Abstract
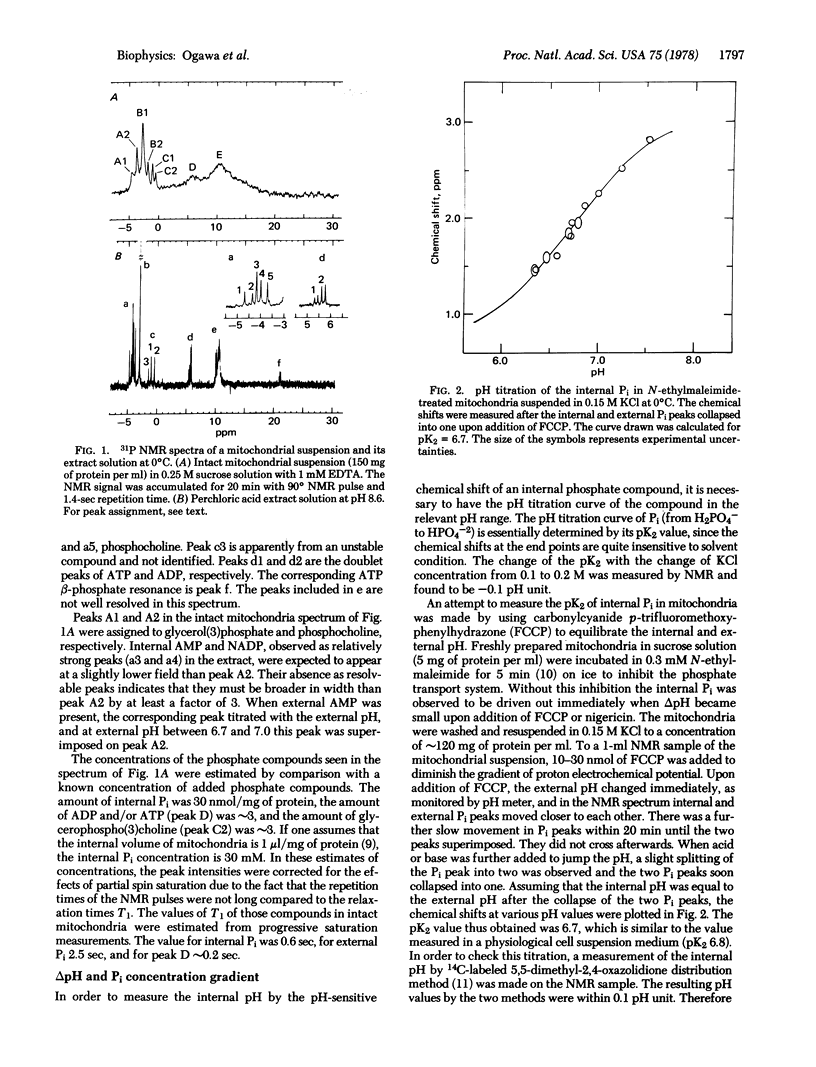
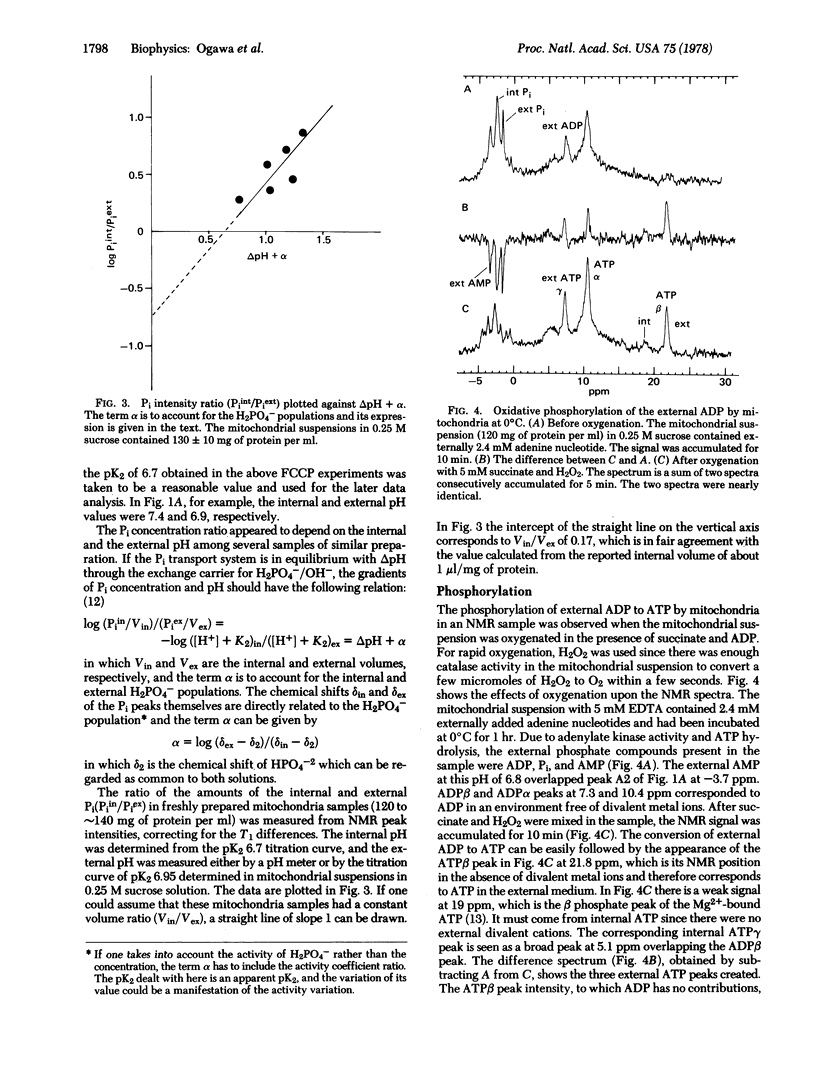
Intact mitochondria were studied by high-resolution 31P nuclear magnetic resonance. Observable internal phosphate compounds included inorganic phosphate (Pi), ADP, and ATP. The internal pH was determined by the chemical shift of the internal Pi, the pK2 (6.7) of which was measured in uncoupled mitochondria. The observed equilibrium relation between the internal and the external Pi was consistent with the exchange equilibrium through the H2PO4-/OH- carrier. The internal ATP and ADP were essentially Mg2+ bound and their resonances were distinguishable from those of the external ATP and ADP by the chemical shift differences due to the Mg2+ concentration gradient and deltapH. Oxidative phosphorylation was followed by the separate resonances of Pi and adenine nucleotides both internal and external to mitochondria. From these resonances the internal and external phosphate potentials could be estimated.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burt C. T., Glonek T., Bárány M. Analysis of phosphate metabolites, the intracellular pH, and the state of adenosine triphosphate in intact muscle by phosphorus nuclear magnetic resonance. J Biol Chem. 1976 May 10;251(9):2584–2591. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHN M., HUGHES T. R., Jr Nuclear magnetic resonance spectra of adenosine di- and triphosphate. II. Effect of complexing with divalent metal ions. J Biol Chem. 1962 Jan;237:176–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOPER C., LEHNINGER A. L. Oxidative phosphorylation by an enzyme complex from extracts of mitochondria. I. The span beta-hydroxybutyrate to oxygen. J Biol Chem. 1956 Mar;219(1):489–506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casey R. P., Njus D., Radda G. K., Sehr P. A. Active proton uptake by chromaffin granules: observation by amine distribution and phosphorus-31 nuclear magnetic resonance techniques. Biochemistry. 1977 Mar 8;16(5):972–977. doi: 10.1021/bi00624a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coty W. A., Pedersen P. L. Phosphate transport in rat liver mitochondria. Kinetics and energy requirements. J Biol Chem. 1974 Apr 25;249(8):2593–2598. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gadian D. G., Hoult D. I., Radda G. K., Seeley P. J., Chance B., Barlow C. Phosphorus nuclear magnetic resonance studies on normoxic and ischemic cardiac tissue. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Dec;73(12):4446–4448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.12.4446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoult D. I., Busby S. J., Gadian D. G., Radda G. K., Richards R. E., Seeley P. J. Observation of tissue metabolites using 31P nuclear magnetic resonance. Nature. 1974 Nov 22;252(5481):285–287. doi: 10.1038/252285a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klingenberg M., Palmieri F., Quagliariello E. Quantitative correlation between the distribution of anions and the pH difference across the mitochondrial membrane. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Dec;17(2):230–238. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb01158.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navon G., Ogawa S., Shulman R. G., Yamane T. High-resolution 31P nuclear magnetic resonance studies of metabolism in aerobic Escherichia coli cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):888–891. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosing J., Slater E. C. The value of G degrees for the hydrolysis of ATP. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 May 25;267(2):275–290. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(72)90116-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottenberg H., Solomon A. K. The osmotic nature of the ion-induced swelling of rat-liver mitochondria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Oct 14;193(1):48–57. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(69)90057-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottenberg H. The mechanism of energy-dependent ion transport in mitochondria. J Membr Biol. 1973;11(2):117–137. doi: 10.1007/BF01869816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sim E., Cullis P. R. 31P nuclear magnetic resonance studies of cell membranes labelled with phosphonium phosphatidylcholine. FEBS Lett. 1977 Jul 15;79(2):340–344. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80816-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


