Abstract
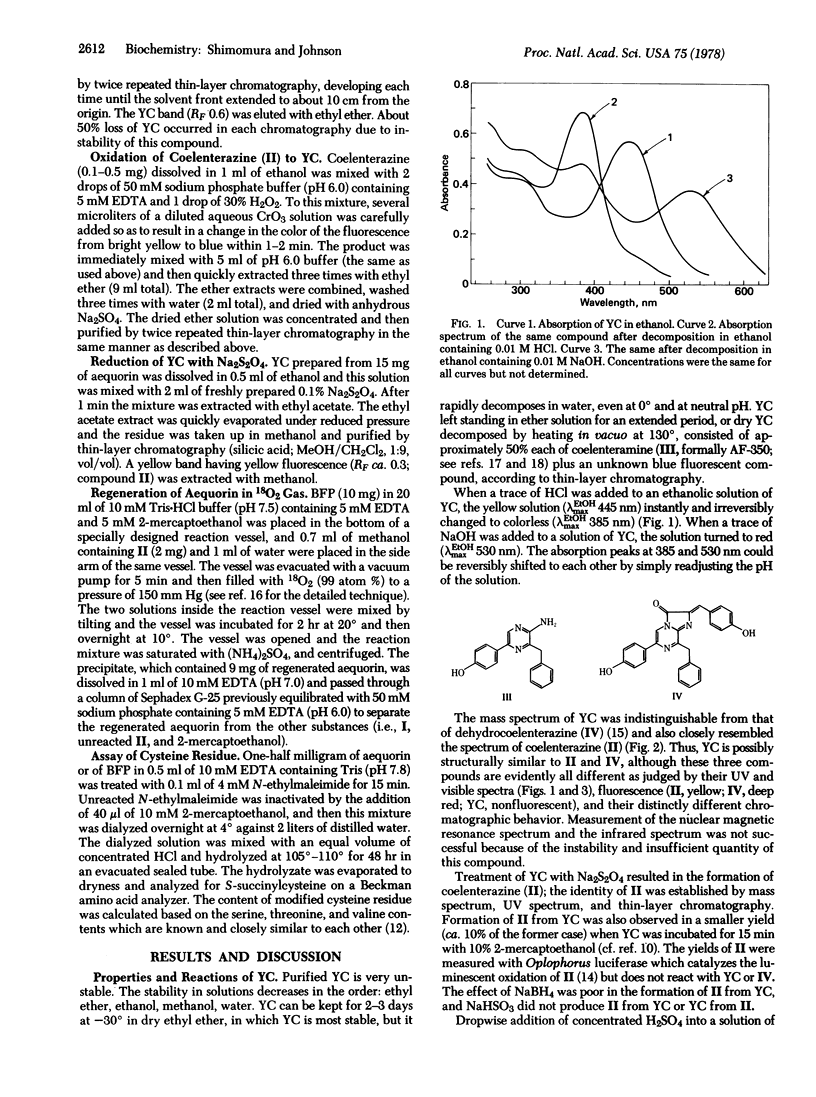
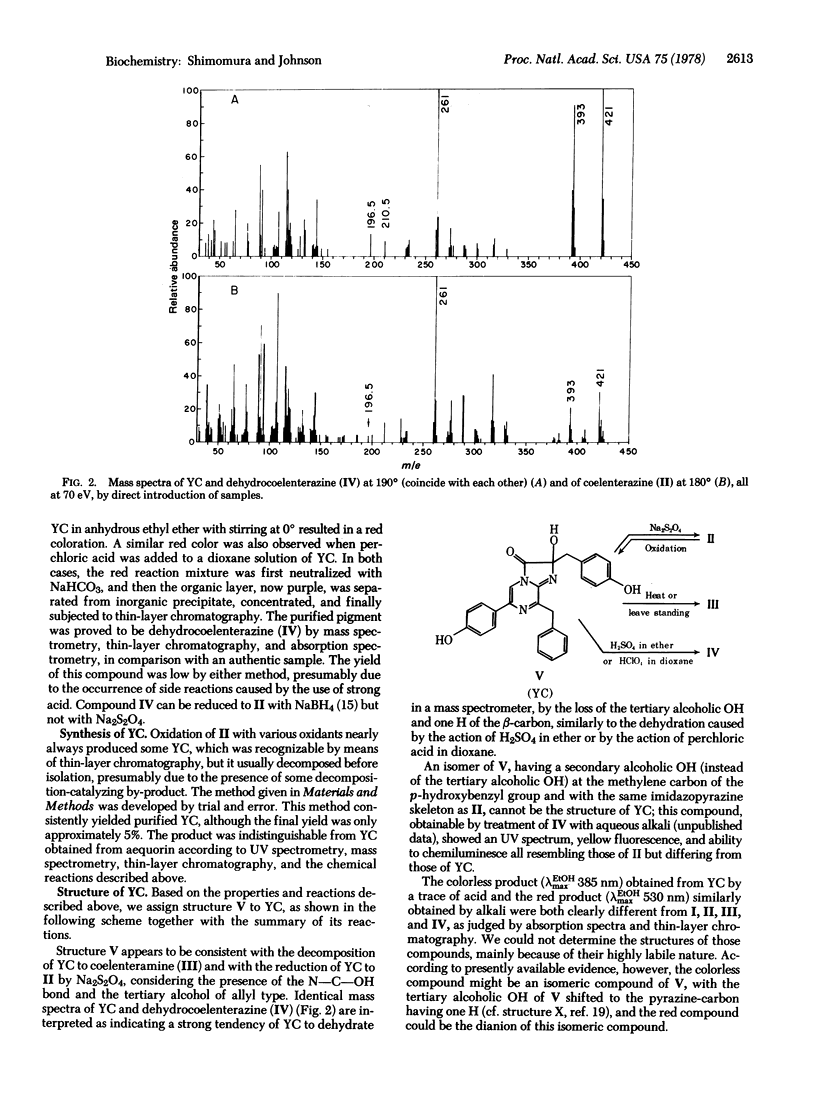
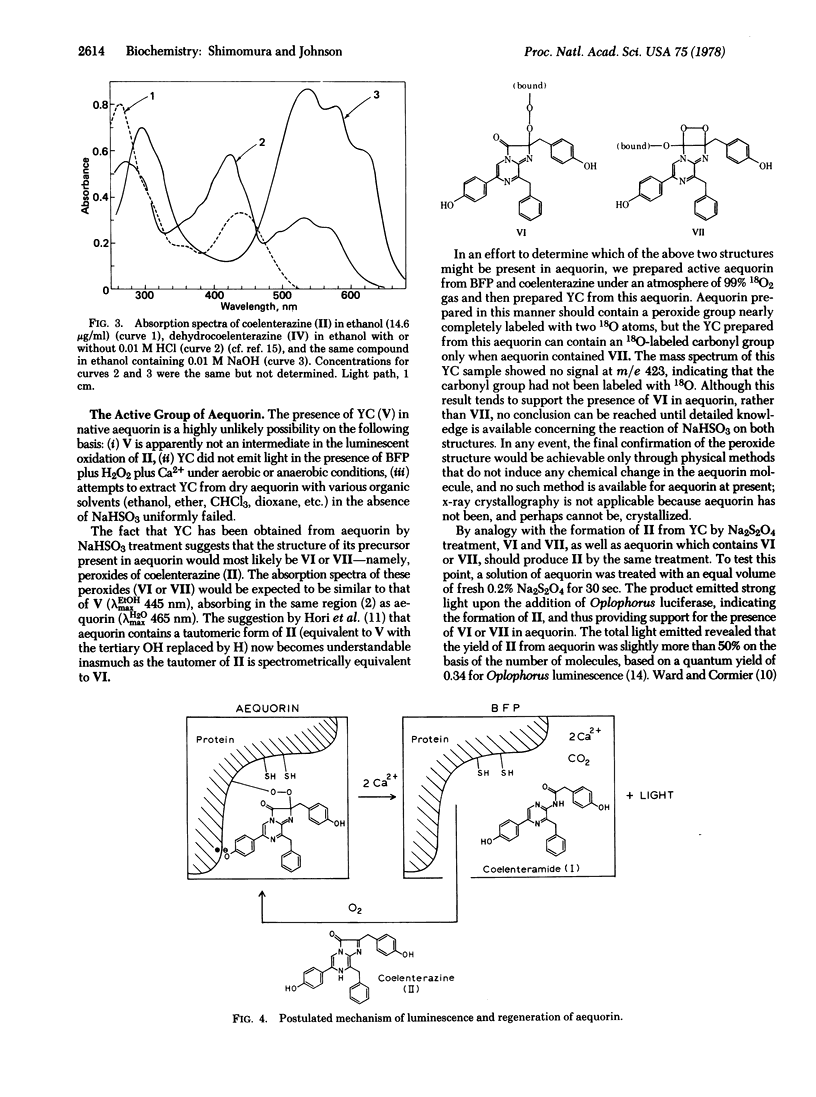
The photoprotein aequorin emits light by an intramolecular reaction when Ca2+ is added under either aerobic or anaerobic conditions. Previously reported evidence has indicated two possibilities: (i) the functional group of aequorin is coelenterazine itself, a compond that plays key roles in the bioluminescence of various other types of organisms, or (ii) it is the enolized form of this compound. Present data rule out both of these possibilities, through elucidation of the structure of the yellow compound that is split off aequorin by treatment with NaHSO3. The yellow compound is now shown to be a tertiary alcohol of coelenterazine on the basis of chemical reactions, mass spectral data, and relationships to known derivatives of coelenterazine. From this structure and the method of forming the yellow compound from aequorin, aequorin evidently contains a peroxide of coelenterazine as the active group. The presence of such a peroxide is consistent with the fact that aequorin yields free coelenterazine upon treatment with Na2S2O4. Although there is no applicable technique at present to determine with assurance the specific state of the peroxide in the protein, a study with 18O tracer indicates that a linear peroxide structure is more likely than the alternative possibility of a dioxetane structure.