Abstract
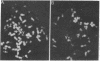
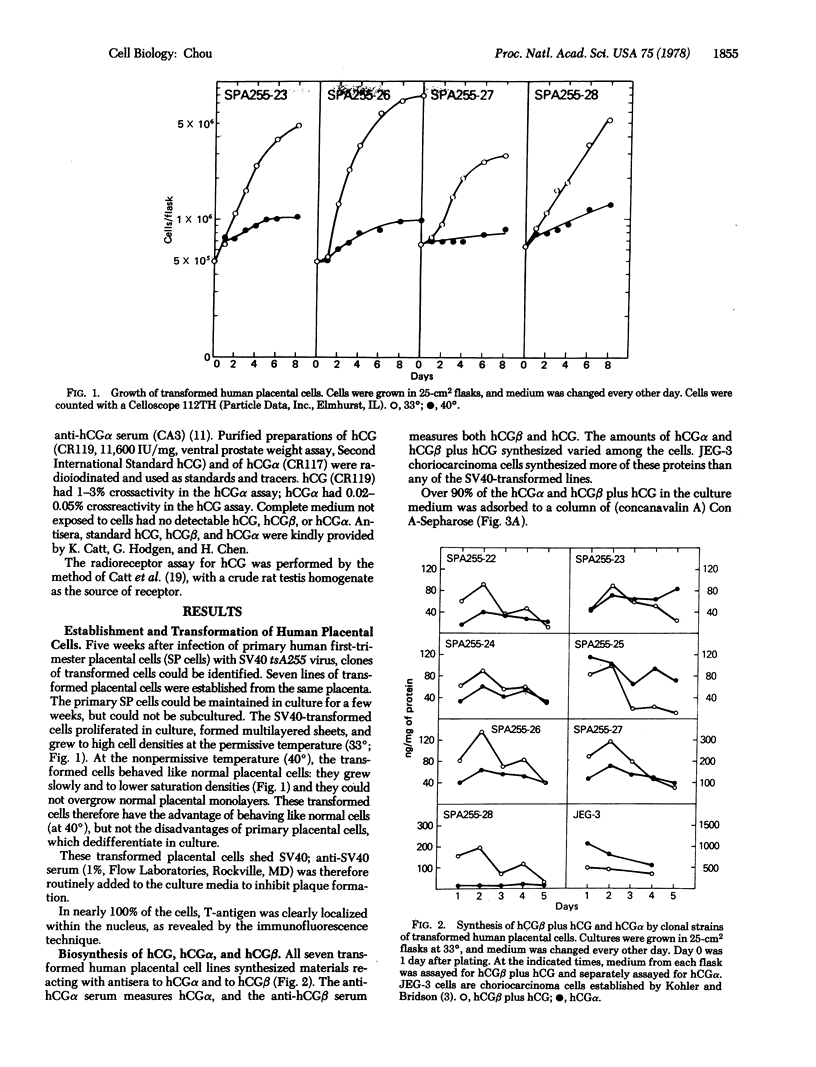
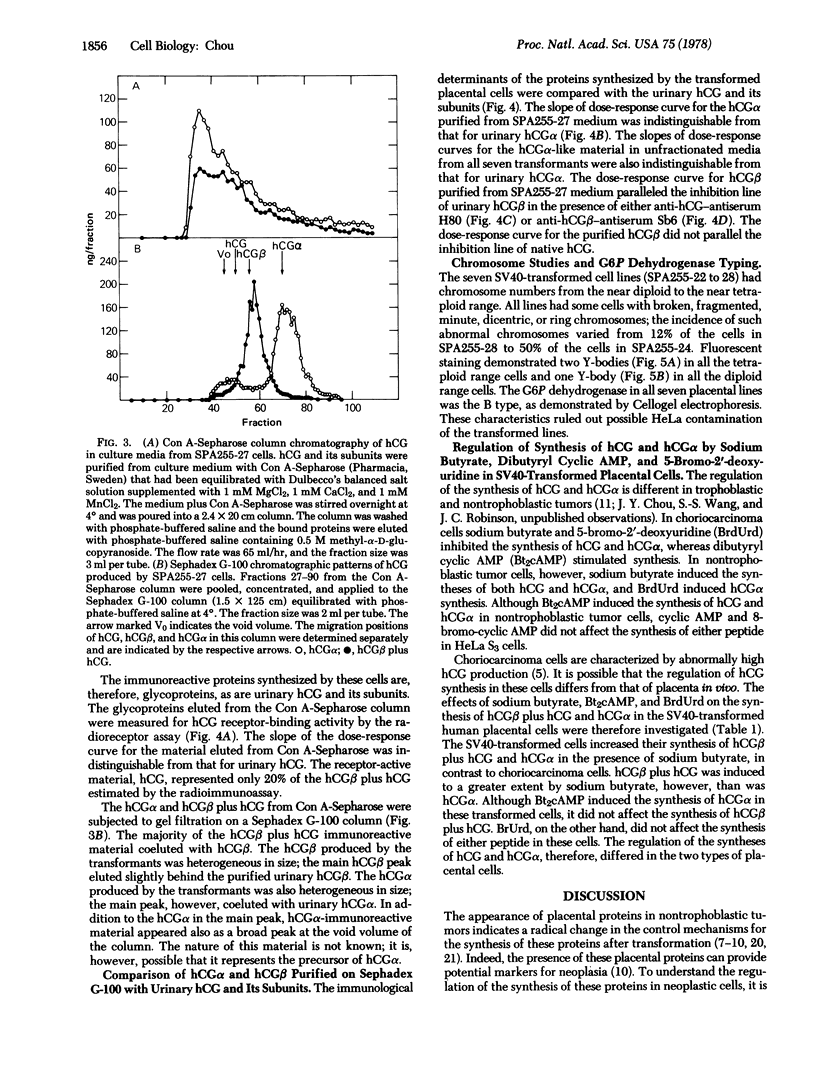
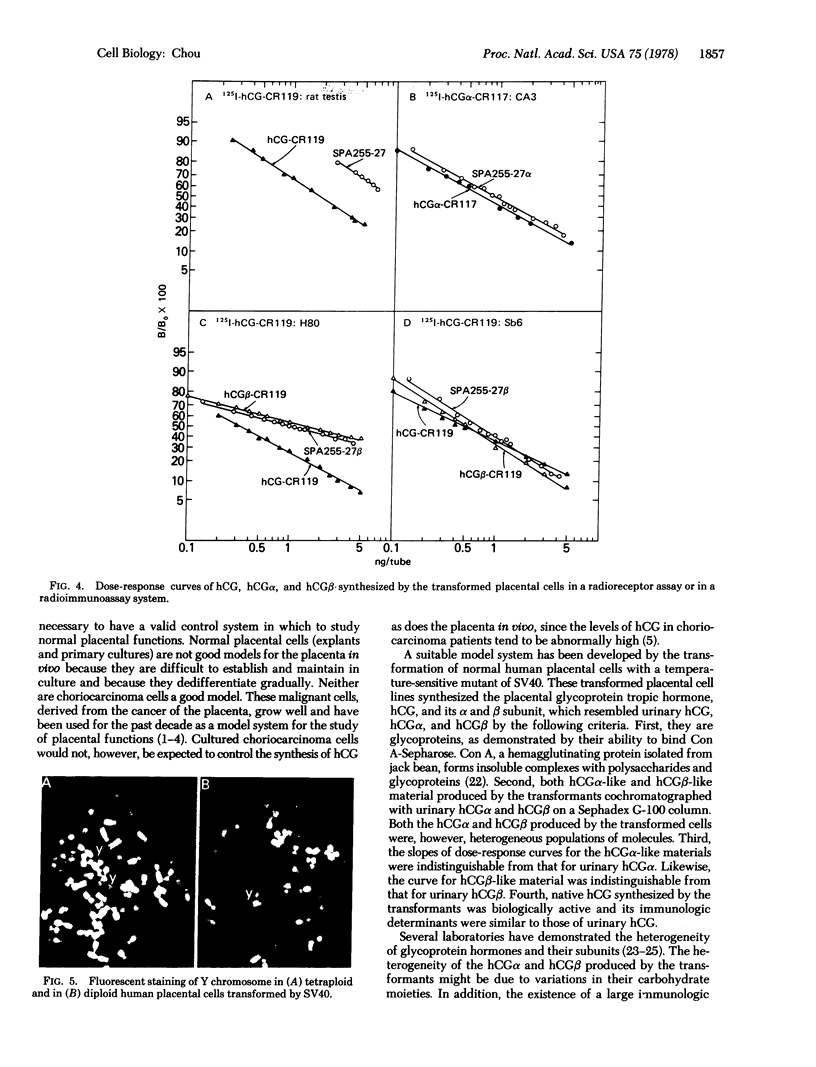
Seven clonal human placental cell lines were established by transformation of human first-trimester placental cells with simian virus 40. These transformed cells synthesized native human choriogonadotropin (chorionic gonadotropin) (hCG) as well as the free alpha and beta subunits of hCG. The amount of native hCG synthesized by these cells was, however, lower than the amount of free beta subunit. (Both hCG and the beta subunit are detected by the radioimmunoassay for beta subunit, but only hCG is detected by the radioreceptor assay.) The alpha and beta subunits produced by these transformed placental cells were heterogeneous in size; the sizes of the predominant alpha and beta species, however, corresponded to those of urinary alpha and beta subunits, respectively. The seven cell lines transformed by simian virus 40 had chromosome numbers from the near diploid to the near tetraploid range. Fluorescent staining demonstrated the Y chromosome in all the transformants. Furthermore, B-type glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (D-glucose-6-phosphate: NADP+ 1-oxidoreductase; EC 1.1.1.49) was present in all seven lines. These characteristics ruled out possible HeLa contamination of the transformed lines. Regulation of the synthesis of alpha and beta subunits plus hCG in these transformed human placental cells differed from the regulation in choriocarcinoma cells.
Full text
PDF
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson J. L., Martin R. G. SV40 transformation of mouse brain cells: critical role of gene A in maintenance of the transformed phenotype. J Cell Physiol. 1976 May;88(1):65–76. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040880109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catt K. J., Dufau M. L., Tsuruhara T. Radioligand-receptor assay of luteinizing hormone and chorionic gonadotropin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1972 Jan;34(1):123–132. doi: 10.1210/jcem-34-1-123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen H. C., Hodgen G. D., Matsuura S., Lin L. J., Gross E., Reichert L. E., Jr, Birken S., Canfield R. E., Ross G. T. Evidence for a gonadotropin from nonpregnant subjects that has physical, immunological, and biological similarities to human chorionic gonadotropin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Aug;73(8):2885–2889. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.8.2885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou J. Y., Martin R. G. Complementation analysis of simian virus 40 mutants. J Virol. 1974 May;13(5):1101–1109. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.5.1101-1109.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou J. Y., Robinson J. C., Wang S. S. Effects of sodium butyrate on synthesis of human chorionic gonadotrophin in trophoblastic and non-trophoblastic tumours. Nature. 1977 Aug 11;268(5620):543–544. doi: 10.1038/268543a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franchimont P., Gaspard U., Reuter A., Heynen G. Polymorphism of protein and polypeptide hormones. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1972 Oct;1(4):315–336. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.1972.tb00402.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDSTEIN I. J., HOLLERMAN C. E., SMITH E. E. PROTEIN-CARBOHYDRATE INTERACTION. II. INHIBITION STUDIES ON THE INTERACTION OF CONCANAVALIN A WITH POLYSACCHARIDES. Biochemistry. 1965 May;4:876–883. doi: 10.1021/bi00881a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene P. J., Sussman H. H. Structual comparison of ectopic and normal placental alkaline phosphatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Oct;70(10):2936–2940. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.10.2936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohler P. O., Bridson W. E., Hammond J. M., Weintraub B., Kirschner M. A., Van Thiel D. H. Clonal lines of human choriocarcinoma cells in culture. Acta Endocrinol Suppl (Copenh) 1971;153:137–153. