Abstract
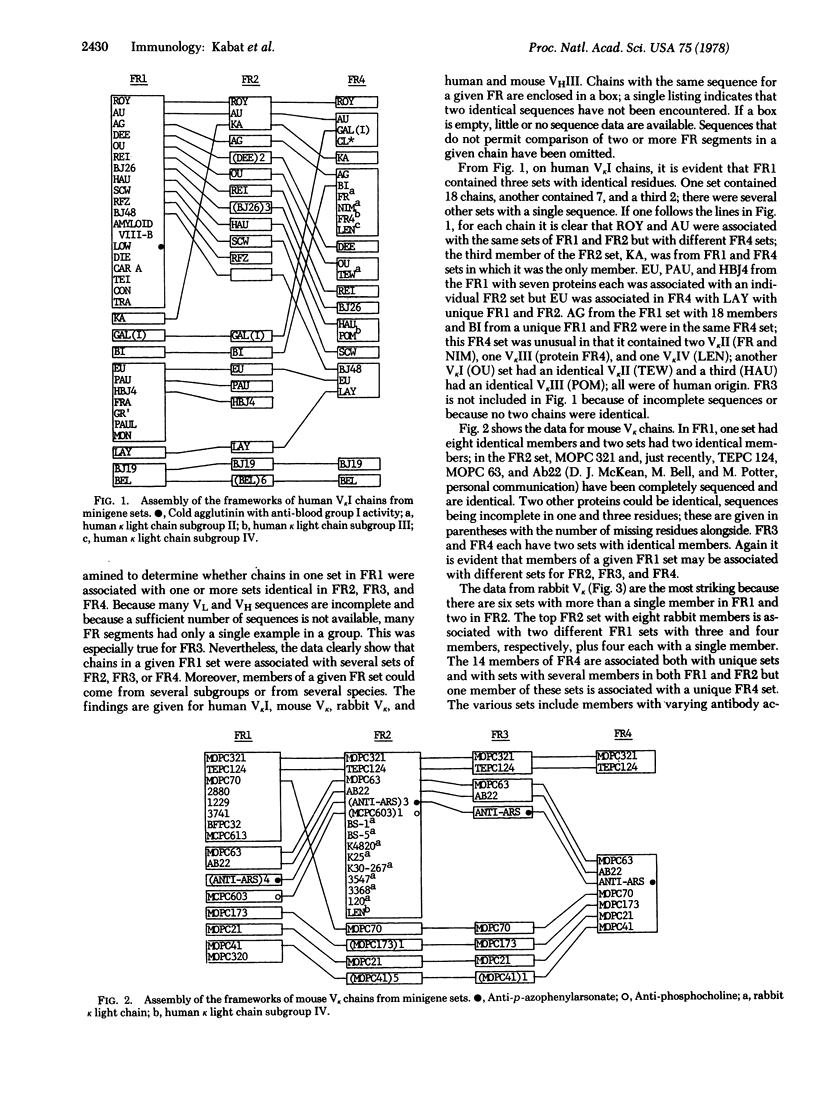
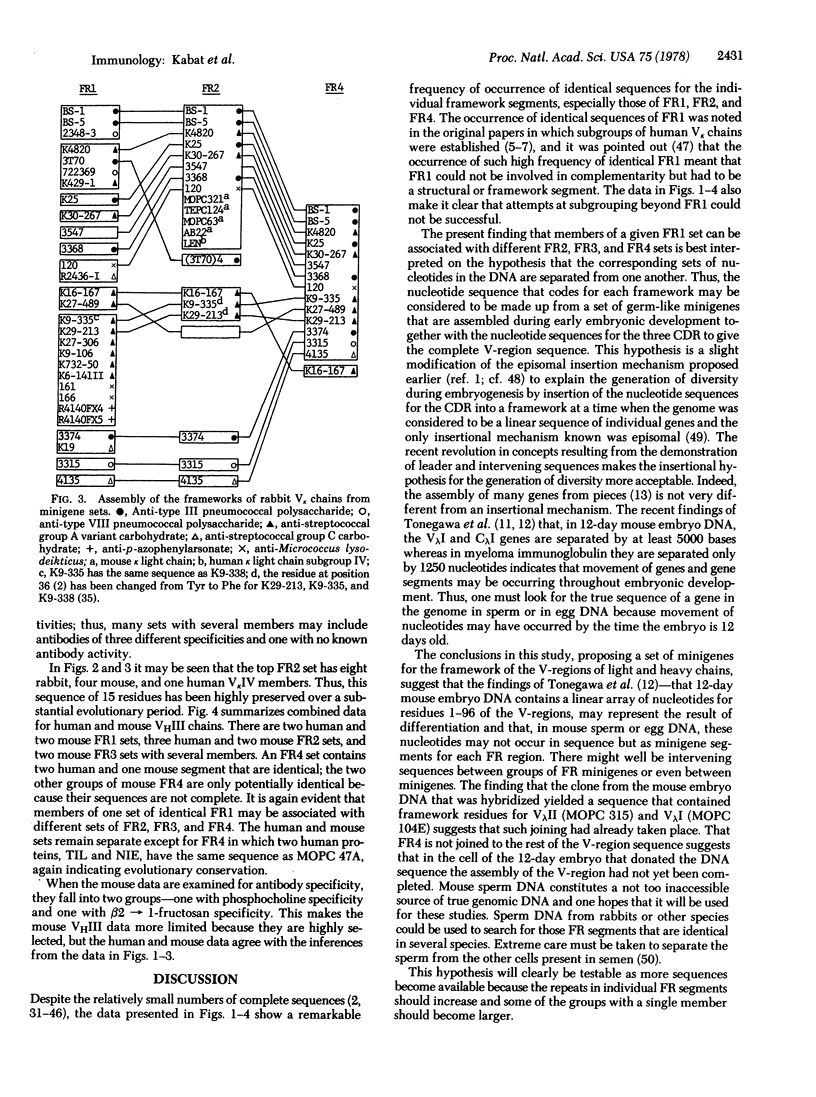
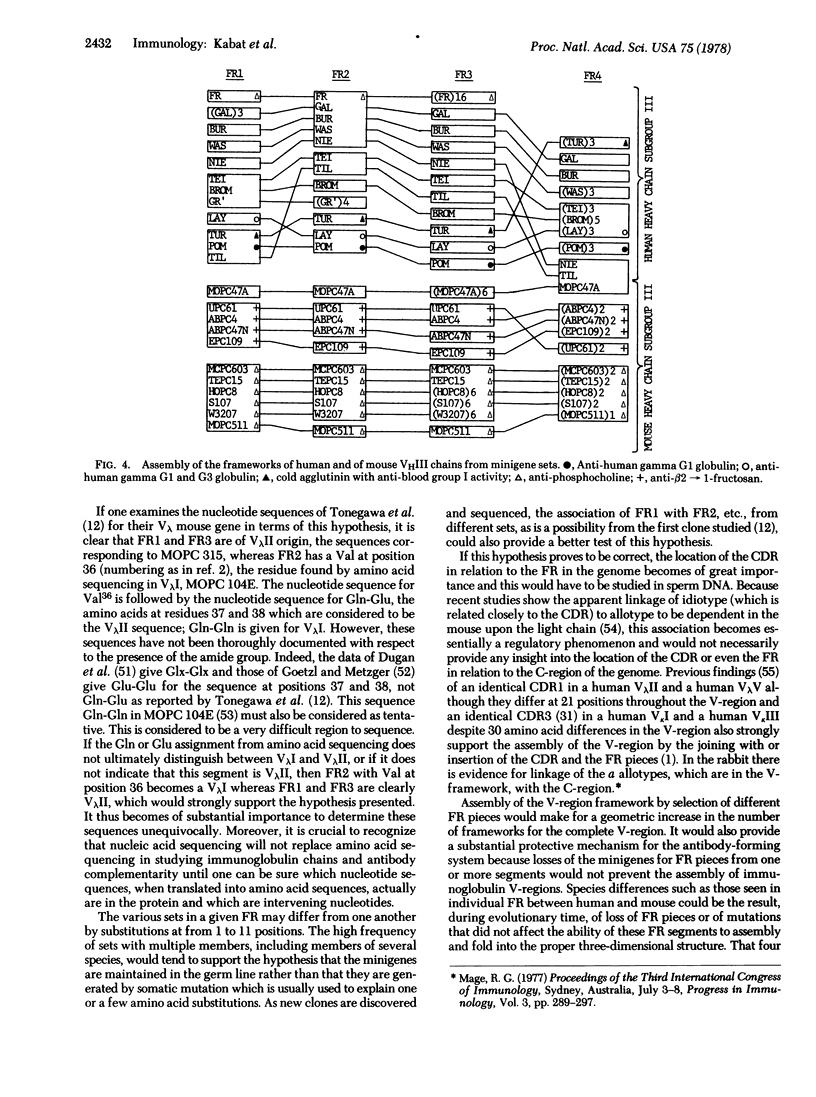
Sequences of each of the four framework segments FR1, FR2, FR3, and FR4 of the variable regions (V-regions) of light and heavy chains of immunoglobulins were grouped into sets with identical sequences. Sets contained from 1 to 18 members. When each V-region was traced from one FR to the next, it was seen that members of the same set in FR1 could be associated with different sets in FR2, FR3, and FR4. This suggests that the framework for the light and heavy chain V-regions is assembled during embryonic development from sets of minigenes for each FR segment. FR4 from three sets of human VkI chains also contained members of VkII, VkIII, and VkIV subgroups; one FR2 set contained eight rabbit Vk, one human VkIV, and four mouse Vk and an FR4 set contained two human VHIII and one mouse VHIII, indicating substantial evolutionary preservation of these sequences and suggesting that the sets of minigenes are highly conserved in the germ line. The clone of Tonegawa et al. [Tonegawa, S., Maxam, A. M., Tizard, R., Bernard, O. & Gilbert, W. (1978) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 75, 1485-1489] could be a hybrid FR1 and FR3 coming from minigenes of MOPC 315 (a VλII) whereas FR2 would come from MOPC 104E (a VλI). That FR4 is not joined to the rest of the V-region in 12-day-old mouse embryo DNA is also in accord with this hypothesis. Mouse sperm DNA should be examined to establish whether the hypothesized minigenes are separated by intervening sequences and whether the complementarity-determining (hypervariable) regions or segments of the V-region are separated from the framework in genomic DNA. Sperm DNA from rabbits or other species could be used to search for minigene segments whose sequences are identical in several species.
Keywords: minigenes, insertional mechanism
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aloni Y., Dhar R., Laub O., Horowitz M., Khoury G. Novel mechanism for RNA maturation: the leader sequences of simian virus 40 mRNA are not transcribed adjacent to the coding sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3686–3690. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appella E. Amino acid sequences of two mouse immunoglobulin lambda chains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Mar;68(3):590–594. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.3.590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barstad P., Farnsworth V., Weigert M., Cohn M., Hood L. Mouse immunoglobulin heavy chains are coded by multiple germ line variable region genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Oct;71(10):4096–4100. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.10.4096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berget S. M., Moore C., Sharp P. A. Spliced segments at the 5' terminus of adenovirus 2 late mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3171–3175. