Abstract
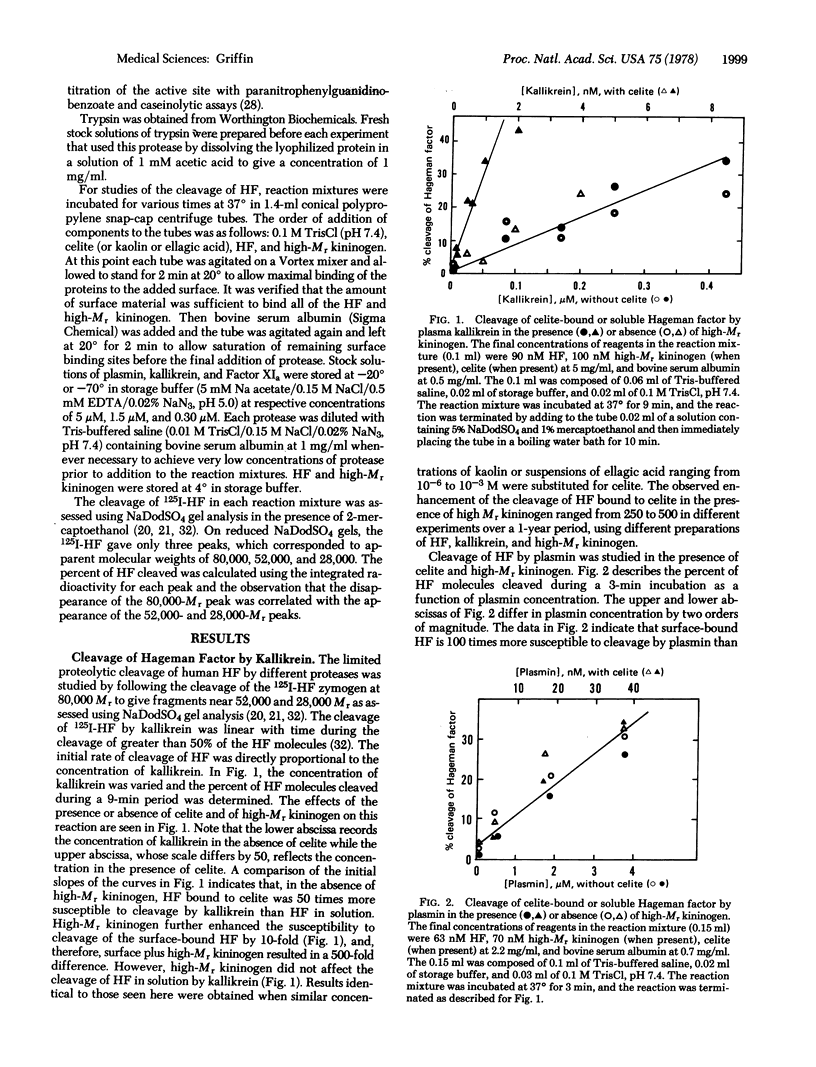
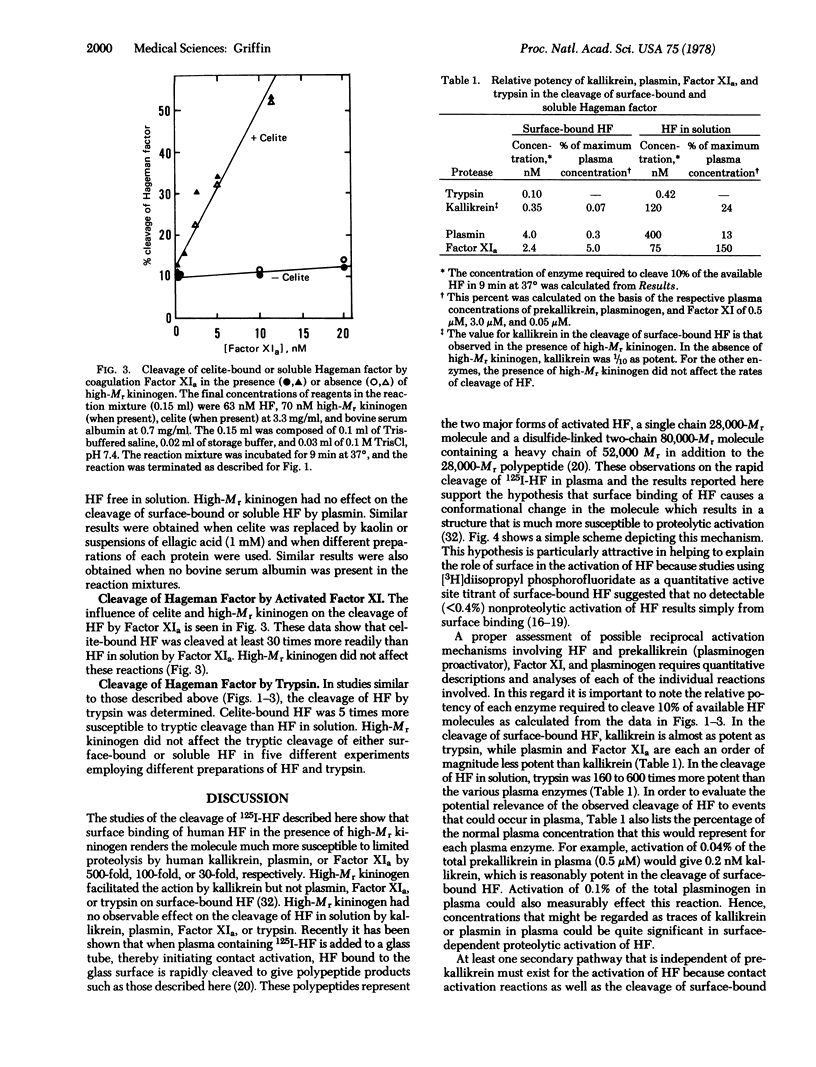
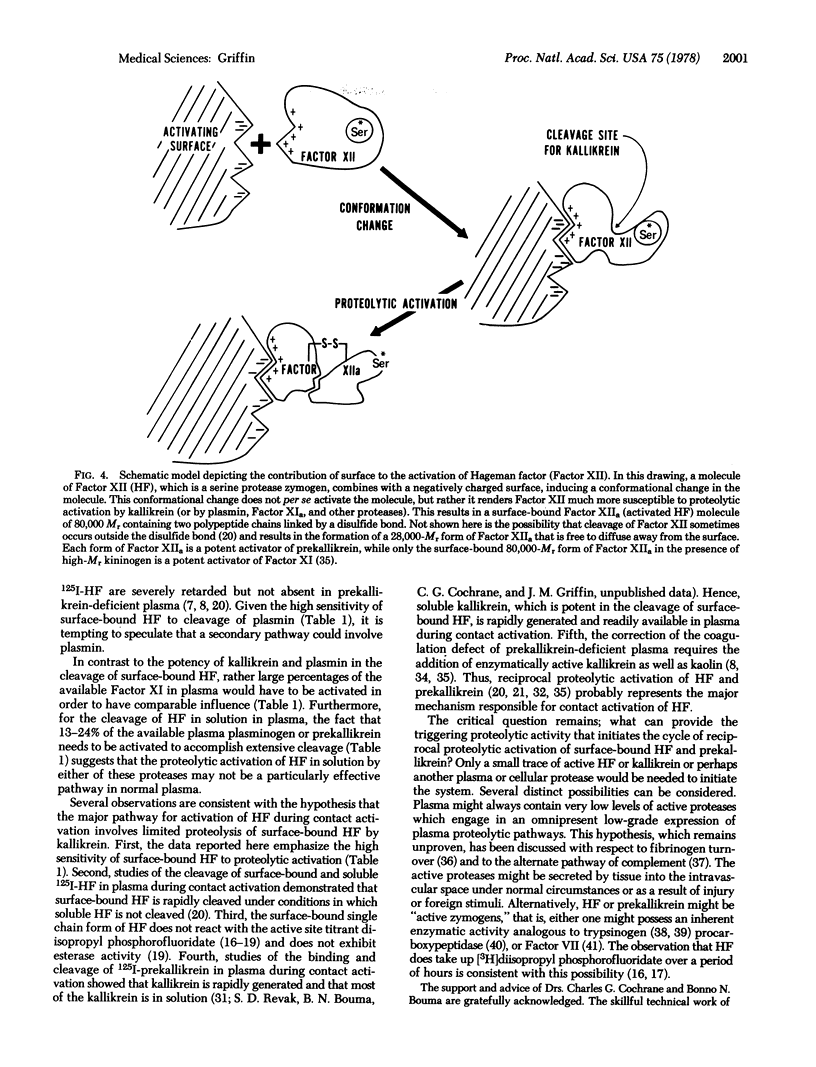
The mechanism by which negatively charged substances such as celite, kaolin, or ellagic acid contribute to the surface-dependent activation of Hageman factor (Factor XII) was studied. Kinetic studies of the proteolytic activation of 125I-labeled human Hageman factor by human plasma kallikrein, plasma, activated Factor XI, and trypsin were performed in the presence and absence of high molecular weight kininogen and surface materials such as celite, kaolin, or ellagic acid. The results showed that surface-bound Hageman factor was 500 times more susceptible than soluble Hageman factor to proteolytic activation by kallikrein in the presence of high molecular weight kininogen. Surface binding of Hageman factor enhanced its cleavage by plasmin, activated Factor XI, and trypsin by 100-fold, 30-fold, and 5-fold, respectively. On a molar basis, trypsin was twice as potent as kallikrein in the cleavage of the surface-bound Hageman factor, while plasmin and activated Factor XI were an order of magnitude less potent than kallikrein. Kallikrein even at concentrations as low as 0.5 nM (i.e., 1/1000th of the concentration of prekallikrein in plasma) was very potent in the limited proteolysis of the surface-bound Hageman factor. These results suggest that substances classically known as “activating surfaces” promote the activation of Hageman factor indirectly by altering its structure such that it is much more susceptible to proteolytic activation by other plasma or cellular proteases.
Keywords: kallikrein, kininogen, plasmin, Factor XI
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bagdasarian A., Lahiri B., Colman R. W. Origin of the high molecular weight activator of prekallikrein. J Biol Chem. 1973 Nov 25;248(22):7742–7747. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behnke W. D., Vallee B. L. The spectrum of cobalt bovine procarboxypeptidase A, an index of catalytic function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Sep;69(9):2442–2445. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.9.2442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouma B. N., Griffin J. H. Deficiency of factor XII-dependent plasminogen proactivator in prekallikrein-deficient plasma. J Lab Clin Med. 1978 Jan;91(1):148–155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouma B. N., Griffin J. H. Human blood coagulation factor XI. Purification, properties, and mechanism of activation by activated factor XII. J Biol Chem. 1977 Sep 25;252(18):6432–6437. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burrowes C. E., Movat H. Z., Soltay M. J. The kinin system of human plasma. VI. The action of plasmin. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1971 Dec;138(3):959–966. doi: 10.3181/00379727-138-36027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochrane C. G., Revak S. D., Wuepper K. D. Activation of Hageman factor in solid and fluid phases. A critical role of kallikrein. J Exp Med. 1973 Dec 1;138(6):1564–1583. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.6.1564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colman R. W., Bagdasarian A., Talamo R. C., Scott C. F., Seavey M., Guimaraes J. A., Pierce J. V., Kaplan A. P. Williams trait. Human kininogen deficiency with diminished levels of plasminogen proactivator and prekallikrein associated with abnormalities of the Hageman factor-dependent pathways. J Clin Invest. 1975 Dec;56(6):1650–1662. doi: 10.1172/JCI108247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson V. H., Glueck H. I., Miller M. A., Movat H. Z., Habal F. Kininogen deficiency in Fitzgerald trait: role of high molecular weight kininogen in clotting and fibrinolysis. J Lab Clin Med. 1976 Feb;87(2):327–337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fearon D. T., Austen K. F. Activation of the alternative complement pathway due to resistance of zymosan-bound amplification convertase to endogenous regulatory mechanisms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Apr;74(4):1683–1687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.4.1683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujikawa K., Kurachi K., Davie E. W. Characterization of bovine factor XIIa (activated Hageman factor). Biochemistry. 1977 Sep 20;16(19):4182–4188. doi: 10.1021/bi00638a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin J. H., Cochrane C. G. Mechanisms for the involvement of high molecular weight kininogen in surface-dependent reactions of Hageman factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Aug;73(8):2554–2558. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.8.2554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hathaway W. E., Belhasen L. P., Hathaway H. S. Evidence for a new plasma thromboplastin factor. I. Case report, coagulation studies and physicochemical properties. Blood. 1965 Nov;26(5):521–532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan A. P., Austen K. F. A prealbumin activator of prekallikrein. II. Derivation of activators of prekallikrein from active Hageman factor by digestion with plasmin. J Exp Med. 1971 Apr 1;133(4):696–712. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.4.696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay J., Kassell B. The autoactivation of trypsinogen. J Biol Chem. 1971 Nov;246(21):6661–6665. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARGOLIS J. Activation of plasma by contact with glass: evidence for a common reaction which releases plasma kinin and initiates coagulation. J Physiol. 1958 Nov 10;144(1):1–22. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp006082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARGOLIS J. The interrelationship of coagulation of plasma and release of peptides. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1963 Feb 4;104:133–145. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1963.tb17659.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConahey P. J., Dixon F. J. A method of trace iodination of proteins for immunologic studies. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1966;29(2):185–189. doi: 10.1159/000229699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meier H. L., Pierce J. V., Colman R. W., Kaplan A. P. Activation and function of human Hageman factor. The role of high molecular weight kininogen and prekallikrein. J Clin Invest. 1977 Jul;60(1):18–31. doi: 10.1172/JCI108754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NIEWIAROWSKI S., PROU-WARTELLE O. [Role of the contact factor (Hageman factor) in fibrinolysis]. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1959 Sep 1;3:593–603. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nossel H. L., Yudelman I., Canfield R. E., Butler V. P., Jr, Spanondis K., Wilner G. D., Qureshi G. D. Measurement of fibrinopeptide A in human blood. J Clin Invest. 1974 Jul;54(1):43–53. doi: 10.1172/JCI107749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RATNOFF O. D., COLOPY J. E. A familial hemorrhagic trait associated with a deficiency of a clot-promoting fraction of plasma. J Clin Invest. 1955 Apr;34(4):602–613. doi: 10.1172/JCI103109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSENTHAL R. L., DRESKIN O. H., ROSENTHAL N. New hemophilia-like disease caused by deficiency of a third plasma thromboplastin factor. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1953 Jan;82(1):171–174. doi: 10.3181/00379727-82-20057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radcliffe R., Nemerson Y. Mechanism of activation of bovine factor VII. Products of cleavage by factor Xa. J Biol Chem. 1976 Aug 25;251(16):4749–4802. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratnoff O. D. The biology and pathology of the initial stages of blood coagulation. Prog Hematol. 