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.068s137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohler P. O., Bridson W. E. Isolation of hormone-producing clonal lines of human choriocarcinoma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1971 May;32(5):683–687. doi: 10.1210/jcem-32-5-683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin C. C., Uchida I. A., Byrnes E. A suggestion for the nomenclature of the fluorescent banding patterns in human metaphase chromosomes. Can J Genet Cytol. 1971 Jun;13(2):361–363. doi: 10.1139/g71-055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruo T. Studies on in vitro synthesis and secretion of human chorionic gonadtropin and its subunits. Endocrinol Jpn. 1976 Apr;23(2):119–128. doi: 10.1507/endocrj1954.23.119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan F. J., Canfield R. E. Nature of the subunits of human chorionic gonadotropin. Endocrinology. 1971 Apr;88(4):1045–1053. doi: 10.1210/endo-88-4-1045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pattillo R. A., Gey G. O. The establishment of a cell line of human hormone-synthesizing trophoblastic cells in vitro. Cancer Res. 1968 Jul;28(7):1231–1236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Placental proteins and their subunits as tumor markers. Ann Intern Med. 1975 Jan;82(1):71–83. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-82-1-71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prentice L. G., Ryan R. J. LH and its subunits in human pituitary, serum and urine. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1975 Feb;40(2):303–312. doi: 10.1210/jcem-40-2-303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rattazzi M. C., Corash L. M., van Zanen G. E., Jaffé E. R., Piomelli S. G6PD deficiency and chronic hemolysis: four new mutants--relationships between clinical syndrome and enzyme kinetics. Blood. 1971 Aug;38(2):205–218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen S. W., Weintraub B. D. Ectopic production of the isolated alpha subunit of the glycoprotein hormones. A quantitative marker in certain cases of cancer. N Engl J Med. 1974 Jun 27;290(26):1441–1447. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197406272902601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seabright M. A rapid banding technique for human chromosomes. Lancet. 1971 Oct 30;2(7731):971–972. