Abstract
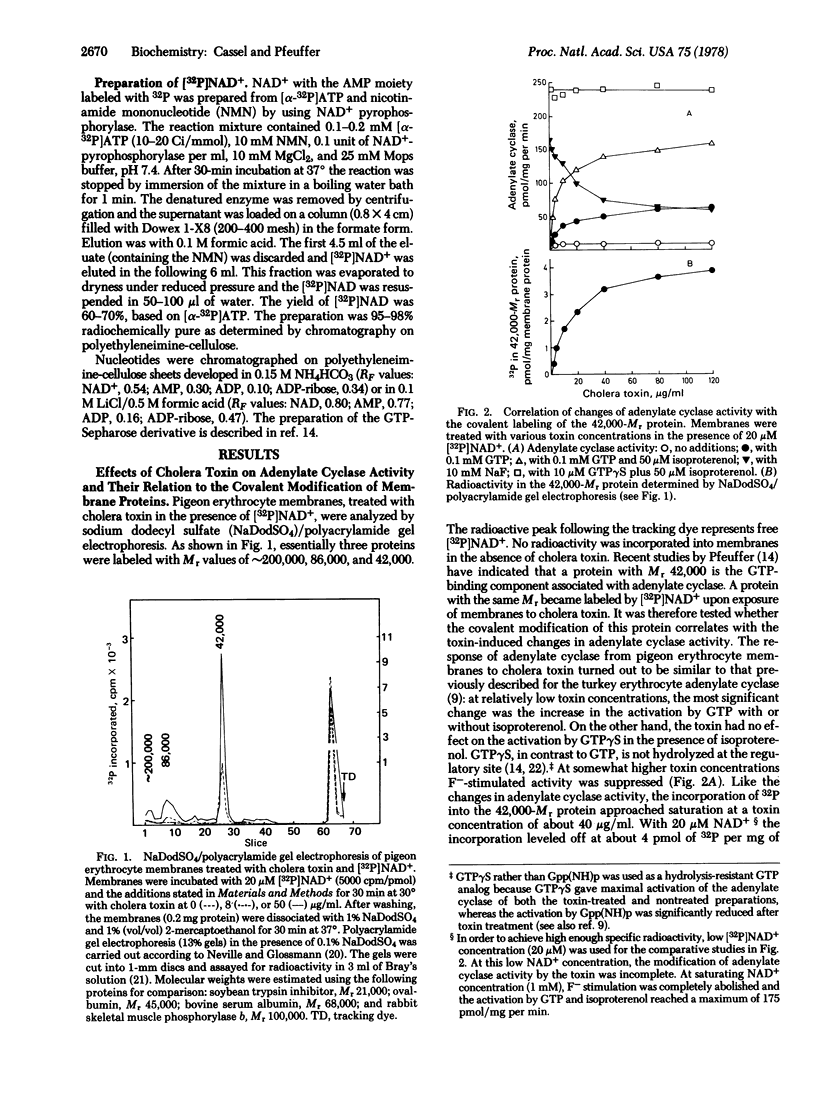
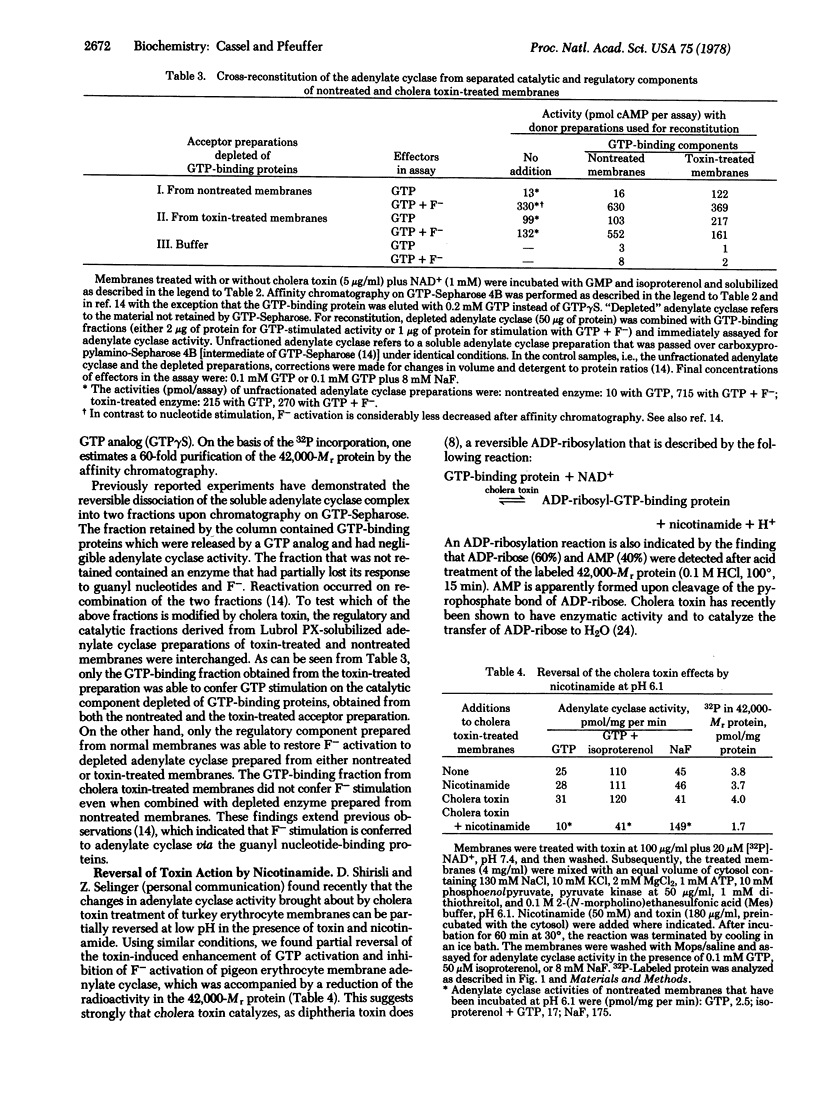
Treatment of pigeon erythrocyte membranes with cholera toxin and NAD+ enhanced the GTP stimulation and suppressed the F- activation of the adenylate cylase [ATP pyrophosphate-lyase (cyclizing), EC 4.6.1.1]. In the presence of NAD+ labeled with 32P in the AMP moiety the toxin catalyzed the covalent incorporation of radioactivity into membrane proteins with molecular weights (Mrs) of 200,000, 86,000, and 42,000. Extraction of toxin-treated membranes with Lubrol PX followed by affinity chromatography on a GTP-Sepharose column resulted in a 200-fold purification of the 42,000-Mr labeled protein and in its complete separation from the other labeled proteins. The fraction containing the purified GTP-binding component from toxin-treated membranes conferred an enhanced GTP-stimulated activity on adenylate cyclase solubilized from nontreated membranes. Likewise, the addition of GTP-binding fraction from nontreated membranes to an enzyme solubilized from toxin-treated membranes restored F- stimulation of the adenylate cyclase. The toxin-induced modification of adenylate cyclase and the incorporation of radioactivity into the 42,000-Mr protein were partially reversed upon incubation with toxin and nicotinamide at pH 6.1. The results indicate that cholera toxin affects the adenylate cyclase system by catalyzing an ADP-ribosylation of the 42,000-Mr component bearing the guanyl nucleotide regulatory site.
Keywords: pigeon erythrocyte membranes, ADP-ribosylation, fluoride activation
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brostrom C. O., Huang Y. C., Breckenridge B. M., Wolff D. J. Identification of a calcium-binding protein as a calcium-dependent regulator of brain adenylate cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jan;72(1):64–68. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.1.64. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassel D., Selinger Z. Activation of turkey erythrocyte adenylate cyclase and blocking of the catecholamine-stimulated GTPase by guanosine 5'-(gamma-thio) triphosphate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Aug 8;77(3):868–873. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(77)80058-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassel D., Selinger Z. Catecholamine-stimulated GTPase activity in turkey erythrocyte membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Dec 8;452(2):538–551. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(76)90206-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassel D., Selinger Z. Mechanism of adenylate cyclase activation by cholera toxin: inhibition of GTP hydrolysis at the regulatory site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3307–3311. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Interaction of Vibrio cholerae enterotoxin with cell membranes. Biochemistry. 1973 Aug 28;12(18):3547–3558. doi: 10.1021/bi00742a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. M. Involvement of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide in the action of cholera toxin in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2064–2068. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2064. