Abstract
Anti-idiotypic antibodies have been raised against antibodies to retinol-binding protein (RBP) and to insulin. After absorption the anti-idiotypic antibodies recognized the antigen-combining sites of the antibodies used as the immunogen but of no other antibodies. Some of the anti-idiotypic antibodies raised against antibodies to RBP bound specifically to rat intestine epithelial cells, which have a physiological cell-surface receptor for RBP. The RBP receptor mediates the uptake of retinol from RBP to the cells. This uptake was abolished in a concentration-dependent manner by the anti-idiotypic antibodies, which obviously competed with RBP for binding to the receptor.
Anti-idiotypic antibodies against antibodies to insulin inhibited the binding of 125I-labeled insulin to isolated rat epididymal fat cells, whereas anti-idiotypic antibodies raised against antibodies to RBP had no effect. Furthermore, on interacting with young rat thymocytes, anti-idiotypic antibodies against antibodies to insulin stimulated the uptake by the cells of α-aminoisobutyric acid, thereby mimicking the effect of insulin.
These results suggest that in some cases anti-idiotypic antibodies may be useful tools in elucidating structure-function relationships for cell-membrane receptors.
Keywords: retinol-binding protein, insulin receptor, insulin effect
Full text
PDF
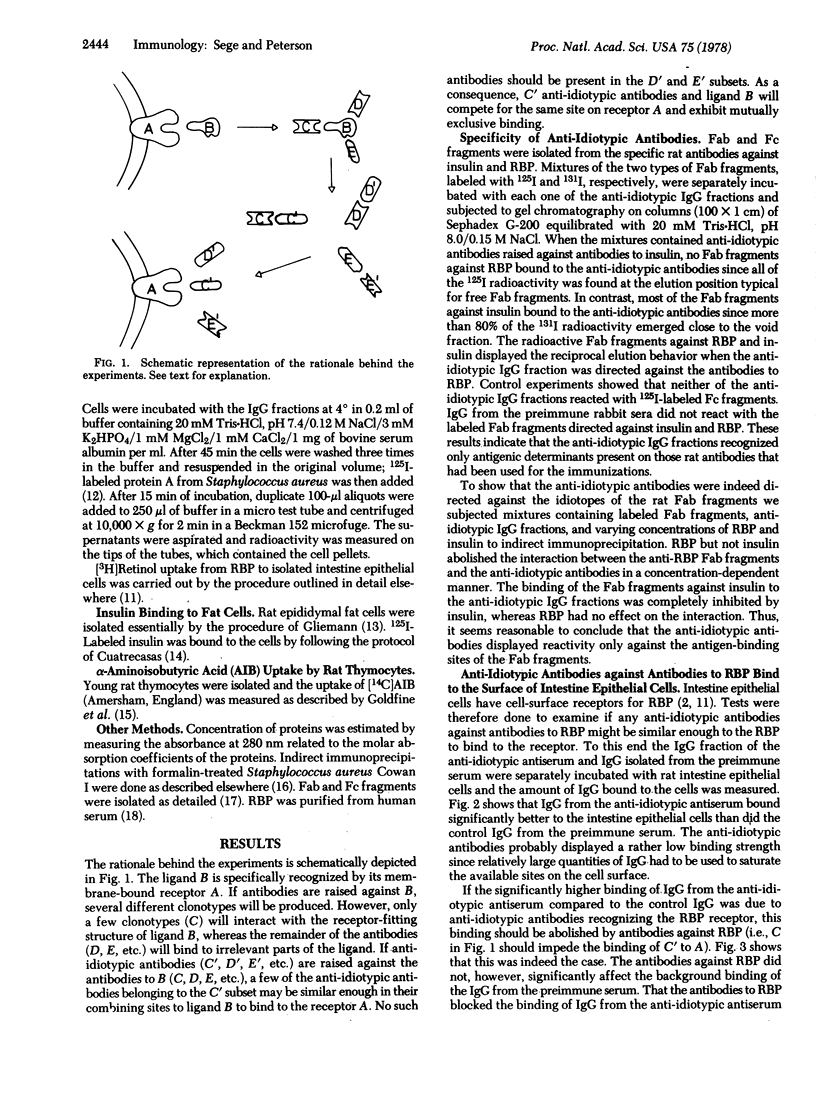
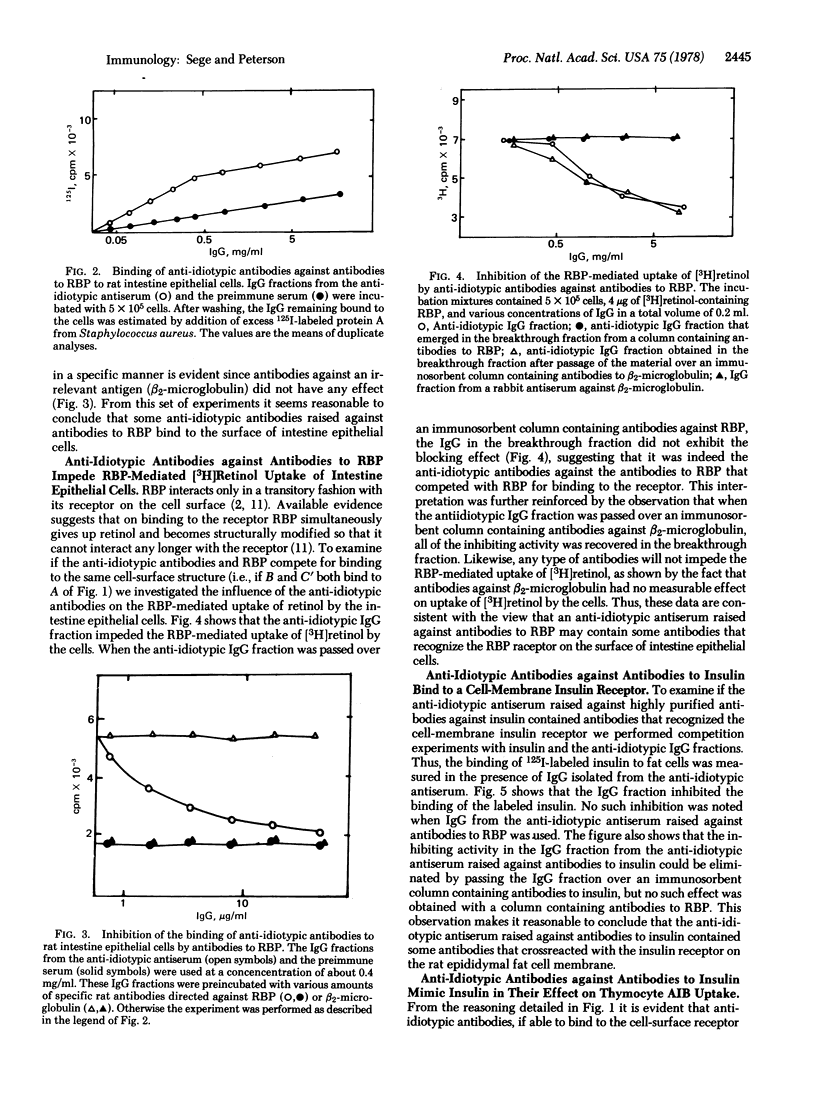
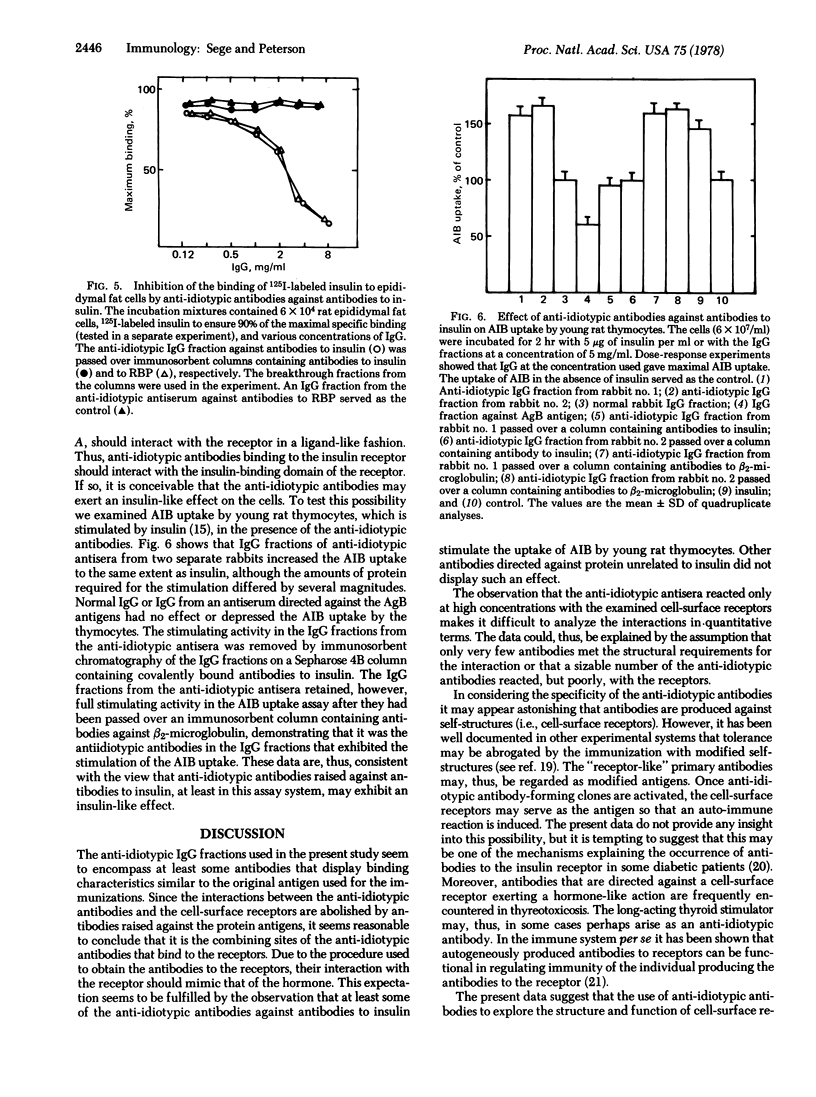

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cuatrecasas P. Insulin--receptor interactions in adipose tissue cells: direct measurement and properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jun;68(6):1264–1268. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.6.1264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorval G., Welsh K. I., Wigzell H. Labeled staphylococcal protein A as an immunological probe in the analysis of cell surface markers. Scand J Immunol. 1974;3(4):405–411. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1974.tb01273.