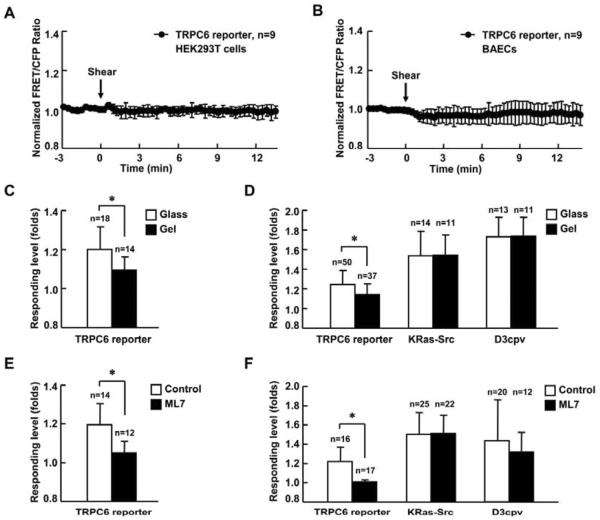
Fig. 4. Substrate rigidity and intercellular tension affect TRPC6 activity.
(A) and (B) Representative time courses of normalized FRET/CFP emission ratio of TRPC6 reporter inresponse to 65 dyn/cm2 shear stress stimulation (time 0) in HEK293T cells (A) or BAECs (B). (C) and (E) Response of TRPC6 reporter to 300 μM OAG stimulation in MEFs (C) cultured on rigid surface (glass) or soft substrate (gel with 600 pa stiffness) or (E) with 5 μM ML-7 pretreatment for 1hr. (D) and (F) Responses of TRPC6, KRas-Src, or D3cpv reporter to 10 ng/ml PDGF stimulation in MEFs (D) cultured on rigid surface (glass) or soft substrate (gel with 600 pa stiffness) or (F) with 5 μM ML-7 pretreatment for 1 hr. MEFs transfected with TRPC6 reporter were pretreated with 1 μM TG for 1 hr before imaging. MEFs transfected with D3cpv were maintained in Ca2+ free HBSS buffer during imaging. “n” represents the cell number in each group. * indicates the significant difference between indicated groups (P < 0.01).