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. M., King C. A. The mechanism of action of cholera toxin in pigeon erythrocyte lysates. J Biol Chem. 1975 Aug 25;250(16):6424–6432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haga T., Haga K., Gilman A. G. Hydrodynamic properties of the beta-adrenergic receptor and adenylate cyclase from wild type and varient S49 lymphoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1977 Aug 25;252(16):5776–5782. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimberg D. V., Field M., Johnson J., Henderson A., Gershon E. Stimulation of intestinal mucosal adenyl cyclase by cholera enterotoxin and prostaglandins. J Clin Invest. 1971 Jun;50(6):1218–1230. doi: 10.1172/JCI106599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss J., Manganiello V. C., Vaughan M. Hydrolysis of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide by choleragen and its A protomer: possible role in the activation of adenylate cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Dec;73(12):4424–4427. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.12.4424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss J., Vaughan M. Choleragen activation of solubilized adenylate cyclase: requirement for GTP and protein activator for demonstration of enzymatic activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4396–4400. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neville D. M., Jr, Glossmann H. Plasma membrane protein subunit composition. A comparative study by discontinuous electrophoresis in sodium dodecyl sulfate. J Biol Chem. 1971 Oct 25;246(20):6335–6338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orly J., Schramm M. Coupling of catecholamine receptor from one cell with adenylate cyclase from another cell by cell fusion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Dec;73(12):4410–4414. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.12.4410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penefsky H. S. Reversible binding of Pi by beef heart mitochondrial adenosine triphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1977 May 10;252(9):2891–2899. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeuffer T., Eckstein F. Topology of the GTP-binding site of adenylyl cyclase from pigeon erythrocytes. FEBS Lett. 1976 Sep 1;67(3):354–358. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80563-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeuffer T. GTP-binding proteins in membranes and the control of adenylate cyclase activity. J Biol Chem. 1977 Oct 25;252(20):7224–7234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeuffer T., Helmreich E. J. Activation of pigeon erythrocyte membrane adenylate cyclase by guanylnucleotide analogues and separation of a nucleotide binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1975 Feb 10;250(3):867–876. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salomon Y., Londos C., Rodbell M. A highly sensitive adenylate cyclase assay. Anal Biochem. 1974 Apr;58(2):541–548. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90222-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp G. W., Hynie S. Stimulation of intestinal adenyl cyclase by cholera toxin. Nature. 1971 Jan 22;229(5282):266–269. doi: 10.1038/229266a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wodnar-Filipowicz A., Lai C. Y. Stimulation of adenylate cyclase in washed pigeon erythrocyte membrane with cholera toxin and its subunits. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 Oct;176(2):465–471. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90189-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


