Abstract
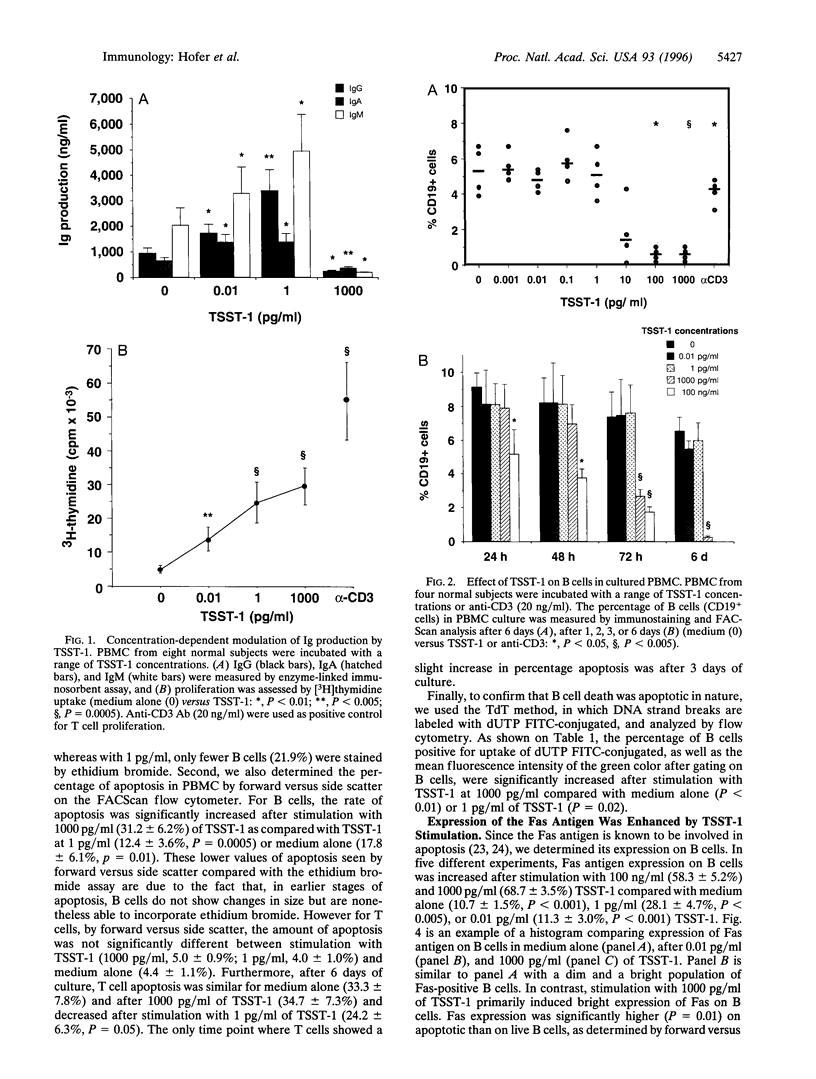
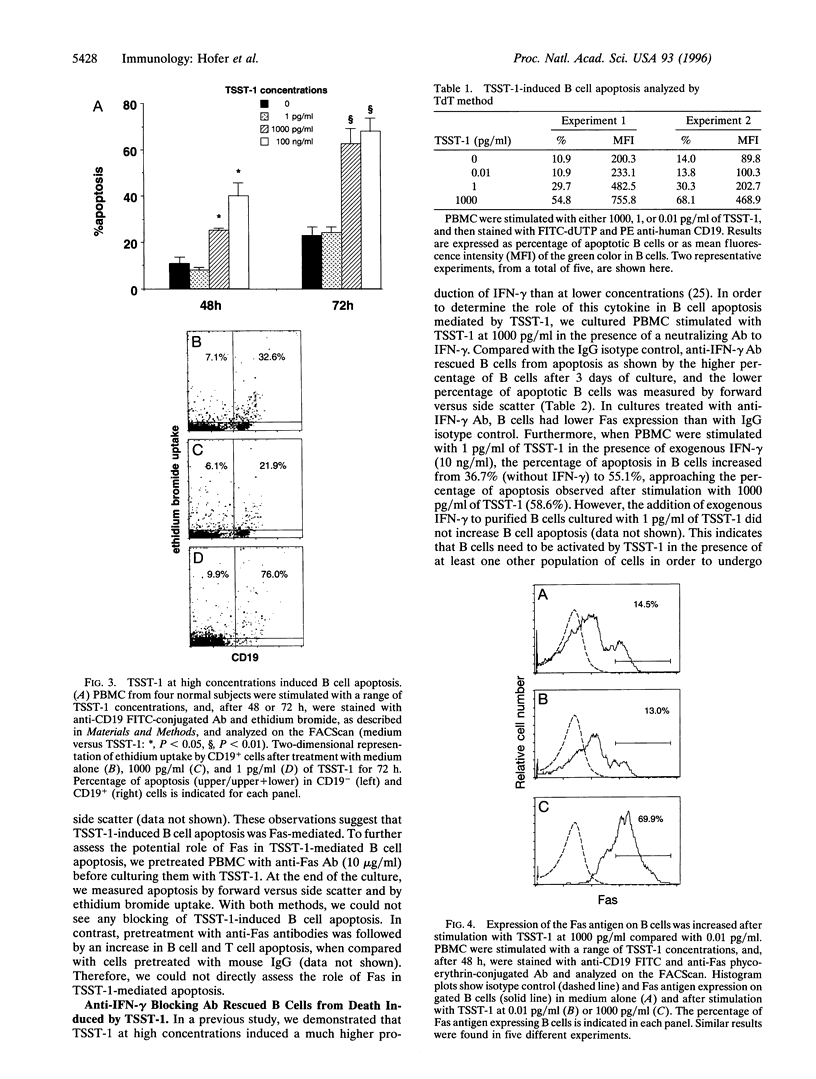
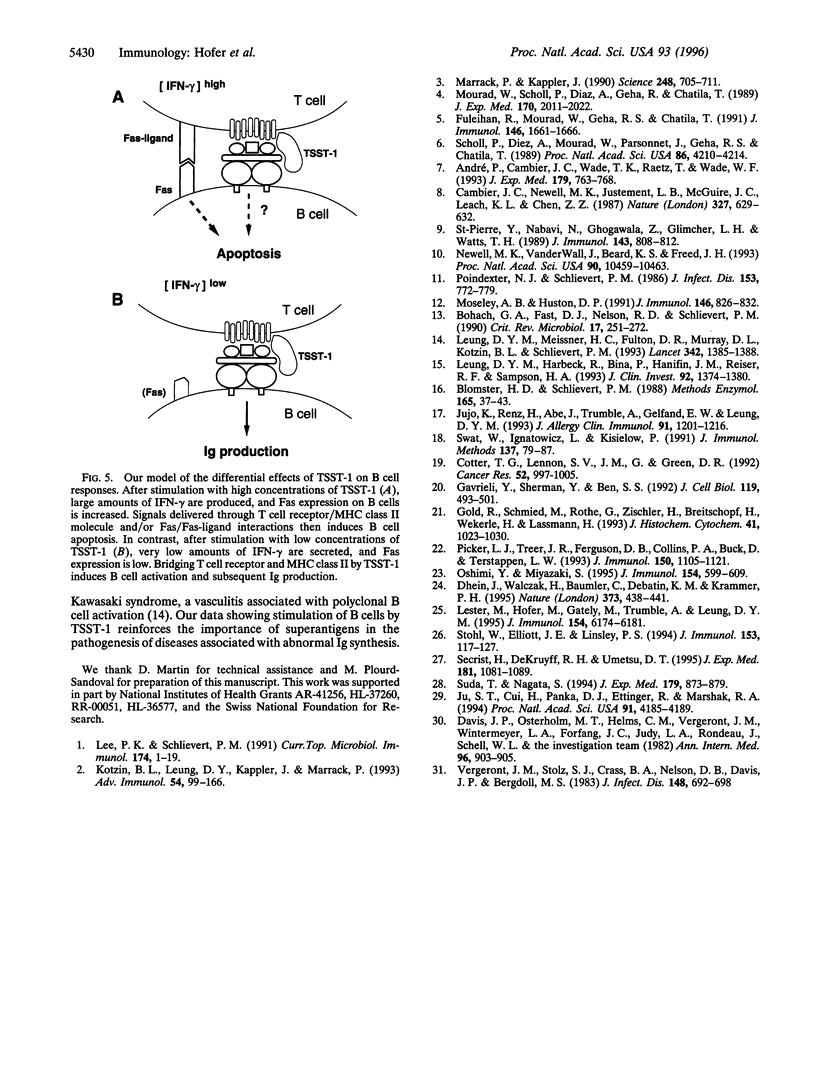
Superantigens, such as toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 (TSST-1), have been implicated in the pathogenesis of several autoimmune and allergic diseases associated with polyclonal B cell activation. In this report, we studied the in vitro effects of TSST-1 on B cell activation. We show herein that TSST-1 produced antagonistic effects on Ig synthesis by peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) from normal subjects, depending on the concentration used; Ig production was inhibited at 1000 pg/ml (P < 0.01) and enhanced at 1 and 0.01 pg/ml (P < 0.01) of toxin. Cultures of PBMC were then examined for morphologic features and DNA fragmentation characteristic for apoptosis. B cells exhibited a significantly higher (P < 0.01) incidence of apoptosis after stimulation with 1000 pg/ml of TSST-1 compared with 1 or 0.01 pg/ml of toxin or medium alone. Abundant expression of Fas, a cell surface protein that mediates apoptosis, was detected on B cells after stimulation with 1000 pg/ml of TSST-1 and was significantly higher on B cells undergoing apoptosis than on live cells (P = 0.01). Additionally, increased Fas expression and B cell death occurred at concentrations of TSST-1 inducing the production of high amounts of gamma interferon (IFN-gamma), and both events could be blocked by neutralizing anti-IFN-gamma antibody. These findings suggest that high concentrations of TSST-1 can induce IFN-gamma-dependent B cell apoptosis, whereas at low concentrations it stimulates Ig synthesis by PBMC from normal subjects. These findings support the concept that staphylococcal toxins have a role in B cell hyperactivity in autoimmunity and allergy.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- André P., Cambier J. C., Wade T. K., Raetz T., Wade W. F. Distinct structural compartmentalization of the signal transducing functions of major histocompatibility complex class II (Ia) molecules. J Exp Med. 1994 Feb 1;179(2):763–768. doi: 10.1084/jem.179.2.763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blomster-Hautamaa D. A., Schlievert P. M. Preparation of toxic shock syndrome toxin-1. Methods Enzymol. 1988;165:37–43. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(88)65009-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohach G. A., Fast D. J., Nelson R. D., Schlievert P. M. Staphylococcal and streptococcal pyrogenic toxins involved in toxic shock syndrome and related illnesses. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1990;17(4):251–272. doi: 10.3109/10408419009105728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cambier J. C., Newell M. K., Justement L. B., McGuire J. C., Leach K. L., Chen Z. Z. Ia binding ligands and cAMP stimulate nuclear translocation of PKC in B lymphocytes. Nature. 1987 Jun 18;327(6123):629–632. doi: 10.1038/327629a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotter T. G., Lennon S. V., Glynn J. M., Green D. R. Microfilament-disrupting agents prevent the formation of apoptotic bodies in tumor cells undergoing apoptosis. Cancer Res. 1992 Feb 15;52(4):997–1005. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhein J., Walczak H., Bäumler C., Debatin K. M., Krammer P. H. Autocrine T-cell suicide mediated by APO-1/(Fas/CD95) Nature. 1995 Feb 2;373(6513):438–441. doi: 10.1038/373438a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuleihan R., Mourad W., Geha R. S., Chatila T. Engagement of MHC-class II molecules by staphylococcal exotoxins delivers a comitogenic signal to human B cells. J Immunol. 1991 Mar 1;146(5):1661–1666. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavrieli Y., Sherman Y., Ben-Sasson S. A. Identification of programmed cell death in situ via specific labeling of nuclear DNA fragmentation. J Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;119(3):493–501. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.3.493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold R., Schmied M., Rothe G., Zischler H., Breitschopf H., Wekerle H., Lassmann H. Detection of DNA fragmentation in apoptosis: application of in situ nick translation to cell culture systems and tissue sections. J Histochem Cytochem. 1993 Jul;41(7):1023–1030. doi: 10.1177/41.7.8515045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ju S. T., Cui H., Panka D. J., Ettinger R., Marshak-Rothstein A. Participation of target Fas protein in apoptosis pathway induced by CD4+ Th1 and CD8+ cytotoxic T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 May 10;91(10):4185–4189. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.10.4185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jujo K., Renz H., Abe J., Trumble A., Gelfand E. W., Leung D. Y. Pokeweed mitogen induces IgE synthesis in the presence of a blocking antibody to the interferon-gamma receptor. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1993 Jun;91(6):1206–1216. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(93)90324-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotzin B. L., Leung D. Y., Kappler J., Marrack P. Superantigens and their potential role in human disease. Adv Immunol. 1993;54:99–166. