Abstract
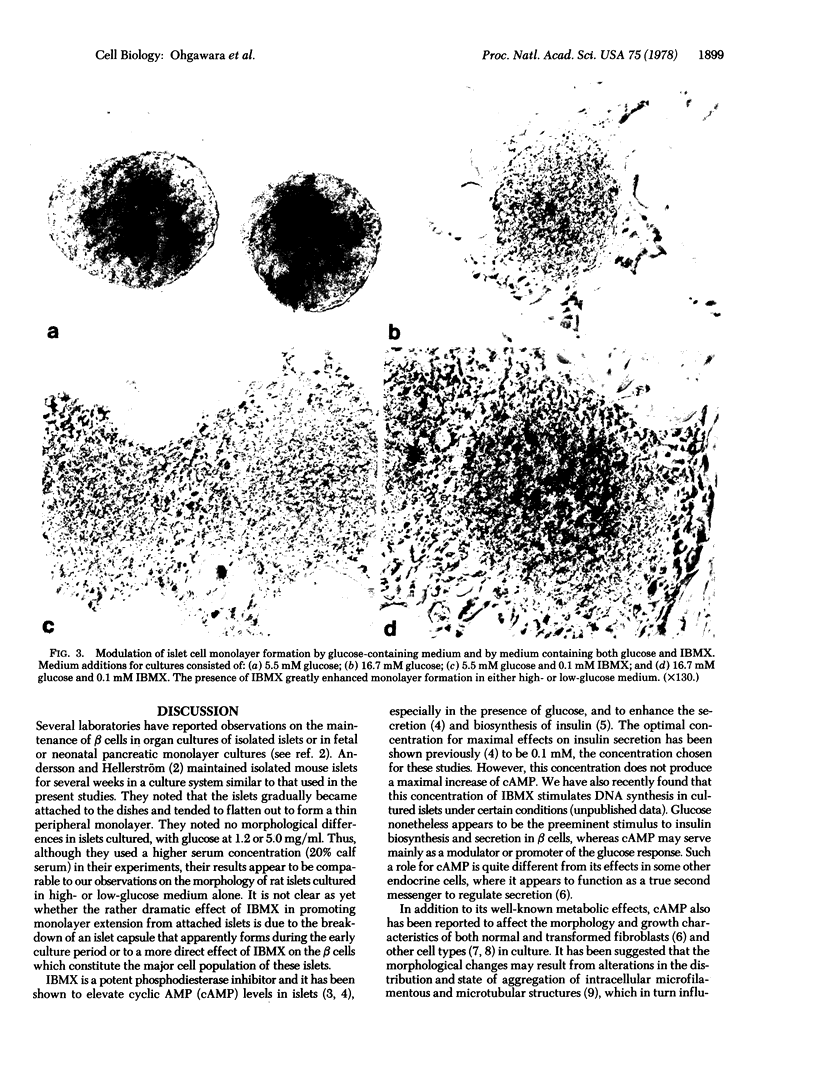
Normal adult rat islets usually remained intact and encapsulated, even after many days in culture. In contrast, islets cultured in the presence of the phosphodiesterase inhibitor 3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine (0.1 mM) attached more readily to the surface of plastic culture dishes and almost uniformly formed monolayers of endocrine cells. The mechanism of this effect is not known but presumably involves increases in cellular cyclic AMP content. Fibroblast growth did not appear to be stimulated by the inhibitor. These adult pancreatic endocrine monolayer cultures can be produced readily and provide useful preparations for further morphological and biochemical studies of factors affecting the differentiation, growth, and regenerative capacity of islet cells.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson A., Hellerström C. Metabolic characteristics of isolated pancreatic islets in tissue culture. Diabetes. 1972;21(2 Suppl):546–554. doi: 10.2337/diab.21.2.s546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman D. L. Role of cyclic nucleotides in cell growth and differentiation. Physiol Rev. 1976 Oct;56(4):652–708. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1976.56.4.652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gingle A. R. cAMP enhanced aggregation of cells from early chick embryos. Dev Biol. 1977 Jul 15;58(2):394–401. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(77)90100-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman R. D., Chang C., Williams J. F. Properties and behavior of hamster embryo cells transformed by human adenovirus type 5. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 1):601–614. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grill V., Cerasi E. Activation by glucose of adenyl cyclase in pancreatic islets of the rat. FEBS Lett. 1973 Jul 15;33(3):311–314. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80218-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellman B., Idahl L. A., Lernmark A., Täljedal I. B. The pancreatic beta-cell recognition of insulin secretagogues: does cyclic AMP mediate the effect of glucose? Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Sep;71(9):3405–3409. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.9.3405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsie A. W., Puck T. T. Morphological transformation of Chinese hamster cells by dibutyryl adenosine cyclic 3':5'-monophosphate and testosterone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Feb;68(2):358–361. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.2.358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lernmark A., Nathans A., Steiner D. F. Preparation and characterization of plasma membrane-enriched fractions from rat pancreatic islets. J Cell Biol. 1976 Nov;71(2):606–623. doi: 10.1083/jcb.71.2.606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maldonato A., Renold A. E., Sharp G. W., Cerasi E. Glucose-induced proinsulin biosynthesis. Role of islet cyclic AMP. Diabetes. 1977 Jun;26(6):538–545. doi: 10.2337/diab.26.6.538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickland S., Beers W. H. Studies on the role of plasminogen activator in ovulation. In vitro response of granulosa cells to gonadotropins, cyclic nucleotides, and prostaglandins. J Biol Chem. 1976 Sep 25;251(18):5694–5702. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willingham M. C., Pastan I. Cyclic AMP modulates microvillus formation and agglutinability in transformed and normal mouse fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1263–1267. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willingham M. C., Pastan I. Cyclic amp and cell morphology in cultured fibroblasts. Effects on cell shape, microfilament and microtubule distribution, and orientation to substratum. J Cell Biol. 1975 Oct;67(1):146–159. doi: 10.1083/jcb.67.1.146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]