Abstract
The entire sequences of the variable region of four heavy chains from BALB/c inulin-binding myeloma proteins have been determined. Among the four proteins there are six amino acid differences, all of which occur in the framework portion of the variable region. All of the six amino acid substitutions can be explained by single base mutations at the DNA level. The pattern of diversity in these proteins is compared to a previously reported group of heavy chains from phosphorylcholine-binding myeloma proteins. Unlike the phosphorylcholine-binding proteins, which (with the exception of two that are identical) have size and sequence differences in their complementarity regions, the inulin-binding heavy chains all have identical complementarity regions with H3 being extremely short. The pattern of variation observed in the anti-inulin heavy chains appears to be most easily explained by a somatic mutation mechanism. However, because none of the substitutions occur in complementarity-determining regions, they presumably would have no selective advantage and would not alter binding specificity. These proteins have further been shown to have crossreacting antigenic determinants (idiotypes). Five of the six sequence differences observed occur at positions that are internal in the molecule and thus presumably would not account for the idiotypic differences. These results suggest that most of the observed idiotypic crossreactivities will be due to differences in the light chains of the anti-inulin proteins.
Keywords: antigen-binding myeloma protein, amino acid sequence, diversity
Full text
PDF
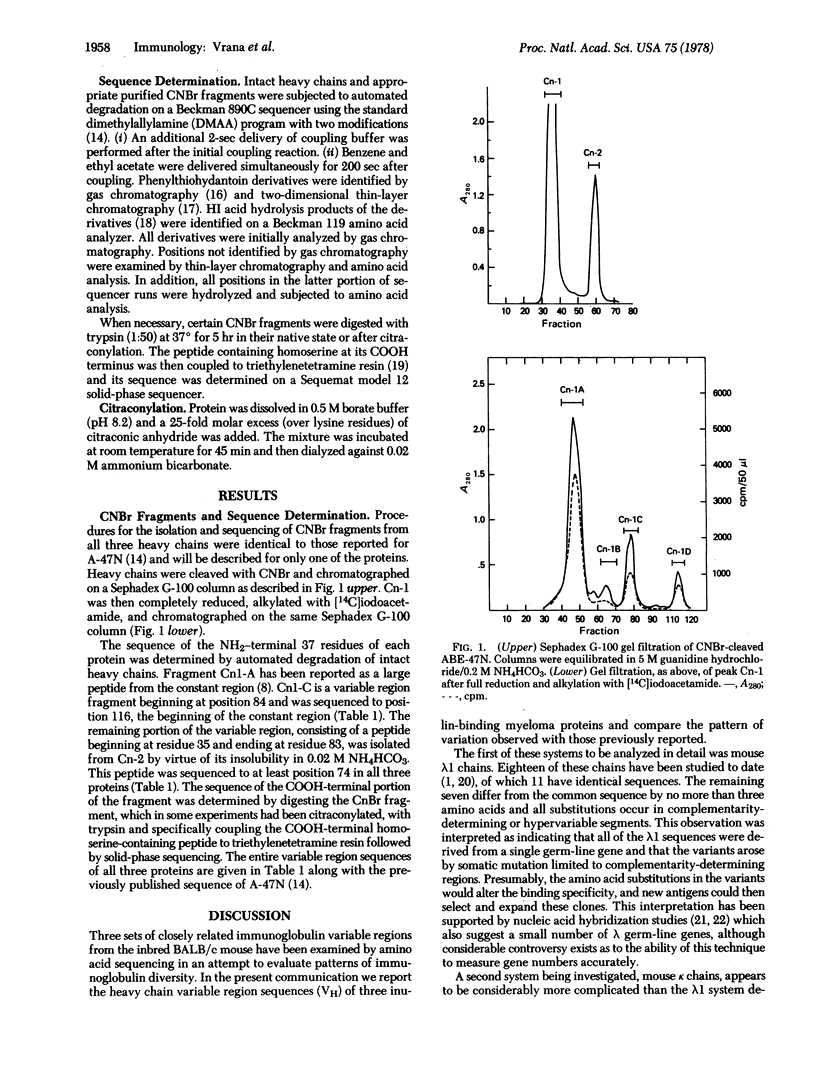
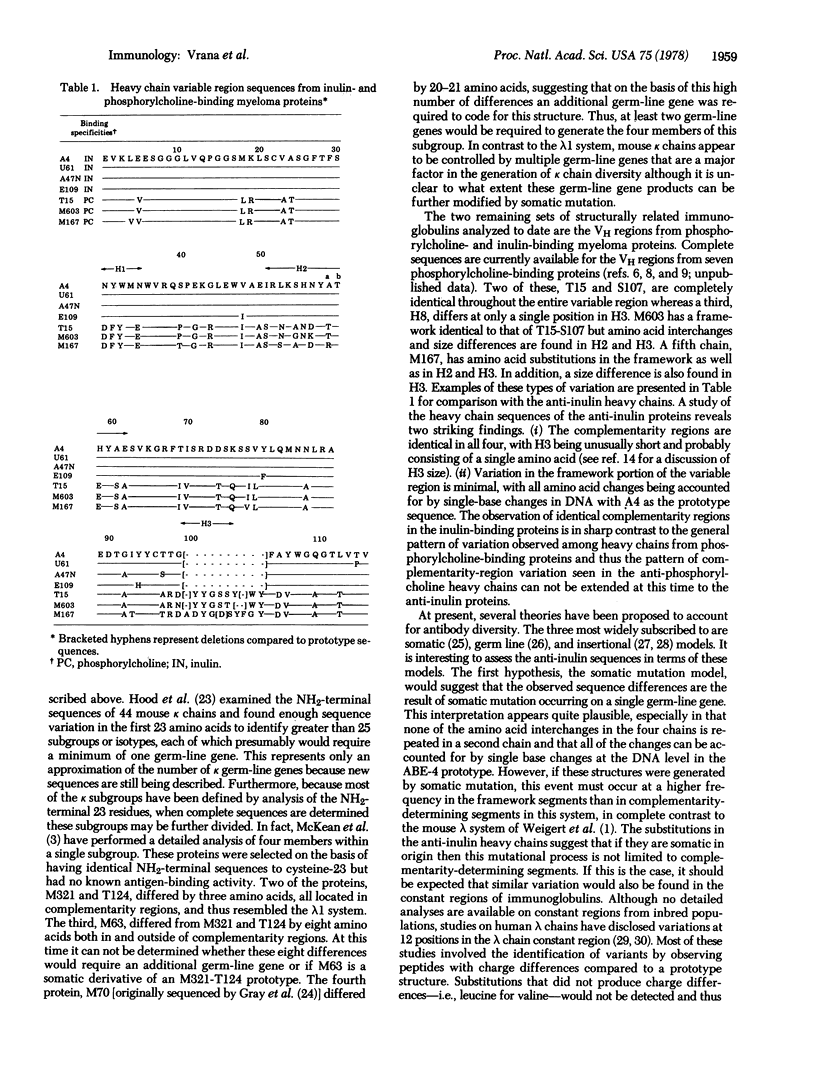


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barstad P., Rudikoff S., Potter M., Cohn M., Konigsberg W., Hood L. Immunoglobulin structure: amino terminal sequences of mouse myeloma proteins that bind phosphorylcholine. Science. 1974 Mar 8;183(4128):962–966. doi: 10.1126/science.183.4128.962. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bridges S. H., Little J. R. Recovery of binding activity in reconstituted mouse myeloma proteins. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2525–2530. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fett J. W., Deutsch H. F. The variability of human lambda-chain constant regions and some relationships to V-regions sequences. Immunochemistry. 1976 Feb;13(2):149–155. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(76)90283-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray W. R., Dreyer W. J., Hood L. Mechanism of antibody synthesis: size differences between mouse kappa chains. Science. 1967 Jan 27;155(3761):465–467. doi: 10.1126/science.155.3761.465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hood L., Campbell J. H., Elgin S. C. The organization, expression, and evolution of antibody genes and other multigene families. Annu Rev Genet. 1975;9:305–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.09.120175.001513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hood L., McKean D., Farnsworth V., Potter M. Mouse immunoglobulin chains. A survey of the amino-terminal sequences of kappa chains. Biochemistry. 