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blinks J. R., Prendergast F. G., Allen D. G. Photoproteins as biological calcium indicators. Pharmacol Rev. 1976 Mar;28(1):1–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cormier M. J., Hori K., Anderson J. M. Bioluminescence in coelenterates. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Oct 31;346(2):137–164. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(74)90007-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hastings J. W., Morin J. G. Calcium-triggered light emission in Renilla. A unitary biochemical scheme for coelenterate bioluminescence. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Oct 22;37(3):493–498. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90942-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hori K., Anderson J. M., Ward W. W., Cormier M. J. Renilla luciferin as the substrate for calcium induced photoprotein bioluminescence. Assignment of luciferin tautomers in aequorin and mnemiopsin. Biochemistry. 1975 Jun 3;14(11):2371–2376. doi: 10.1021/bi00682a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHIMOMURA O., JOHNSON F. H., SAIGA Y. Extraction, purification and properties of aequorin, a bioluminescent protein from the luminous hydromedusan, Aequorea. J Cell Comp Physiol. 1962 Jun;59:223–239. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030590302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimomura O., Goto T., Johnson F. H. Source of oxygen in the CO(2) produced in the bioluminescent oxidation of firefly luciferin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):2799–2802. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.2799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimomura O., Johnson F. H. Chemical nature of bioluminescence systems in coelenterates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1546–1549. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimomura O., Johnson F. H., Morise H. Mechanism of the luminescent intramolecular reaction of aequorin. Biochemistry. 1974 Jul 30;13(16):3278–3286. doi: 10.1021/bi00713a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimomura O., Johnson F. H. Properties of the bioluminescent protein aequorin. Biochemistry. 1969 Oct;8(10):3991–3997. doi: 10.1021/bi00838a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimomura O., Johnson F. H. Regeneration of the photoprotein aequorin. Nature. 1975 Jul 17;256(5514):236–238. doi: 10.1038/256236a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimomura O., Johnson F. H. Structure of the light-emitting moiety of aequorin. Biochemistry. 1972 Apr 25;11(9):1602–1608. doi: 10.1021/bi00759a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimomura O., Masugi T., Johnson F. H., Haneda Y. Properties and reaction mechanism of the bioluminescence system of the deep-sea shrimp Oplophorus gracilorostris. Biochemistry. 1978 Mar 21;17(6):994–998. doi: 10.1021/bi00599a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward W. W., Cormier M. J. Extraction of Renilla-type luciferin from the calcium-activated photoproteins aequorin, mnemiopsin, and berovin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jul;72(7):2530–2534. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.7.2530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


