Abstract
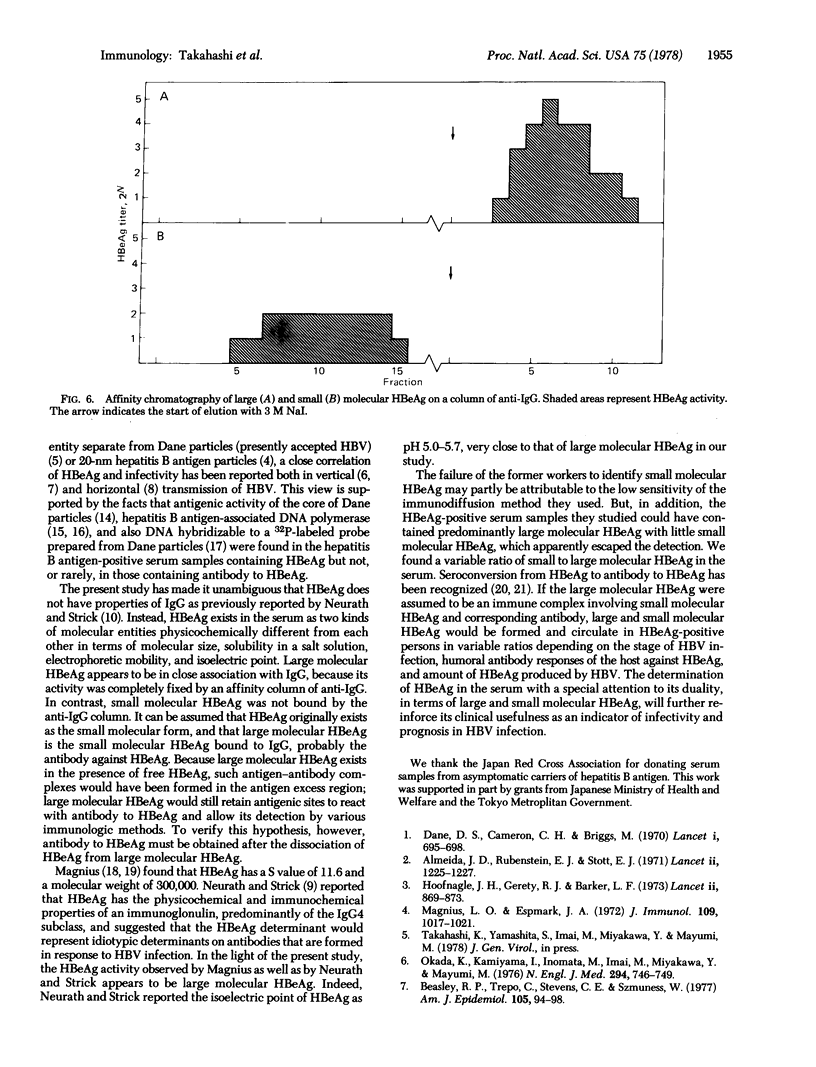
Hepatitis B e antigen (HBeAg) is detected in the serum of some persons infected with hepatitis B virus. Owing to a close correlation of HBeAg and hepatitis B virus in the serum, it has been used as a practical indicator of infectivity. Two entities of HBeAg activity physicochemically different from each other were demonstrated in the serum of persons infected with hepatitis B virus. One was associated with a molecule that precipitated in 1.33 M ammonium sulfate solution, was larger than IgG, and had an electrophoretic mobility in the beta- to gamma-globulin regions and an isoelectric point of approximately pH 5.7. In contrast, the other HBeAg activity was associated with a molecule that was soluble in 1.33 M ammonium sulfate solution, was smaller than IgG, and had an electrophoretic mobility in the alpha-globulin region and an isoelectric point at pH 4.8. In spite of their marked physicochemical differences, a line of antigenic identity was clearly observed for them when they were tested against antibody to HBeAg by a them when they were tested against antibody to HBeAg by a double immunodiffusion method. The HBeAg activity associated with the large molecule was completely removed by an affinity column of anti-IgG, whereas the activity of the small molecule was not. These results indicate that, in the serum, HBeAg exists as a molecule smaller than IgG and also in association with IgG.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aikawa T., Sairenji H., Furuta S., Kiyosawa K., Shikata T., Imai M., Miyakawa Y., Yanase Y., Mayumi M. Seroconversion from hepatitis B e antigen to anti-HBe in acute hepatitis B virus infection. N Engl J Med. 1978 Feb 23;298(8):439–441. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197802232980807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almeida J. D., Rubenstein D., Stott E. J. New antigen-antibody system in Australia-antigen-positive hepatitis. Lancet. 1971 Dec 4;2(7736):1225–1227. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)90543-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alter H. J., Seeff L. B., Kaplan P. M., McAuliffe V. J., Wright E. C., Gerin J. L., Purcell R. H., Holland P. V., Zimmerman H. J. Type B hepatitis: the infectivity of blood positive for e antigen and DNA polymerase after accidental needlestick exposure. N Engl J Med. 1976 Oct 21;295(17):909–913. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197610212951701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beasley R. P., Trepo C., Stevens C. E., Szmuness W. The e antigen and vertical transmission of hepatitis B surface antigen. Am J Epidemiol. 1977 Feb;105(2):94–98. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dane D. S., Cameron C. H., Briggs M. Virus-like particles in serum of patients with Australia-antigen-associated hepatitis. Lancet. 1970 Apr 4;1(7649):695–698. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)90926-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRABAR P., URIEL J., COURCON J. [Immuno-electrophoretic analysis of normal human serum. IV. Electrophoretic mobilities]. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1960 Jul;99:13–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoofnagle J. H., Gerety R. J., Barker L. F. Antibody to hepatitis-B-virus core in man. Lancet. 