1973 Feb;12(4):741–749. doi: 10.1021/bi00728a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn M. J., Laursen R. A. Solid-phase edman degradation: attachment of carboxyl-terminal homoserine peptides to an insoluble resin. FEBS Lett. 1973 Nov 1;36(3):285–288. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80392-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leder P., Honjo T., Seidman J., Swan D. Origin of immunoglobulin gene diversity: the evidence and a restriction-modification model. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1977;41(Pt 2):855–862. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1977.041.01.095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman R., Potter M., Humphrey W., Jr, Mushinski E. B., Vrana M. Multiple individual and cross-specific indiotypes on 13 levan-binding myeloma proteins of BALB/c mice. J Exp Med. 1975 Jul 1;142(1):106–119. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.1.106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieu T. S., Deutsch H. F., Tischendorf F. W. Human lambda-chain sequence variations and serologic associations. Immunochemistry. 1977 Jun;14(6):429–433. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(77)90168-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKean D., Potter M., Hood L. Mouse immunoglobulin chains. Pattern of sequence variation among kappa chains with limited sequence differences. Biochemistry. 1973 Feb;12(4):760–771. doi: 10.1021/bi00728a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padlan E. A. Structural basis for the specificity of antibody-antigen reactions and structural mechanisms for the diversification of antigen-binding specificities. Q Rev Biophys. 1977 Feb;10(1):35–65. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500000135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pisano J. J., Bronzert T. J., Brewer H. B., Jr Advances in the gas chromatographic analysis of amino acid phenyl- and methylthiohydantoins. Anal Biochem. 1972 Jan;45(1):43–59. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90006-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poljak R. J., Amzel L. M., Chen B. L., Phizackerley R. P., Saul F. The three-dimensional structure of the fab' fragment of a human myeloma immunoglobulin at 2.0-angstrom resolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Sep;71(9):3440–3444. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.9.3440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter M., Rudikoff S., Vrana M., Rao D. N., Mushinski E. B. Primary structural differences in myeloma proteins that bind the same haptens. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1977;41(Pt 2):661–666. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1977.041.01.075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudikoff S., Claflin J. L. Expression of equivalent clonotypes in BALB/c and A/J mice after immunization with phosphorylcholine. J Exp Med. 1976 Nov 2;144(5):1294–1304. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.5.1294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudikoff S., Potter M. Size differences among immunoglobulin heavy chains from phosphorylcholine-binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jun;73(6):2109–2112. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.6.2109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudikoff S., Potter M. Variable region sequence of the heavy chain from a phosphorylcholine binding myeloma protein. Biochemistry. 1974 Sep 10;13(19):4033–4038. doi: 10.1021/bi00716a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal D. M., Padlan E. A., Cohen G. H., Rudikoff S., Potter M., Davies D. R. The three-dimensional structure of a phosphorylcholine-binding mouse immunoglobulin Fab and the nature of the antigen binding site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Nov;71(11):4298–4302. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.11.4298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smithies O., Gibson D., Fanning E. M., Goodfliesh R. M., Gilman J. G., Ballantyne D. L. Quantitative procedures for use with the Edman-Begg sequenator. Partial sequences of two unusual immunoglobulin light chains, Rzf and Sac. Biochemistry. 1971 Dec 21;10(26):4912–4921. doi: 10.1021/bi00802a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streefkerk D. G., Glaudemans C. P. Binding studies on anti-fructofuranan mouse myeloma immunoglobulins A47N, A4, U61, and E109. Biochemistry. 1977 Aug 23;16(17):3760–3765. doi: 10.1021/bi00636a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers M. R., Smythers G. W., Oroszlan S. Thin-layer chromatography of sub-nanomole amounts of phenylthiohydantoin (PTH) amino acids on polyamide sheets. Anal Biochem. 1973 Jun;53(2):624–628. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90114-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonegawa S., Hozumi N., Matthyssens G., Schuller R. Somatic changes in the content and context of immunoglobulin genes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1977;41(Pt 2):877–889. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1977.041.01.097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vrana M., Rudikoff S., Potter M. Heavy-chain variable-region sequence from an inulin-binding myeloma protein. Biochemistry. 1977 Mar 22;16(6):1170–1175. doi: 10.1021/bi00625a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vrana M., Tomasić J., Glaudemans C. P. Purification of homogeneous murine immunoglobulins with anti-fructofuranan specificity. J Immunol. 1976 Jun;116(6):1662–1663. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigert M. G., Cesari I. M., Yonkovich S. J., Cohn M. Variability in the lambda light chain sequences of mouse antibody. Nature. 1970 Dec 12;228(5276):1045–1047. doi: 10.1038/2281045a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigert M., Riblet R. Genetic control of antibody variable regions. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1977;41(Pt 2):837–846. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1977.041.01.093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu T. T., Kabat E. A. An analysis of the sequences of the variable regions of Bence Jones proteins and myeloma light chains and their implications for antibody complementarity. J Exp Med. 1970 Aug 1;132(2):211–250. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.2.211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