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun D. G., Huser H., Riesen W. F. Rabbit antibody light chains: selective breeding narrows variability in framework and complementarity-determining residues. Eur J Immunol. 1976 Aug;6(8):570–578. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830060809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Mandel J. L., Chambon P. Ovalbumin gene is split in chicken DNA. Nature. 1977 Nov 24;270(5635):314–319. doi: 10.1038/270314a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capra J. D., Hopper J. E. Comparative studies on monotypic IgM lambda and IgG kappa from an individual patient--III. The complete amino acid sequence of the VH region of the IgM paraprotein. Immunochemistry. 1976 Dec;13(12):995–999. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(76)90271-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capra J. D., Kehoe J. M. Hypervariable regions, idiotypy, and the antibody-combining site. Adv Immunol. 1975;20:1–40. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60205-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capra J. D., Klapper D. G., Tung A. S., Nisonoff A. Identical hypervariable regions in light chains of differing V kappa subgroups. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1977;41(Pt 2):847–853. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1977.041.01.094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celma M. L., Dhar R., Pan J., Weissman S. M. Comparison of the nucleotide sequence of the messenger RNA for the major structural protein of SV40 with the DNA sequence encoding the amino acids of the protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Aug;4(8):2549–2550. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow L. T., Gelinas R. E., Broker T. R., Roberts R. J. An amazing sequence arrangement at the 5' ends of adenovirus 2 messenger RNA. Cell. 1977 Sep;12(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90180-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford L. V., Cole C. N., Smith A. E., Paucha E., Tegtmeyer P., Rundell K., Berg P. Organization and expression of early genes of simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):117–121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dugan E. S., Bradshaw R. A., Simms E. S., Eisen H. N. Amino acid sequence of the light chain of a mouse myeloma protein (MOPC-315). Biochemistry. 1973 Dec 18;12(26):5400–5416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman M. H., Guyer R. B., Terry W. D. Isolation and characterization of electrophoretically homogeneous rabbit antihapten antibody populations. 3. NH 2 -terminal light chain sequence analyses of focused anti-p-azophenyltrimethylammonium and anti-p-azobenzenearsonate antibody fractions. J Biol Chem. 1972 Nov 10;247(21):7051–7061. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert W. Why genes in pieces? Nature. 