1973 Oct 20;2(7834):869–873. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)92004-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imai M., Tachibana F. C., Moritsugu Y., Miyakawa Y., Mayumi M. Hepatitis B antigen-associated deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase activity and e antigen/anti-e system. Infect Immun. 1976 Sep;14(3):631–635. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.3.631-635.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnius L. O. Characterization of a new antigen-antibody system associated with hepatitis B. Clin Exp Immunol. 1975 May;20(2):209–216. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnius L. O., Espmark J. A. New specificities in Australia antigen positive sera distinct from the Le Bouvier determinants. J Immunol. 1972 Nov;109(5):1017–1021. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maynard J. E., Barrett D. H., Murphy B. L., Bradley D. W., Berquist K. R., Bender T. R. Relation of e antigen to hepatitis B virus infection in an area of hyperendemicity. J Infect Dis. 1976 Mar;133(3):339–342. doi: 10.1093/infdis/133.3.339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neurath A. R., Strick N. Host specificity of a serum marker for hepatitis B: evidence that "e antigen" has the properties of an immunoglobulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Apr;74(4):1702–1706. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.4.1702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordenfelt E., Andrén-Sandberg M. Dane particle-associated DNA polymerase and e antigen: relation to chronic hepatitis among carriers of hepatitis B surface antigen. J Infect Dis. 1976 Jul;134(1):85–89. doi: 10.1093/infdis/134.1.85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada K., Kamiyama I., Inomata M., Imai M., Miyakawa Y. e antigen and anti-e in the serum of asymptomatic carrier mothers as indicators of positive and negative transmission of hepatitis B virus to their infants. N Engl J Med. 1976 Apr 1;294(14):746–749. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197604012941402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porath J., Axen R., Ernback S. Chemical coupling of proteins to agarose. Nature. 1967 Sep 30;215(5109):1491–1492. doi: 10.1038/2151491a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi K., Fukuda M., Baba K., Imai M., Miyakawa Y., Mayumi M. Determination of e antigen and antibody to e by means of passive hemagglutination method. J Immunol. 1977 Nov;119(5):1556–1559. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi K., Imai M., Tsuda F., Takahashi T., Miyakawa Y. Association of dane particles with e antigen in the serum of asymptomatic carriers of hepatitis B surface antigen. J Immunol. 1976 Jul;117(1):102–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner B. G., O'Connell A. P., Summers J. Association of e antigen with Dane particle DNA in sera from asymptomatic carriers of hepatitis B surface antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 May;74(5):2149–2151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.5.2149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]