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flier J. S., Kahn C. R., Roth J., Bar R. S. Antibodies that impair insulin receptor binding in an unusual diabetic syndrome with severe insulin resistance. Science. 1975 Oct 3;190(4209):63–65. doi: 10.1126/science.170678. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freychet P., Roth J., Neville D. M., Jr Insulin receptors in the liver: specific binding of ( 125 I)insulin to the plasma membrane and its relation to insulin bioactivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Aug;68(8):1833–1837. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.8.1833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENWOOD F. C., HUNTER W. M., GLOVER J. S. THE PREPARATION OF I-131-LABELLED HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE OF HIGH SPECIFIC RADIOACTIVITY. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:114–123. doi: 10.1042/bj0890114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gliemann J. Assay of insulin-like activity by the isolated fat cell method. I. Factors influencing the response to crystalline insulin. Diabetologia. 1967 Aug;3(4):382–388. doi: 10.1007/BF02342631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfine I. D., Gardner J. D., Neville D. M., Jr Insulin action in isolated rat thymocytes. I. Binding of 125 I-insulin and stimulation of -aminoisobutyric acid transport. J Biol Chem. 1972 Nov 10;247(21):6919–6926. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hjelm H., Hjelm K., Sjöquist J. Protein A from Staphylococcus aureus. Its isolation by affinity chromatography and its use as an immunosorbent for isolation of immunoglobulins. FEBS Lett. 1972 Nov 15;28(1):73–76. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80680-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn C. R. Membrane receptors for hormones and neurotransmitters. J Cell Biol. 1976 Aug;70(2 Pt 1):261–286. doi: 10.1083/jcb.70.2.261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostberg L., Sege K., Rask L., Peterson P. A. Isolation of radiolabelled H-2 antigens [proceedings]. Folia Biol (Praha) 1976;22(6):372–373. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson P. A. Characteristics of a vitamin A-transporting protein complex occurring in human serum. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jan 10;246(1):34–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson P. A., Evrin P. E., Berggård I. Differentiation of glomerular, tubular, and normal proteinuria: determinations of urinary excretion of beta-2-macroglobulin, albumin, and total protein. J Clin Invest. 1969 Jul;48(7):1189–1198. doi: 10.1172/JCI106083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson P. A., Nilsson S. F., Ostberg L., Rask L., Vahlquist A. Aspects of the metabolism of retinol-binding protein and retinol. Vitam Horm. 1974;32:181–214. doi: 10.1016/s0083-6729(08)60012-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson P. A., Rask L., Lindblom J. B. Highly purified papain-solubilized HL-A antigens contain beta2-microglobulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jan;71(1):35–39. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.1.35. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rask L., Peterson P. A. In vitro uptake of vitamin A from the retinol-binding plasma protein to mucosal epithelial cells from the monkey's small intestine. J Biol Chem. 1976 Oct 25;251(20):6360–6366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowley D. A., Köhler H., Schreiber H., Kaye S. T., Lorbach I. Suppression by autogenous complementary idiotypes: the priority of the first response. J Exp Med. 1976 Oct 1;144(4):946–959. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.4.946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E., Wigzell H. Breakage of tolerance to alpha foetoprotein in monkeys. Nature. 1975 Jun 26;255(5511):716–717. doi: 10.1038/255716a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sege K., Peterson P. A. Anti-idiotypic antibodies against anti-vitamin A transporting protein react with prealbumin. Nature. 1978 Jan 12;271(5641):167–168. doi: 10.1038/271167a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vahlquist A., Peterson P. A. Combination of specific antibodies with the human vitamin A-transporting protein complex. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jun 10;248(11):4040–4046. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


