Abstract
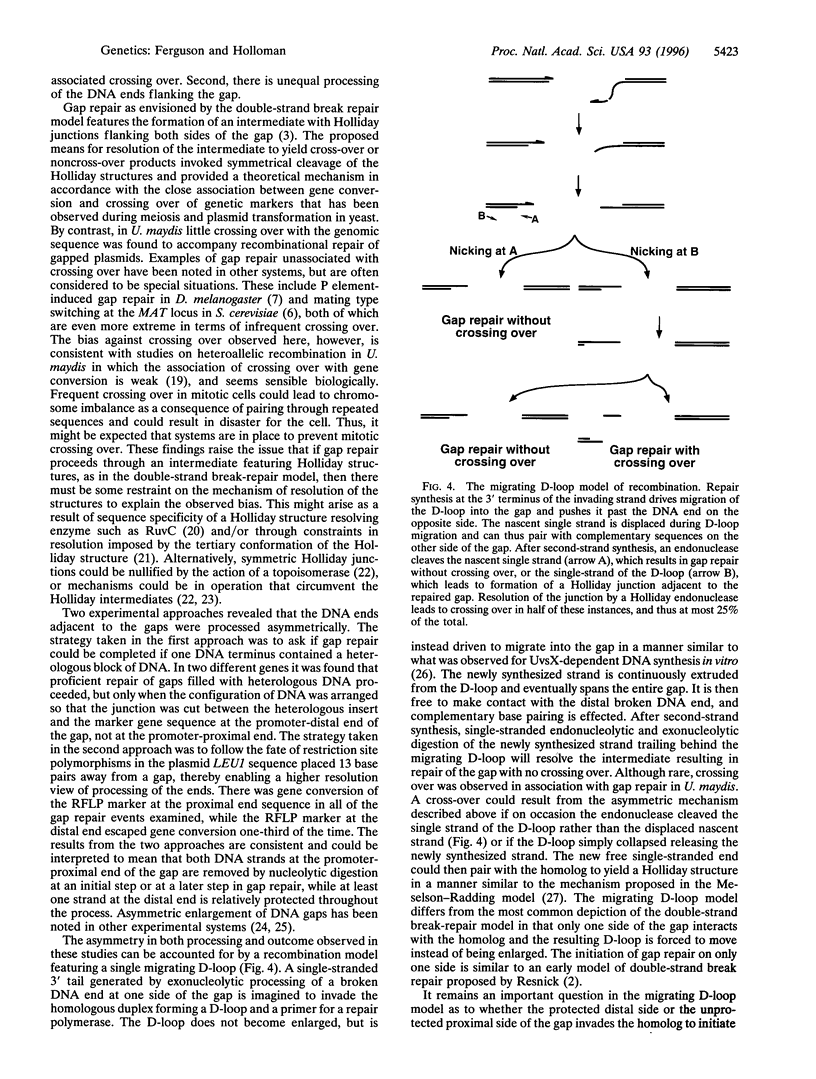
Recombinational repair of double-stranded DNA gaps was investigated in Ustilago maydis. The experimental system was designed for analysis of repair of an autonomously replicating plasmid containing a cloned gene disabled by an internal deletion. It was discovered that crossing over rarely accompanied gap repair. The strong bias against crossing over was observed in three different genes regardless of gap size. These results indicate that gap repair in U. maydis is unlikely to proceed by the mechanism envisioned in the double-stranded break repair model of recombination, which was developed to account for recombination in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Experiments aimed at exploring processing of DNA ends were performed to gain understanding of the mechanism responsible for the observed bias. A heterologous insert placed within a gap in the coding sequence of two different marker genes strongly inhibited repair if the DNA was cleaved at the promoter-proximal junction joining the insert and coding sequence but had little effect on repair if the DNA was cleaved at the promoter-distal junction. Gene conversion of plasmid restriction fragment length polymorphism markers engineered in sequences flanking both sides of a gap accompanied repair but was directionally biased. These results are interpreted to mean that the DNA ends flanking a gap are subject to different types of processing. A model featuring a single migrating D-loop is proposed to explain the bias in gap repair outcome based on the observed asymmetry in processing the DNA ends.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennett R. J., Dunderdale H. J., West S. C. Resolution of Holliday junctions by RuvC resolvase: cleavage specificity and DNA distortion. Cell. 1993 Sep 24;74(6):1021–1031. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90724-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clegg R. M., Murchie A. I., Zechel A., Carlberg C., Diekmann S., Lilley D. M. Fluorescence resonance energy transfer analysis of the structure of the four-way DNA junction. Biochemistry. 1992 May 26;31(20):4846–4856. doi: 10.1021/bi00135a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishman-Lobell J., Rudin N., Haber J. E. Two alternative pathways of double-strand break repair that are kinetically separable and independently modulated. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;12(3):1292–1303. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.3.1292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Formosa T., Alberts B. M. DNA synthesis dependent on genetic recombination: characterization of a reaction catalyzed by purified bacteriophage T4 proteins. Cell. 1986 Dec 5;47(5):793–806. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90522-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fotheringham S., Holloman W. K. Cloning and disruption of Ustilago maydis genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;9(9):4052–4055. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.9.4052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fotheringham S., Holloman W. K. Extrachromosomal recombination is deranged in the rec2 mutant of Ustilago maydis. Genetics. 1991 Dec;129(4):1052–1060. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fotheringham S., Holloman W. K. Pathways of transformation in Ustilago maydis determined by DNA conformation. Genetics. 1990 Apr;124(4):833–843. doi: 10.1093/genetics/124.4.833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gloor G. B., Nassif N. A., Johnson-Schlitz D. M., Preston C. R., Engels W. R. Targeted gene replacement in Drosophila via P element-induced gap repair. Science. 1991 Sep 6;253(5024):1110–1117. doi: 10.1126/science.1653452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hastings P. J. Recombination in the eukaryotic nucleus. Bioessays. 1988 Aug-Sep;9(2-3):61–64. doi: 10.1002/bies.950090206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holliday R., Halliwell R. E., Evans M. W., Rowell V. Genetic characterization of rec-1, a mutant of Ustilago maydis defective in repair and recombination. Genet Res. 1976 Jun;27(3):413–453. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300016621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronstad J. W., Wang J., Covert S. F., Holden D. W., McKnight G. L., Leong S. A. Isolation of metabolic genes and demonstration of gene disruption in the phytopathogenic fungus Ustilago maydis. Gene. 1989 Jun 30;79(1):97–106. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90095-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meselson M. S., Radding C. M. A general model for genetic recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jan;72(1):358–361. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.1.358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nassif N., Penney J., Pal S., Engels W. R., Gloor G. B. Efficient copying of nonhomologous sequences from ectopic sites via P-element-induced gap repair. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Mar;14(3):1613–1625. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.3.1613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickoloff J. A., Singer J. D., Hoekstra M. F., Heffron F. Double-strand breaks stimulate alternative mechanisms of recombination repair. J Mol Biol. 1989 Jun 5;207(3):527–541. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90462-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr-Weaver T. L., Szostak J. W. Yeast recombination: the association between double-strand gap repair and crossing-over. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4417–4421. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plessis A., Dujon B. Multiple tandem integrations of transforming DNA sequences in yeast chromosomes suggest a mechanism for integrative transformation by homologous recombination. Gene. 1993 Nov 30;134(1):41–50. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(93)90172-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray B. L., White C. I., Haber J. E. Heteroduplex formation and mismatch repair of the "stuck" mutation during mating-type switching in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):5372–5380. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.5372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnick M. A. The repair of double-strand breaks in DNA; a model involving recombination. J Theor Biol. 1976 Jun;59(1):97–106. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5193(76)80025-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin B. P., Li D., Holloman W. K. The LEU1 gene of Ustilago maydis. Gene. 1994 Mar 11;140(1):131–135. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(94)90743-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strathern J. N., Klar A. J., Hicks J. B., Abraham J. A., Ivy J. M., Nasmyth K. A., McGill C. Homothallic switching of yeast mating type cassettes is initiated by a double-stranded cut in the MAT locus. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):183–192. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90418-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugawara N., Ivanov E. L., Fishman-Lobell J., Ray B. L., Wu X., Haber J. E. DNA structure-dependent requirements for yeast RAD genes in gene conversion. Nature. 1995 Jan 5;373(6509):84–86. doi: 10.1038/373084a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweetser D. B., Hough H., Whelden J. F., Arbuckle M., Nickoloff J. A. Fine-resolution mapping of spontaneous and double-strand break-induced gene conversion tracts in Saccharomyces cerevisiae reveals reversible mitotic conversion polarity. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jun;14(6):3863–3875. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.6.3863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweetser D. B., Hough H., Whelden J. F., Arbuckle M., Nickoloff J. A. Fine-resolution mapping of spontaneous and double-strand break-induced gene conversion tracts in Saccharomyces cerevisiae reveals reversible mitotic conversion polarity. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jun;14(6):3863–3875. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.6.3863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szostak J. W., Orr-Weaver T. L., Rothstein R. J., Stahl F. W. The double-strand-break repair model for recombination. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):25–35. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90331-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukuda T., Carleton S., Fotheringham S., Holloman W. K. Isolation and characterization of an autonomously replicating sequence from Ustilago maydis. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;8(9):3703–3709. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.9.3703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White C. I., Haber J. E. Intermediates of recombination during mating type switching in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. EMBO J. 1990 Mar;9(3):663–673. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08158.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]