Abstract
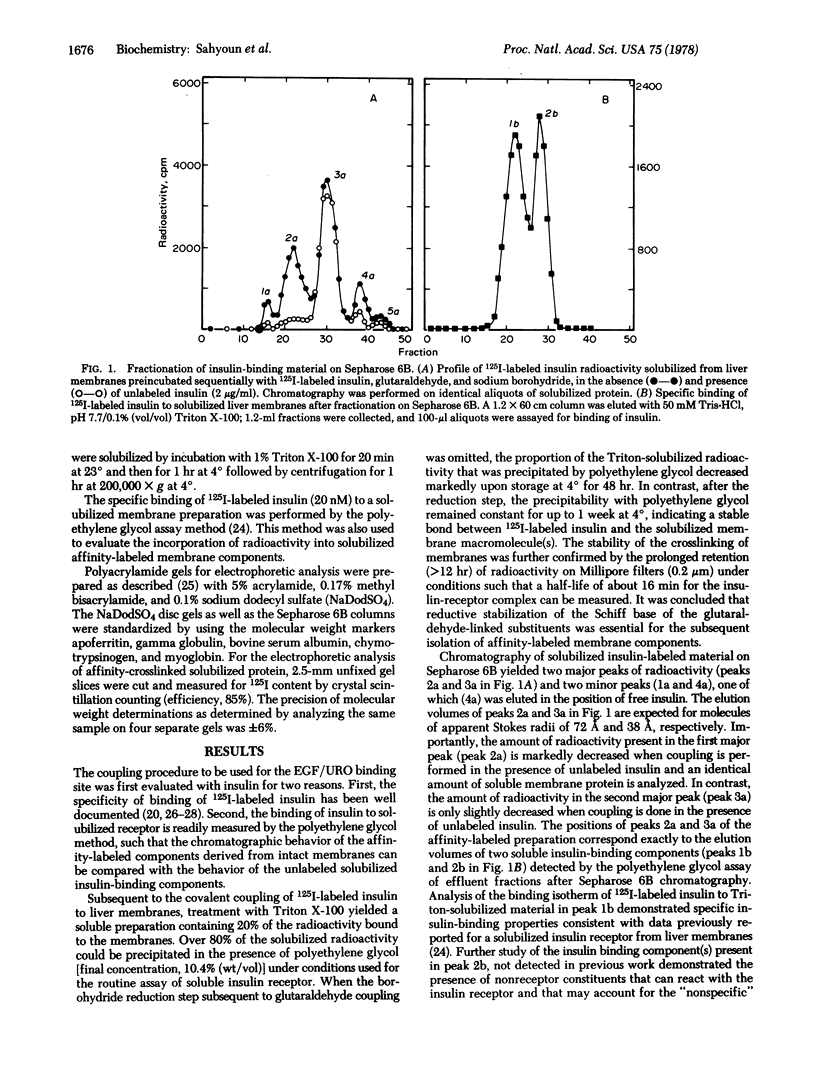
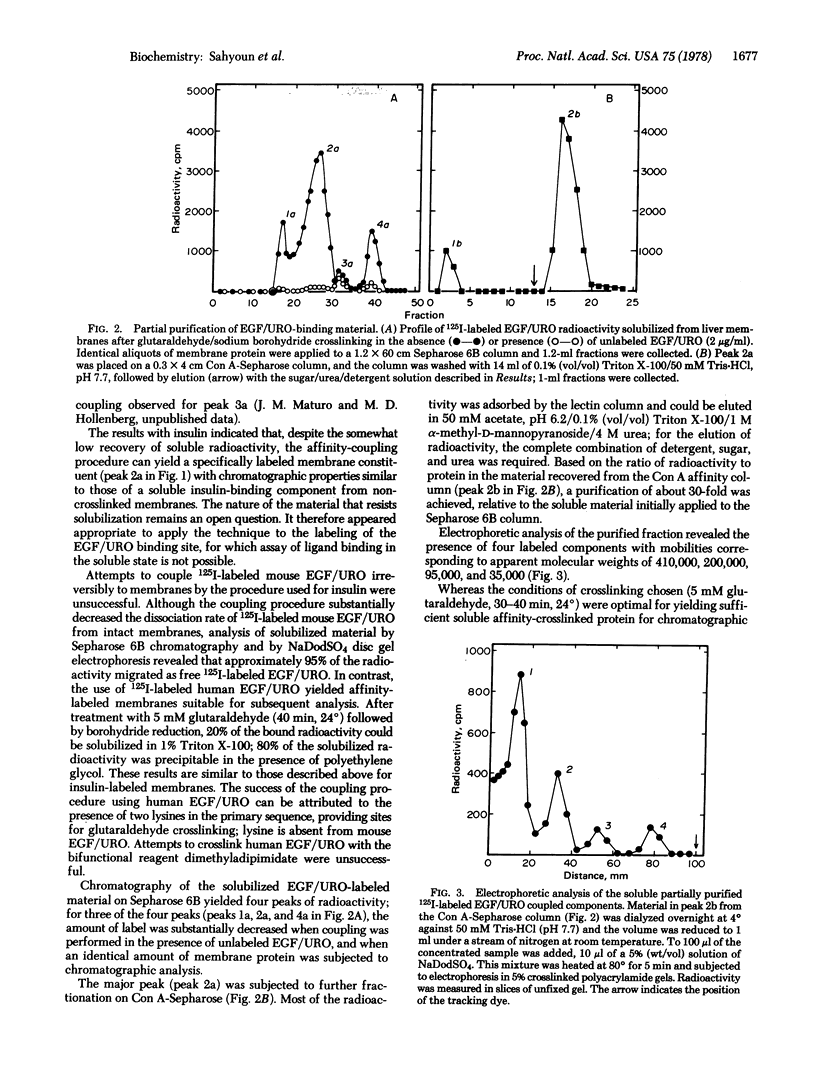
Both insulin and human epidermal growth factor-urogastrone (EGF/URO) can be covalently linked to specific rat liver membrane binding sites by glutaraldehyde coupling followed by sodium borohydride reduction to yield affinity-labeled membrane constituents sufficiently stable for solubilization and further analysis by various techniques. Solubilization of membranes covalently labeled with 125I-labeled insulin yields a component with chromatographic properties identical to those of a soluble insulin receptor characterized in previous studies. A second soluble insulin-binding component that is not revealed by the affinity-labeling method and that has not yet been reported can also be detected. Membranes similarly labeled with 125I-labeled EGF/URO yield one major and two minor ligand-specific soluble (Triton X-100) affinity-labeled components, as detected by chromatography on Sepharose 6B. Further analysis of the EGF/URO-labeled components by affinity chromatography on concanavalin A-Sepharose, by disc gel electrophoresis, and by enzymatic digestion suggests that the major specific binding component for EGF/URO in liver membranes is a glycoprotein subunit of approximately 100,000 daltons that possesses a 20,000-dalton portion inaccessible to proteolytic cleavage when the subunit is anchored in the membrane. The affinity labeling approach described should prove of use for the study of other polypeptide receptors that, like the EGF/URO receptor, lose their ligand recognition property subsequent to membrane solubilization.