1966;5:204–245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Revak S. D., Cochrane C. G., Bouma B. N., Griffin J. H. Surface and fluid phase activities of two forms of activated Hageman factor produced during contact activation of plasma. J Exp Med. 1978 Mar 1;147(3):719–729. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.3.719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Revak S. D., Cochrane C. G., Griffin J. H. The binding and cleavage characteristics of human Hageman factor during contact activation. A comparison of normal plasma with plasmas deficient in factor XI, prekallikrein, or high molecular weight kininogen. J Clin Invest. 1977 Jun;59(6):1167–1175. doi: 10.1172/JCI108741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson N. C., Neurath H., Walsh K. A. The relation of the -amino group of trypsin to enzyme function and zymogen activation. Biochemistry. 1973 Jan 30;12(3):420–426. doi: 10.1021/bi00727a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito H., Ratnoff O. D., Donaldson V. H. Defective activation of clotting, fibrinolytic, and permeability-enhancing systems in human Fletcher trait plasma. Circ Res. 1974 May;34(5):641–651. doi: 10.1161/01.res.34.5.641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito H., Ratnoff O. D., Waldmann R., Abraham J. P. Fitzgerald Trait: Deficiency of a Hitherto Unrecognized Agent, Fitzgerald Factor, Participating in Surface-Mediated Reactions of Clotting, Fibrinolysis, Generation of Kinins, and the Property of Diluted Plasma Enhancing Vascular Permeability (PF/Dil). J Clin Invest. 1975 May;55(5):1082–1089. doi: 10.1172/JCI108009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiffman S., Lee P. Partial purification and characterization of contact activation cofactor. J Clin Invest. 1975 Nov;56(5):1082–1092. doi: 10.1172/JCI108182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiggins R. C., Bouma B. N., Cochrane C. G., Griffin J. H. Role of high-molecular-weight kininogen in surface-binding and activation of coagulation Factor XI and prekallikrein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4636–4640. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wuepper K. D., Miller D. R., Lacombe M. J. Flaujeac trait. Deficiency of human plasma kininogen. J Clin Invest. 1975 Dec;56(6):1663–1672. doi: 10.1172/JCI108248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wuepper K. D. Prekallikrein deficiency in man. J Exp Med. 1973 Dec 1;138(6):1345–1355. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.6.1345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


