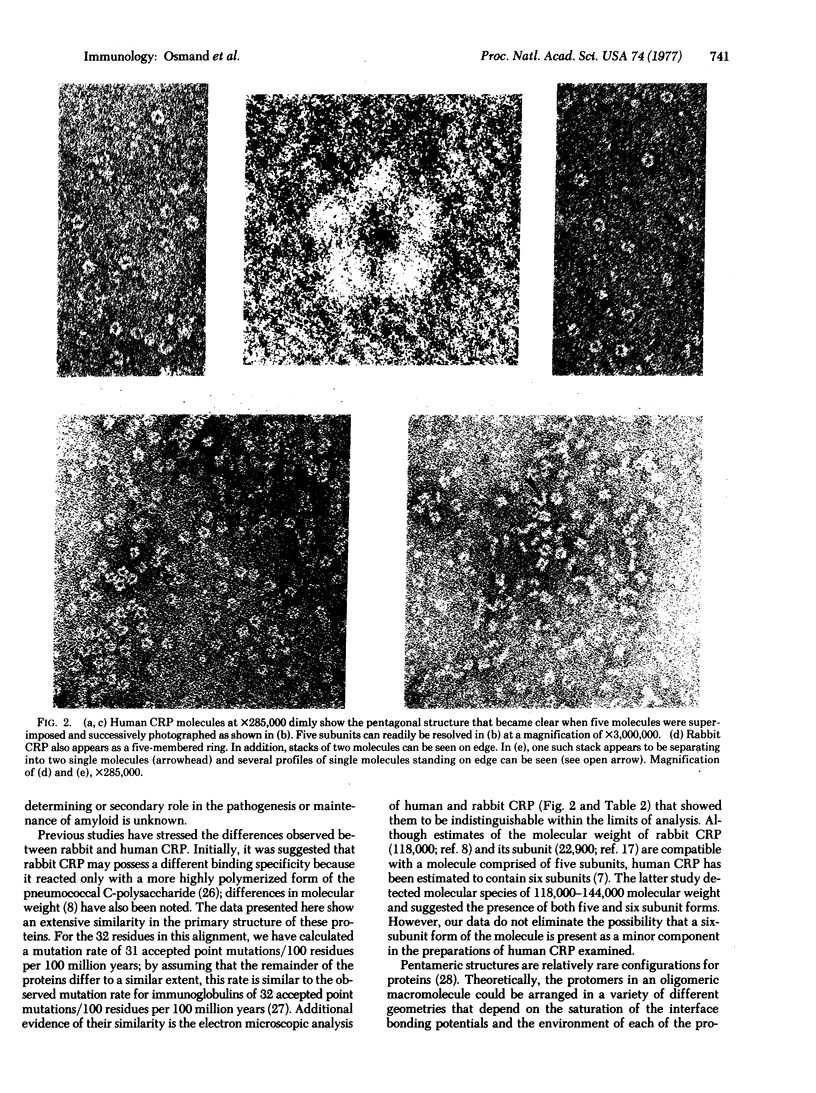
Partial amino acid sequences of rabbit C-reactive protein, a peptide derived from human C-reactive protein by cyanogen bromide cleavage, and the C1t subcomponent of the human complement component C1 have been determined. Extensive sequence homology between these proteins establish their evolutionary relationships. In addition, examination of C-reactive proteins by negative-stain electron microscopy revealed that the protein is composed of five subunits arranged in cyclic symmetry. This structure is similar to that reported for both C1t and the amyloid P-component. The extensive structural relationship suggests similar or overlapping functions and the term pentraxin is proposed to describe these homologous proteins.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDERSON H. C., McCARTY M. The occurrence in the rabbit of an acute phase protein analogous to human C reactive protein. J Exp Med. 1951 Jan;93(1):25–36. doi: 10.1084/jem.93.1.25. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Assimeh S. N., Painter R. H. The macromolecular structure of the first component of complement. J Immunol. 1975 Aug;115(2):488–494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bladen H. A., Nylen M. U., Glenner G. G. The ultrastructure of human amyloid as revealed by the negative staining technique. J Ultrastruct Res. 1966 Mar;14(5):449–459. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(66)80075-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiedel B. A., Gewurz H. Effects of C-reactive protein on platelet function. I. Inhibition of platelet aggregation and release reactions. J Immunol. 1976 May;116(5):1289–1294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedenson B., Hora J., Wang L. S. Partial sequence of the variable region of an anti-p-azobenzoate antibody light chain: a one solvent sequenator program. Biochemistry. 1976 Nov 2;15(22):4876–4880. doi: 10.1021/bi00667a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotschlich E. C., Edelman G. M. C-reactive protein: a molecule composed of subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Aug;54(2):558–566. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.2.558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermodson M. A., Ericsson L. H., Titani K., Neurath H., Walsh K. A. Application of sequenator analyses to the study of proteins. Biochemistry. 1972 Nov 21;11(24):4493–4502. doi: 10.1021/bi00774a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan M. H., Volanakis J. E. Interaction of C-reactive protein complexes with the complement system. I. Consumption of human complement associated with the reaction of C-reactive protein with pneumococcal C-polysaccharide and with the choline phosphatides, lecithin and sphingomyelin. J Immunol. 1974 Jun;112(6):2135–2147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kindmark C. O. Stimulating effect of C-reactive protein on phagocytosis of various species of pathogenic bacteria. Clin Exp Immunol. 