Abstract
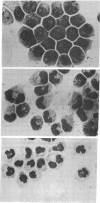
A human leukemic cell line (designated HL-60) has recently been established from the peripheral blood leukocytes of a patient with acute promyelocytic leukemia. This cell line displays distinct morphological and histochemical commitment towards myeloid differentiation. The cultured cells are predominantly promyelocytes, but the addition of dimethyl sulfoxide to the culture induces them to differentiate into myelocytes, metamyelocytes, and banded and segmented neutrophils. All 150 clones developed from the HL-60 culture show similar morphological differentiation in the presence of dimethyl sulfoxide. Unlike the morphologically immature promyelocytes, the dimethyl sulfoxide-induced mature cells exhibit functional maturity as exemplified by phagocytic activity. A number of other compounds previously shown to induce erythroid differentiation of mouse erythroleukemia (Friend) cells can induce analogous maturation of the myeloid HL-60 cells. The marked similarity in behavior of HL-60 cells and Friend cells in the presence of these inducing agents suggests that similar molecular mechanisms are involved in the induction of differentiation of these human myeloid and murine erythroid leukemic cells.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Azumi J. I., Sachs L. Chromosome mapping of the genes that control differentiation and malignancy in myeloid leukemic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jan;74(1):253–257. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.1.253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins S. J., Gallo R. C., Gallagher R. E. Continuous growth and differentiation of human myeloid leukaemic cells in suspension culture. Nature. 1977 Nov 24;270(5635):347–349. doi: 10.1038/270347a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew S. I., Terasaki P. I., Billing R. J., Bergh O. J., Minowada J., Klein E. Group-specific human granulocyte antigens on a chronic myelogenous leukemia cell line with a Philadelphia chromosome marker. Blood. 1977 May;49(5):715–718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fibach E., Sachs L. Control of normal differentiation of myeloid leukemic cells. VIII. Induction of differentiation to mature granulocytes in mass culture. J Cell Physiol. 1975 Oct;86(2 Pt 1):221–230. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040860205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friend C., Scher W., Holland J. G., Sato T. Hemoglobin synthesis in murine virus-induced leukemic cells in vitro: stimulation of erythroid differentiation by dimethyl sulfoxide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Feb;68(2):378–382. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.2.378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallagher R. E., Salahuddin S. Z., Hall W. T., McCredie K. B., Gallo R. C. Growth and differentiation in culture of leukemic leukocytes from a patient with acute myelogenous leukemia and re-identification of type-C virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):4137–4141. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.4137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichikawa Y. Differentiation of a cell line of myeloid leukemia. J Cell Physiol. 1969 Dec;74(3):223–234. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040740303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikawa Y., Furusawa M., Sugano H. Erythrocyte membrane-specific antigens in Friend virus-induced leukemia cells. Bibl Haematol. 1973;39:955–967. doi: 10.1159/000427928. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimhi Y., Palfrey C., Spector I., Barak Y., Littauer U. Z. Maturation of neuroblastoma cells in the presence of dimethylsulfoxide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):462–466. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kluge N., Gaedicke G., Steinheider G., Dube S., Ostertag W. Globin synthesis in Friend-erythroleukemia mouse cells in protein- and lipid-free medium. Effects of dimethyl-sulfoxide, iron and erythropoietin. Exp Cell Res. 1974 Oct;88(2):257–262. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(74)90239-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kluge N., Ostertag W., Sugiyama T., Arndt-Jovin D., Steinheider G., Furusawa M., Dube S. K. Dimethylsulfoxide-induced differentiation and hemoglobin synthesis in tissue cultures of rat erythroleukemia cells transformed by 7,12-dimethylbenz(a)anthracene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Apr;73(4):1237–1240. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.4.1237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krystosek A., Sachs L. Control of lysozyme induction in the differentiation of myeloid leukemic cells. Cell. 1976 Dec;9(4 Pt 2):675–684. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90131-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leder A., Leder P. Butyric acid, a potent inducer of erythroid differentiation in cultured erythroleukemic cells. Cell. 1975 Jul;5(3):319–322. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90107-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lozzio C. B., Lozzio B. B. Human chronic myelogenous leukemia cell-line with positive Philadelphia chromosome. Blood. 1975 Mar;45(3):321–334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan D. A., Ruscetti F. W., Gallo R. Selective in vitro growth of T lymphocytes from normal human bone marrows. Science. 1976 Sep 10;193(4257):1007–1008. doi: 10.1126/science.181845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preisler H. D., Christoff G., Taylor E. Cryoprotective agents as inducers of erythroleukemic cell differentiation in vitro. Blood. 1976 Mar;47(3):363–368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preisler H. D., Lyman G. Differentiation of erythroleukemia cells in vitro: properties of chemical inducers. Cell Differ. 1975 Jun;4(3):179–185. doi: 10.1016/0045-6039(75)90039-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuben R. C., Wife R. L., Breslow R., Rifkind R. A., Marks P. A. A new group of potent inducers of differentiation in murine erythroleukemia cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Mar;73(3):862–866. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.3.862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross J., Ikawa Y., Leder P. Globin messenger-RNA induction during erythroid differentiation of cultured leukemia cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Dec;69(12):3620–3623. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.12.3620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka M., Levy J., Terada M., Breslow R., Rifkind R. A., Marks P. A. Induction of erythroid differentiation in murine virus infected eythroleukemia cells by highly polar compounds. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1003–1006. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]