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60534-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee P. K., Schlievert P. M. Molecular genetics of pyrogenic exotoxin "superantigens" of group A streptococci and Staphylococcus aureus. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1991;174:1–19. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-50998-8_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lester M. R., Hofer M. F., Gately M., Trumble A., Leung D. Y. Down-regulating effects of IL-4 and IL-10 on the IFN-gamma response in atopic dermatitis. J Immunol. 1995 Jun 1;154(11):6174–6181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung D. Y., Harbeck R., Bina P., Reiser R. F., Yang E., Norris D. A., Hanifin J. M., Sampson H. A. Presence of IgE antibodies to staphylococcal exotoxins on the skin of patients with atopic dermatitis. Evidence for a new group of allergens. J Clin Invest. 1993 Sep;92(3):1374–1380. doi: 10.1172/JCI116711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung D. Y., Meissner H. C., Fulton D. R., Murray D. L., Kotzin B. L., Schlievert P. M. Toxic shock syndrome toxin-secreting Staphylococcus aureus in Kawasaki syndrome. Lancet. 1993 Dec 4;342(8884):1385–1388. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)92752-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrack P., Kappler J. The staphylococcal enterotoxins and their relatives. Science. 1990 May 11;248(4956):705–711. doi: 10.1126/science.2185544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moseley A. B., Huston D. P. Mechanism of Staphylococcus aureus exotoxin A inhibition of Ig production by human B cells. J Immunol. 1991 Feb 1;146(3):826–832. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mourad W., Scholl P., Diaz A., Geha R., Chatila T. The staphylococcal toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 triggers B cell proliferation and differentiation via major histocompatibility complex-unrestricted cognate T/B cell interaction. J Exp Med. 1989 Dec 1;170(6):2011–2022. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.6.2011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newell M. K., VanderWall J., Beard K. S., Freed J. H. Ligation of major histocompatibility complex class II molecules mediates apoptotic cell death in resting B lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Nov 15;90(22):10459–10463. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.22.10459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oshimi Y., Miyazaki S. Fas antigen-mediated DNA fragmentation and apoptotic morphologic changes are regulated by elevated cytosolic Ca2+ level. J Immunol. 