Keywords: polypeptide hormone receptors, glutaraldehyde coupling, receptor solubilization and characterization, membrane labeling, affinity chromatography
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brew K., Shaper J. H., Olsen K. W., Trayer I. P., Hill R. L. Cross-linking of the components of lactose synthetase with dimethylpimelimidate. J Biol Chem. 1975 Feb 25;250(4):1434–1444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN S. Isolation of a mouse submaxillary gland protein accelerating incisor eruption and eyelid opening in the new-born animal. J Biol Chem. 1962 May;237:1555–1562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter G., Lembach K. J., Morrison M. M., Cohen S. Characterization of the binding of 125-I-labeled epidermal growth factor to human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jun 10;250(11):4297–4304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. B., Changeux J. P. The cholinergic receptor protein in its membrane environment. Annu Rev Pharmacol. 1975;15:83–103. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.15.040175.000503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S., Carpenter G. Human epidermal growth factor: isolation and chemical and biological properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1317–1321. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. Epidermal growth factor. J Invest Dermatol. 1972 Jul;59(1):13–16. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12625690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P., Desbuquois B., Krug F. Insulin-receptor interactions in liver cell membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Jul 16;44(2):333–339. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90604-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P., Hollenberg M. D. Membrane receptors and hormone action. Adv Protein Chem. 1976;30:251–451. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60481-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Insulin receptor of liver and fat cell membranes. Fed Proc. 1973 Aug;32(8):1838–1846. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Insulin--receptor interactions in adipose tissue cells: direct measurement and properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jun;68(6):1264–1268. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.6.1264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Isolation of the insulin receptor of liver and fat-cell membranes (detergent-solubilized-( 125 I)insulin-polyethylene glycol precipitation-sephadex). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Feb;69(2):318–322. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.2.318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Membrane receptors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1974;43(0):169–214. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.43.070174.001125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Properties of the insulin receptor isolated from liver and fat cell membranes. J Biol Chem. 1972 Apr 10;247(7):1980–1991. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das M., Miyakawa T., Fox C. F., Pruss R. M., Aharonov A., Herschman H. R. Specific radiolabeling of a cell surface receptor for epidermal growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):2790–2794. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.2790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desbuquois B., Krug F., Cuatrecasas P. Inhibitors of glucagon inactivation. Effect on glucagon--receptor interactions and glucagon-stimulated adenylate cyclase activity in liver cell membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Mar 20;343(1):101–120. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(74)90242-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freychet P., Roth J., Neville D. M., Jr Insulin receptors in the liver: specific binding of ( 125 I)insulin to the plasma membrane and its relation to insulin bioactivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Aug;68(8):1833–1837. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.8.1833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregory H. Isolation and structure of urogastrone and its relationship to epidermal growth factor. Nature. 1975 Sep 25;257(5524):325–327. doi: 10.1038/257325a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollenberg M. D., Cuatrecasas P. Epidermal growth factor: receptors in human fibroblasts and modulation of action by cholera toxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Oct;70(10):2964–2968. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.10.2964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollenberg M. D., Cuatrecasas P. Insulin and epidermal growth factor. Human fibroblast receptors related to deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis and amino acid uptake. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):3845–3853. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollenberg M. D., Gregory H. Human urogastrone and mouse epidermal growth factor share a common receptor site in cultured human fibroblasts. Life Sci. 1977 Jan 15;20(2):267–274. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(77)90321-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn C. R. Membrane receptors for hormones and neurotransmitters. J Cell Biol. 1976 Aug;70(2 Pt 1):261–286. doi: 10.1083/jcb.70.2.261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien R. D., Eldefrawi M. E., Eldefrawi A. T. Isolation of acetylcholine receptors. Annu Rev Pharmacol. 1972;12:19–34. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.12.040172.000315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Keefe E., Hollenberg M. D., Cuatrecasas P. Epidermal growth factor. Characteristics of specific binding in membranes from liver, placenta, and other target tissues. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1974 Oct;164(2):518–526. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(74)90062-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth J. Peptide hormone binding to receptors: a review of direct studies in vitro. Metabolism. 1973 Aug;22(8):1059–1073. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(73)90225-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage C. R., Jr, Cohen S. Epidermal growth factor and a new derivative. Rapid isolation procedures and biological and chemical characterization. J Biol Chem. 1972 Dec 10;247(23):7609–7611. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