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)90287-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stolbach L. L., Krant M. J., Fishman W. H. Ectopic production of an alkaline phosphatase isoenzyme in patients with cancer. N Engl J Med. 1969 Oct 2;281(14):757–762. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196910022811403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tashjian A. H., Jr, Weintraub B. D., Barowsky N. J., Rabson A. S., Rosen S. W. Subunits of human chorionic gonadotropin: unbalanced synthesis and secretion by clonal cell strains derived from a bronchogenic carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 May;70(5):1419–1422. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.5.1419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaitukaitis J. L., Braunstein G. D., Ross G. T. A radioimmunoassay which specifically measures human chorionic gonadotropin in the presence of human luteinizing hormone. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1972 Jul 15;113(6):751–758. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(72)90553-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaitukaitis J. L. Changing placental concentrations of human chorionic gonadotropin and its subunits during gestation. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1974 May;38(5):755–760. doi: 10.1210/jcem-38-5-755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaitukaitis J. L., Ross G. T., Braunstein G. D., Rayford P. L. Gonadotropins and their subunits: basic and clinical studies. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1976;32:289–331. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571132-6.50019-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub B. D., Rosen S. W. Competitive radioassays and "specific" tumor markers. Metabolism. 1973 Aug;22(8):1119–1127. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(73)90231-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub B. D., Stannard B. S., Rosen S. W. Combination of ectopic and standard human glycoprotein hormone alpha with beta subunits: discordance of immunologic and receptor-binding activity. Endocrinology. 1977 Jul;101(1):225–235. doi: 10.1210/endo-101-1-225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]