1995 Jan 15;154(2):599–609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picker L. J., Treer J. R., Ferguson-Darnell B., Collins P. A., Buck D., Terstappen L. W. Control of lymphocyte recirculation in man. I. Differential regulation of the peripheral lymph node homing receptor L-selectin on T cells during the virgin to memory cell transition. J Immunol. 1993 Feb 1;150(3):1105–1121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poindexter N. J., Schlievert P. M. Suppression of immunoglobulin-secreting cells from human peripheral blood by toxic-shock-syndrome toxin-1. J Infect Dis. 1986 Apr;153(4):772–779. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.4.772. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholl P., Diez A., Mourad W., Parsonnet J., Geha R. S., Chatila T. Toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 binds to major histocompatibility complex class II molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(11):4210–4214. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.11.4210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Secrist H., DeKruyff R. H., Umetsu D. T. Interleukin 4 production by CD4+ T cells from allergic individuals is modulated by antigen concentration and antigen-presenting cell type. J Exp Med. 1995 Mar 1;181(3):1081–1089. doi: 10.1084/jem.181.3.1081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St-Pierre Y., Nabavi N., Ghogawala Z., Glimcher L. H., Watts T. H. A functional role for signal transduction via the cytoplasmic domains of MHC class II proteins. J Immunol. 1989 Aug 1;143(3):808–812. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stohl W., Elliott J. E., Linsley P. S. Human T cell-dependent B cell differentiation induced by staphylococcal superantigens. J Immunol. 1994 Jul 1;153(1):117–127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suda T., Nagata S. Purification and characterization of the Fas-ligand that induces apoptosis. J Exp Med. 1994 Mar 1;179(3):873–879. doi: 10.1084/jem.179.3.873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swat W., Ignatowicz L., Kisielow P. Detection of apoptosis of immature CD4+8+ thymocytes by flow cytometry. J Immunol Methods. 1991 Mar 1;137(1):79–87. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(91)90396-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vergeront J. M., Stolz S. J., Crass B. A., Nelson D. B., Davis J. P., Bergdoll M. S. Prevalence of serum antibody to staphylococcal enterotoxin F among Wisconsin residents: implications for toxic-shock syndrome. J Infect Dis. 1983 Oct;148(4):692–698. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.4.692. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



