Abstract
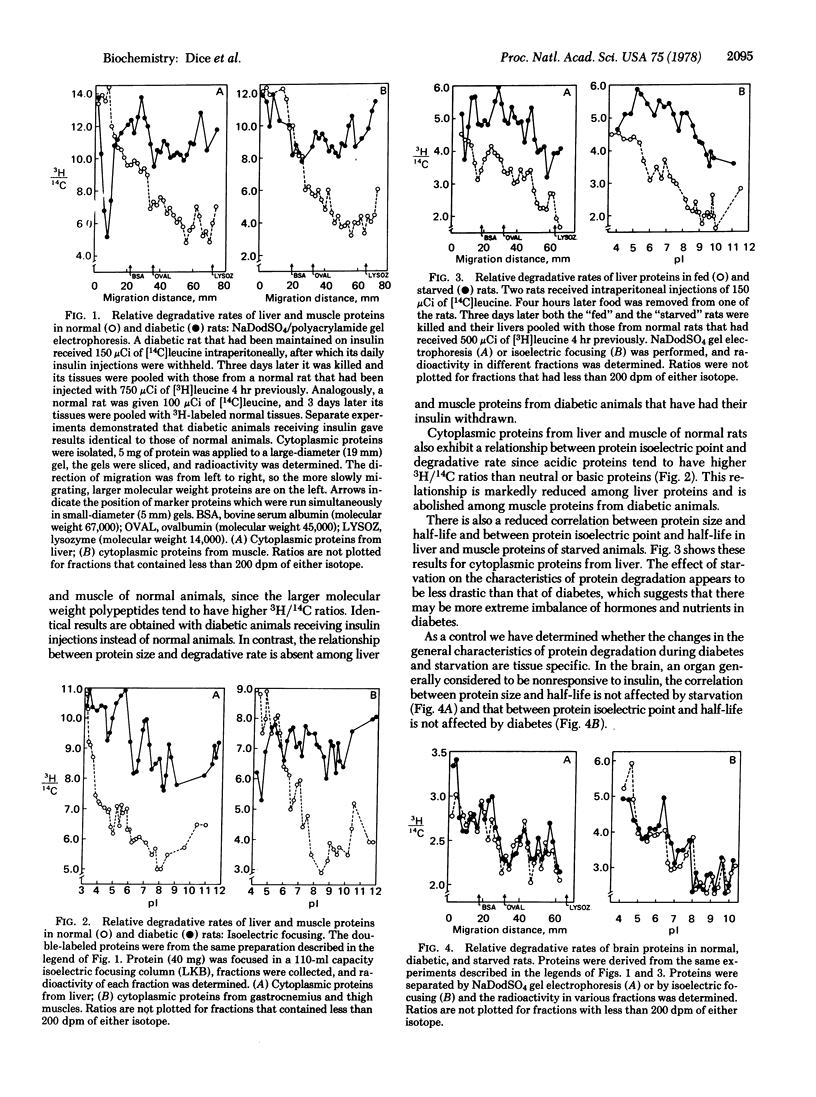
The enhanced protein degradation associated with diabetes and starvation is fundamentally different from normal protein catabolism. In normal eukaryotic cells large molecular weight proteins tend to be degraded more rapidly than small proteins, acidic proteins tend to be degraded more rapidly than neutral or basic proteins, and glycoproteins tend to be degraded more rapidly than nonglycoproteins. All three of these general correlations are absent or markedly reduced in liver and muscle of diabetic and starved rats. In contrast, the correlations between proteins size and half-life, between protein net charge and half-life, and between protein carbohydrate content and half-life are not affected in brain of diabetic or starved animals. These results suggest that diabetes and starvation alter the general characteristics of intracellular protein degradation in target tissues of insulin. Degradation of serum proteins is also affected in diabetes and starvation. In normal animals a general correlation exists between isoelectric points of serum proteins and their degradative rates. This relationship is abolished in diabetes and starvation, as it is among liver and muscle proteins. The implications of our findings are discussed with regard to possible mechanisms of the enhanced protein breakdown.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradley M. O. Regulation of protein degradation in normal and transformed human cells. Effects of growth state, medium composition, and viral transformation. J Biol Chem. 1977 Aug 10;252(15):5310–5315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dice J. F., Dehlinger P. J., Schimke R. T. Studies on the correlation between size and relative degradation rate of soluble proteins. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jun 25;248(12):4220–4228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dice J. F., Goldberg A. L. Relationship between in vivo degradative rates and isoelectric points of proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3893–3897. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dive J. F., Goldberg A. L. Structural properties of rat serum proteins which correlate with their degradative rates in vivo. Nature. 1976 Aug 5;262(5568):514–516. doi: 10.1038/262514a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein D., Elias-Bishko S., Hershko A. Requirement for protein synthesis in the regulation of protein breakdown in cultured hepatoma cells. Biochemistry. 1975 Nov 18;14(23):5199–5204. doi: 10.1021/bi00694a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREEN M., MILLER L. L. Protein catabolism and protein synthesis in perfused livers of normal and alloxan-diabetic rats. J Biol Chem. 1960 Nov;235:3202–3208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass R. D., Doyle D. On the measurement of protein turnover in animal cells. J Biol Chem. 1972 Aug 25;247(16):5234–5242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg A. L., Dice J. F. Intracellular protein degradation in mammalian and bacterial cells. Annu Rev Biochem. 1974;43(0):835–869. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.43.070174.004155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg A. L., St John A. C. Intracellular protein degradation in mammalian and bacterial cells: Part 2. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:747–803. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.003531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurd J. W., Evans W. H. Relative rates of degradation of mouse-liver surface-membrane proteins. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Jul 2;36(1):273–279. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02910.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jefferson L. S., Li J. B., Rannels S. R. Regulation by insulin of amino acid release and protein turnover in the perfused rat hemicorpus. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 25;252(4):1476–1483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Junod A., Lambert A. E., Orci L., Pictet R., Gonet A. E., Renold A. E. Studies of the diabetogenic action of streptozotocin. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1967 Oct;126(1):201–205. doi: 10.3181/00379727-126-32401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan J., Moskowitz M. Studies on the turnover of plasma membranes in cultured mammalian cells. II. Demonstration of heterogeneous rates of turnover for plasma membrane proteins and glycoproteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 May 6;389(2):306–313. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90323-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles S. E., Ballard F. J. Selective control of the degradation of normal and aberrant proteins in Reuber H35 hepatoma cells. Biochem J. 1976 Jun 15;156(3):609–617. doi: 10.1042/bj1560609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J. B., Goldberg A. L. Effects of food deprivation on protein synthesis and degradation in rat skeletal muscles. Am J Physiol. 1976 Aug;231(2):441–448. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1976.231.2.441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majerus P. W., Kilburn E. Acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase. The roles of synthesis and degradation in regulation of enzyme levels in rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1969 Nov 25;244(22):6254–6262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews R. A., Johnson T. C., Hudson J. E. Synthesis and turnover of plasma-membrane proteins and glycoproteins in a neuroblastoma cell line. Biochem J. 1976 Jan 15;154(1):57–64. doi: 10.1042/bj1540057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M., Khassis S., Shafrir E. Determination of trypsin by its accelerating effect on the onset of trypsinogen activation. Anal Biochem. 1974 Mar;58(1):25–29. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90436-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millward D. J., Garlick P. J., Nnanyelugo D. O., Waterlow J. C. The relative importance of muscle protein synthesis and breakdown in the regulation of muscle mass. Biochem J. 1976 Apr 15;156(1):185–188. doi: 10.1042/bj1560185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naya J., Vigne J. L., De Castro F. T. The dynamic state of Tetrahymena pyriformis cytosol proteins during culture development. FEBS Lett. 1977 Apr 15;76(2):269–273. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80166-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neely A. N., Cox J. R., Fortney J. A., Schworer C. M., Mortimore G. E. Alterations of lysosomal size and density during rat liver perfusion. Suppression by insulin and amino acids. J Biol Chem. 1977 Oct 10;252(19):6948–6954. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parving H. H., Rossing N., Sander E. Increased metabolic turnover rate and transcapillary escape rate of albumin in long-term juvenile diabetics. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1975 Jan;35(1):59–66. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poole B. The kinetics of disappearance of labeled leucine from the free leucine pool of rat liver and its effect on the apparent turnover of catalase and other hepatic proteins. J Biol Chem. 1971 Nov;246(21):6587–6591. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poole B., Wibo M. Protein degradation in cultured cells. The effect of fresh medium, fluoride, and iodoacetate on the digestion of cellular protein of rat fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1973 Sep 10;248(17):6221–6226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rannels D. E., Kao R., Morgan H. E. Effect of insulin on protein turnover in heart muscle. J Biol Chem. 1975 Mar 10;250(5):1694–1701. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHIMKE R. T. THE IMPORTANCE OF BOTH SYNTHESIS AND DEGRADATION IN THE CONTROL OF ARGINASE LEVELS IN RAT LIVER. J Biol Chem. 1964 Nov;239:3808–3817. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swick R. W., Ip M. M. Measurement of protein turnover in rat liver with (14C)carbonate. Protein turnover during liver regeneration. J Biol Chem. 1974 Nov 10;249(21):6836–6841. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zak R., Martin A. F., Prior G., Rabinowitz M. Comparison of turnover of several myofibrillar proteins and critical evaluation of double isotope method. J Biol Chem. 1977 May 25;252(10):3430–3435. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



