Abstract
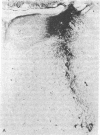
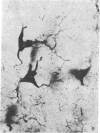
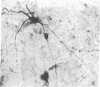
The unlabeled peroxidase-antiperoxidase method has been used with an antiserum against rat dopamine-beta-hydroxylase (DBH) to obtain a three-dimensional image of noradrenergic cell bodies and their processes in thick Vibratome sections of rat brain. This method stains DBH-positive neurons exclusively with a result similar to that of the Golgi method, which makes it possible to analyze the geometric plan of these neurons and their projections in the central nervous system. In 100-micron sections, DBH-positive axons can be followed over long distances, and the results indicate that their distribution in cerebral and cerebellar cortex is not diffuse but has a strict geometric order.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chan-Palay V., Palay S. L. Ultrastructural identification of substance P cells and their processes in rat sensory ganglia and their terminals in the spinal cord by immunocytochemistry. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):4050–4054. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.4050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Descarries L., Watkins K. C., Lapierre Y. Noradrenergic axon terminals in the cerebral cortex of rat. III. Topometric ultrastructural analysis. Brain Res. 1977 Sep 16;133(2):197–222. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90759-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erlandsen S. L., Parsons J. A., Burke J. P., Redick J. A., Van Orden D. E., Van Orden L. S. A modification of the unlabeled antibody enzyme method using heterologous antisera for the light microscopic and ultrastructural localization of insulin, glucagon and growth hormone. J Histochem Cytochem. 1975 Sep;23(9):666–677. doi: 10.1177/23.9.1176760. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman R., Foote S. L., Bloom F. E. Histochemical characterization of a neocortical projection of the nucleus locus coeruleus in the squirrel monkey. J Comp Neurol. 1975 Nov 15;164(2):209–231. doi: 10.1002/cne.901640205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geffen L. B., Livett B. G., Rush R. A. Immunohistochemical localizatio of protein components of catecholamine storage vesicles. J Physiol. 1969 Oct;204(3):593–605. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grzanna R., Coyle J. T. Rat adrenal dopamine-beta-hydroxylase: purification and immunologic characteristics. J Neurochem. 1976 Nov;27(5):1091–1096. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1976.tb00313.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartman B. K. Immunofluorescence of dopamine- -hydroxylase. Application of improved methodology to the localization of the peripheral and central noradrenergic nervous system. J Histochem Cytochem. 1973 Apr;21(4):312–332. doi: 10.1177/21.4.312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hökfelt T., Fuxe K., Goldstein M. Applications of immunohistochemistry to studies on monoamine cell systems with special reference to nervous tissues. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Jun 30;254:407–432. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb29192.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawarai Y., Nakane P. K. Localization of tissue antigens on the ultrathin sections with peroxidase-labeled antibody method. J Histochem Cytochem. 1970 Mar;18(3):161–166. doi: 10.1177/18.3.161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman A. R. Comments on the fine structural organization of the dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus of the mouse. Anat Embryol (Berl) 1974;145(3):261–267. doi: 10.1007/BF00519637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin B. J., Barber R., Saito K., Roberts E., Wu J. Y. Immunocytochemical localization of glutamate decarboxylase in rat spinal cord. J Comp Neurol. 1975 Dec 1;164(3):305–321. doi: 10.1002/cne.901640304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raichle M. E., Hartman B. K., Eichling J. O., Sharpe L. G. Central noradrenergic regulation of cerebral blood flow and vascular permeability. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3726–3730. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramon-Moliner E. The locus coeruleus of cat. 3. Light and electron microscopic studies. Cell Tissue Res. 1974;149(2):205–221. doi: 10.1007/BF00222274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd G. M. Physiological evidence for dendrodendritic synaptic interactions in the rabbit's olfactory glomerulus. Brain Res. 1971 Sep 10;32(1):212–217. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(71)90168-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternberger L. A., Hardy P. H., Jr, Cuculis J. J., Meyer H. G. The unlabeled antibody enzyme method of immunohistochemistry: preparation and properties of soluble antigen-antibody complex (horseradish peroxidase-antihorseradish peroxidase) and its use in identification of spirochetes. J Histochem Cytochem. 1970 May;18(5):315–333. doi: 10.1177/18.5.315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson L. W. The locus coeruleus: a cytoarchitectonic, Golgi and immunohistochemical study in the albino rat. Brain Res. 1976 Jun 25;110(1):39–56. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90207-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Torre J. C. Evidence for central innervation of intracerebral blood vessels: local cerebral blood flow measurements and histofluorescence analysis by the sucrose-phosphate-glyoxylic acid (SPG) method. Neuroscience. 1976 Dec;1(6):455–457. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(76)90096-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]