1971 Jun;8(6):941–948. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kushner I., Somerville J. A. Estimation of the molecular size of C-reactive protein and CX-reactive protein in serum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Apr 28;207(1):105–114. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(70)90140-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medicus R. G., Schreiber R. D., Götze O., Müller-Eberhard H. J. A molecular concept of the properdin pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):612–616. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortensen R. F., Osmand A. P., Gewurz H. Effects on C-reactive protein on the lymphoid system. I. Binding to thymus-dependent lymphocytes and alteration of their functions. J Exp Med. 1975 Apr 1;141(4):821–839. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Eberhard H. J. Complement. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:697–724. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.003405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinteric L., Assimeh S. N., Kells D. I., Painter R. H. The ultrastructure of C1t, a subcomponent of the first component of complement: an E.M. and ultracentrifuge study. J Immunol. 1976 Jul;117(1):79–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pisano J. J., Bronzert T. J. Analysis of amino acid phenylthiohydantoins by gas chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1969 Oct 25;244(20):5597–5607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubert K. R., Switzer R. L., Shelton E. Studies of the quaternary structure and the chemical properties of phosphoribosylpyrophosphate synthetase from Salmonella typhimurium. J Biol Chem. 1975 Sep 25;250(18):7492–7500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel J., Osmand A. P., Wilson M. F., Gewurz H. Interactions of C-reactive protein with the complement system. II. C-reactive protein-mediated consumption of complement by poly-L-lysine polymers and other polycations. J Exp Med. 1975 Sep 1;142(3):709–721. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.3.709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinner M., Cohen A. S., Shirahama T., Cathcart E. S. P-component (pentagonal unit) of amyloid: isolation, characterization, and sequence analysis. J Lab Clin Med. 1974 Oct;84(4):604–614. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smithies O., Gibson D., Fanning E. M., Goodfliesh R. M., Gilman J. G., Ballantyne D. L. Quantitative procedures for use with the Edman-Begg sequenator. Partial sequences of two unusual immunoglobulin light chains, Rzf and Sac. Biochemistry. 1971 Dec 21;10(26):4912–4921. doi: 10.1021/bi00802a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volanakis J. E., Kaplan M. H. Interaction of C-reactive protein complexes with the complement system. II. Consumption of guinea pig complement by CRP complexes: requirement for human C1q. J Immunol. 1974 Jul;113(1):9–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]