1978 Feb 9;271(5645):501–501. doi: 10.1038/271501a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glover D. M., Hogness D. S. A novel arrangement of the 18S and 28S sequences in a repeating unit of Drosophila melanogaster rDNA. Cell. 1977 Feb;10(2):167–176. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90212-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goetzl E. J., Metzger H. Affinity labeling of a mouse myeloma protein which binds nitrophenyl ligands. Sequence and position of a labeled tryptic peptide. Biochemistry. 1970 Sep 29;9(20):3862–3871. doi: 10.1021/bi00822a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman H. M., Olson M. V., Hall B. D. Nucleotide sequence of a mutant eukaryotic gene: the yeast tyrosine-inserting ochre suppressor SUP4-o. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5453–5457. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haber E., Margolies M. N., Cannon L. E. Origins of antibody diversity: insight gained from amino acid sequence studies of elicited antibodies. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1977;41(Pt 2):647–659. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1977.041.01.074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hood L., Loh E., Hubert J., Barstad P., Eaton B., Early P., Fuhrman J., Johnson N., Kronenberg M., Schilling J. The structure and genetics of mouse immunoglobulins: an analysis of NZB myeloma proteins and sets of BALB/c myeloma proteins binding particular haptens. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1977;41(Pt 2):817–836. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1977.041.01.092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffreys A. J., Flavell R. A. The rabbit beta-globin gene contains a large large insert in the coding sequence. Cell. 1977 Dec;12(4):1097–1108. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90172-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabat E. A. Unique features of the variable regions of Bence Jones proteins and their possible relation to antibody complementarity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Feb;59(2):613–619. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.2.613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabat E. A., Wu T. T. Attempts to locate complementarity-determining residues in the variable positions of light and heavy chains. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1971 Dec 31;190:382–393. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1971.tb13550.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitchingman G. R., Lai S. P., Westphal H. Loop structures in hybrids of early RNA and the separated strands of adenovirus DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4392–4395. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klapper D. G., Capra J. D. The amino acid sequence of the variable regions of the light chains from two idiotypically cross reactive IgM anti-gamma globulins. Ann Immunol (Paris) 1976 Jun-Jul;127(3-4):261–271. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klessig D. F. Two adenovirus mRNAs have a common 5' terminal leader sequence encoded at least 10 kb upstream from their main coding regions. Cell. 1977 Sep;12(1):9–21. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90181-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskin J. A., Gray A., Nisonoff A., Klinman N. R., Gottlieb P. D. Segregation at a locus determining an immunoglobulin genetic marker for the light chain variable region affects inheritance of expression of an idiotype. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4600–4604. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Y. S., Low T. L., Infante A., Putnam F. W. Complete covalent structure of a human IgA1 immunoglobulin. Science. 1976 Sep 10;193(4257):1017–1020. doi: 10.1126/science.821146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milstein C. Linked groups of residues in immunoglobulin k chains. Nature. 1967 Oct 28;216(5113):330–332. doi: 10.1038/216330a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niall H. D., Edman P. Two structurally distinct classes of kappa-chains in human immunoglobulins. Nature. 1967 Oct 21;216(5112):262–263. doi: 10.1038/216262a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellegrini M., Manning J., Davidson N. Sequence arrangement of the rDNA of Drosophila melanogaster. Cell. 1977 Feb;10(2):213–214. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90215-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter M. Antigen-binding myeloma proteins of mice. Adv Immunol. 1977;25:141–211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter M., Rudikoff S., Vrana M., Rao D. N., Mushinski E. B. Primary structural differences in myeloma proteins that bind the same haptens. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1977;41(Pt 2):661–666. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1977.041.01.075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raub W. F. The PROPHET system and resource sharing. Fed Proc. 1974 Dec;33(12):2390–2392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riesen W. F., Braun D. G., Jaton J. C. Human and murine phosphorycholine-binding immunoglobulins: conserved subgroup and first hypervariable region of heavy chains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jun;73(6):2096–2100. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.6.2096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson E. A., Appella E. Amino acid sequence of the first 217 residues of a mouse heavy chain (MOPC 47A) with a domain deletion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jun;74(6):2465–2469. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.6.2465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strosberg A. D., Van Hoegaerden M., Schreiber A. B. Evolution de la réponse immunitaire à micrococcus lysodeikticus. Ann Immunol (Paris) 1977 Jan-Mar;128(1-2):345–349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilghman S. M., Curtis P. J., Tiemeier D. C., Leder P., Weissmann C. The intervening sequence of a mouse beta-globin gene is transcribed within the 15S beta-globin mRNA precursor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1309–1313. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilghman S. M., Tiemeier D. C., Polsky F., Edgell M. H., Seidman J. G., Leder A., Enquist L. W., Norman B., Leder P. Cloning specific segments of the mammalian genome: bacteriophage lambda containing mouse globin and surrounding gene sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4406–4410. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonegawa S., Brack C., Hozumi N., Schuller R. Cloning of an immunoglobulin variable region gene from mouse embryo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3518–3522. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonegawa S., Maxam A. M., Tizard R., Bernard O., Gilbert W. Sequence of a mouse germ-line gene for a variable region of an immunoglobulin light chain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1485–1489. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vrana M., Rudikoff S., Potter M. Heavy-chain variable-region sequence from an inulin-binding myeloma protein. Biochemistry. 1977 Mar 22;16(6):1170–1175. doi: 10.1021/bi00625a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang A. C., Wang I. Y., Fudenberg H. H. Immunoglobulin structure and genetics. Identity between variable regions of a mu and a gamma2 chain. J Biol Chem. 1977 Oct 25;252(20):7192–7199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstock R., Sweet R., Weiss M., Cedar H., Axel R. Intragenic DNA spacers interrupt the ovalbumin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1299–1303. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellauer P. K., Dawid I. B. The structural organization of ribosomal DNA in Drosophila melanogaster. Cell. 1977 Feb;10(2):193–212. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90214-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White R. L., Hogness D. S. R loop mapping of the 18S and 28S sequences in the long and short repeating units of Drosophila melanogaster rDNA. Cell. 1977 Feb;10(2):177–192. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90213-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu T. T., Kabat E. A. An analysis of the sequences of the variable regions of Bence Jones proteins and myeloma light chains and their implications for antibody complementarity. J Exp Med. 1970 Aug 1;132(2):211–250. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.2.211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu T. T., Kabat E. A., Bilofsky H. Similarities among hypervariable segments of immunoglobulin chains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):5107–5110. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.5107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


