In the original paper, there was an error in Figure 2(c). Figures 2(b) and 2(c) were the same, and here we provide the right form of Figure 2(c).
Figure 2.
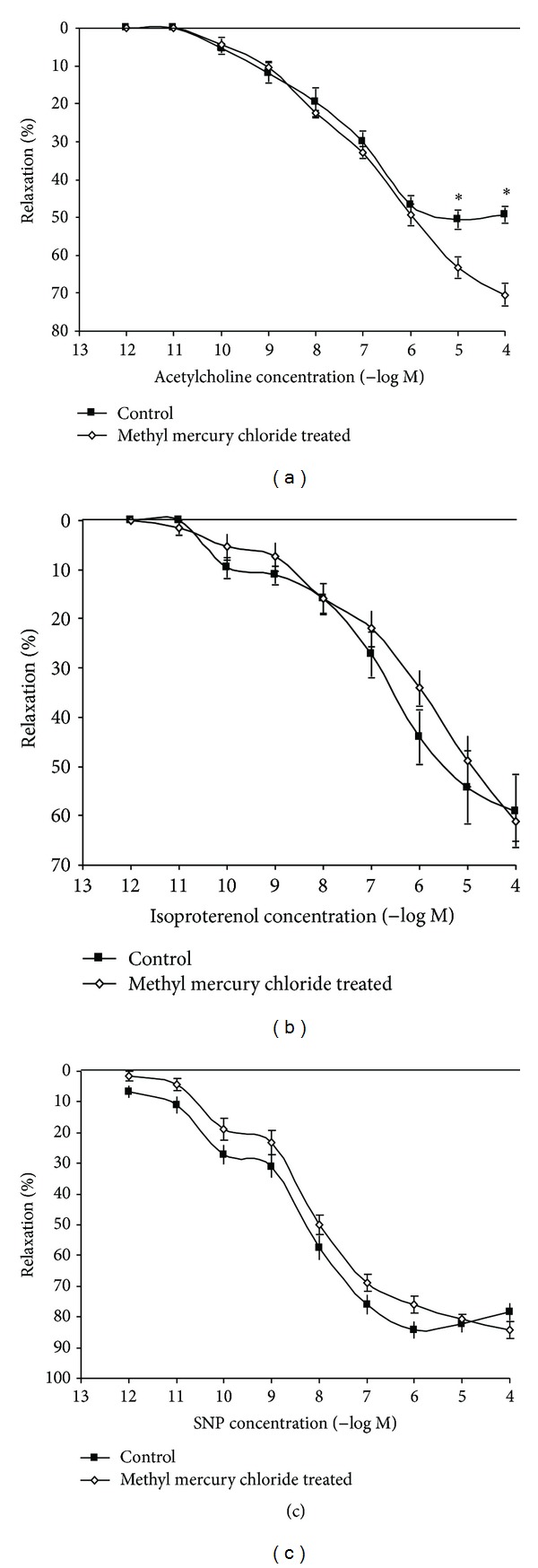
Effect of methyl mercury chloride treatment on the vascular relaxation response to acetylcholine, isoproterenol, and sodium nitroprusside. Concentration-response curves to (a) acetylcholine (ACh), (b) isoproterenol (IP), and (c) sodium nitroprusside (SNP) in the aortas of rats untreated, treated with methyl mercury chloride (n = 10) precontracted with PE. The results (mean ± SEM) are expressed as percentage of the response to PE. t-test, *P < 0.05.


