Abstract
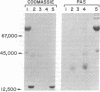
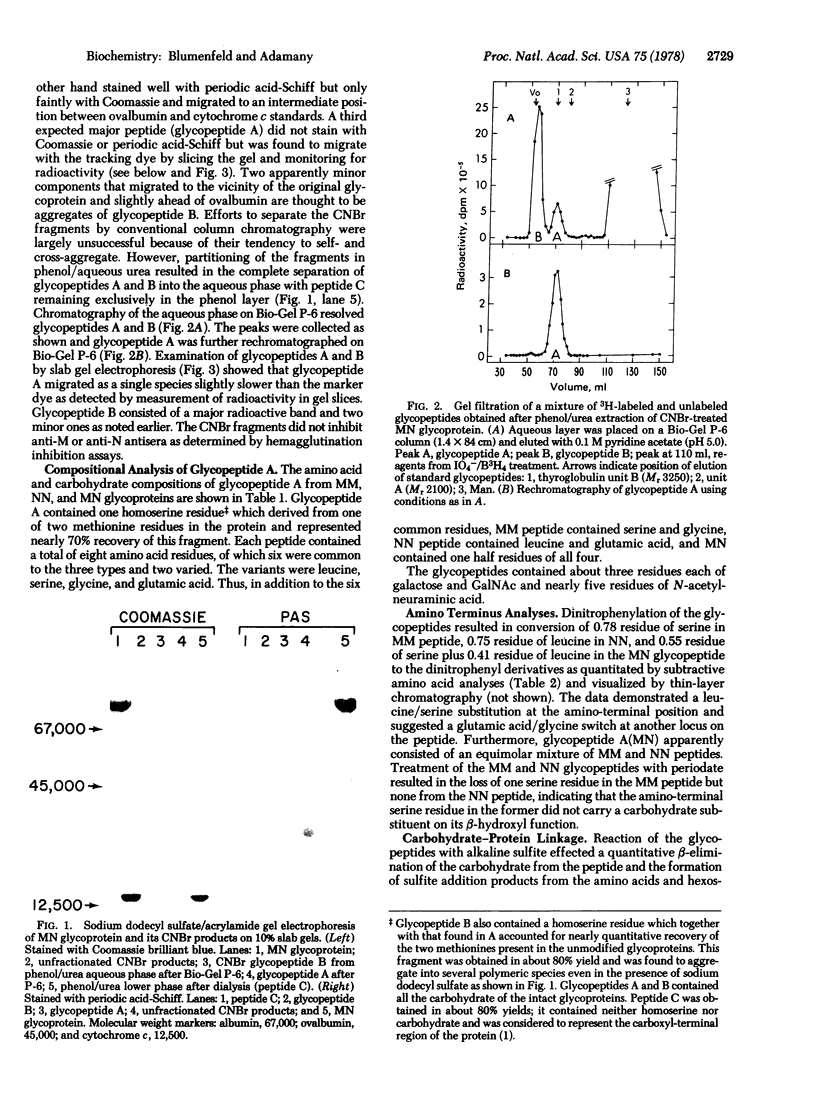
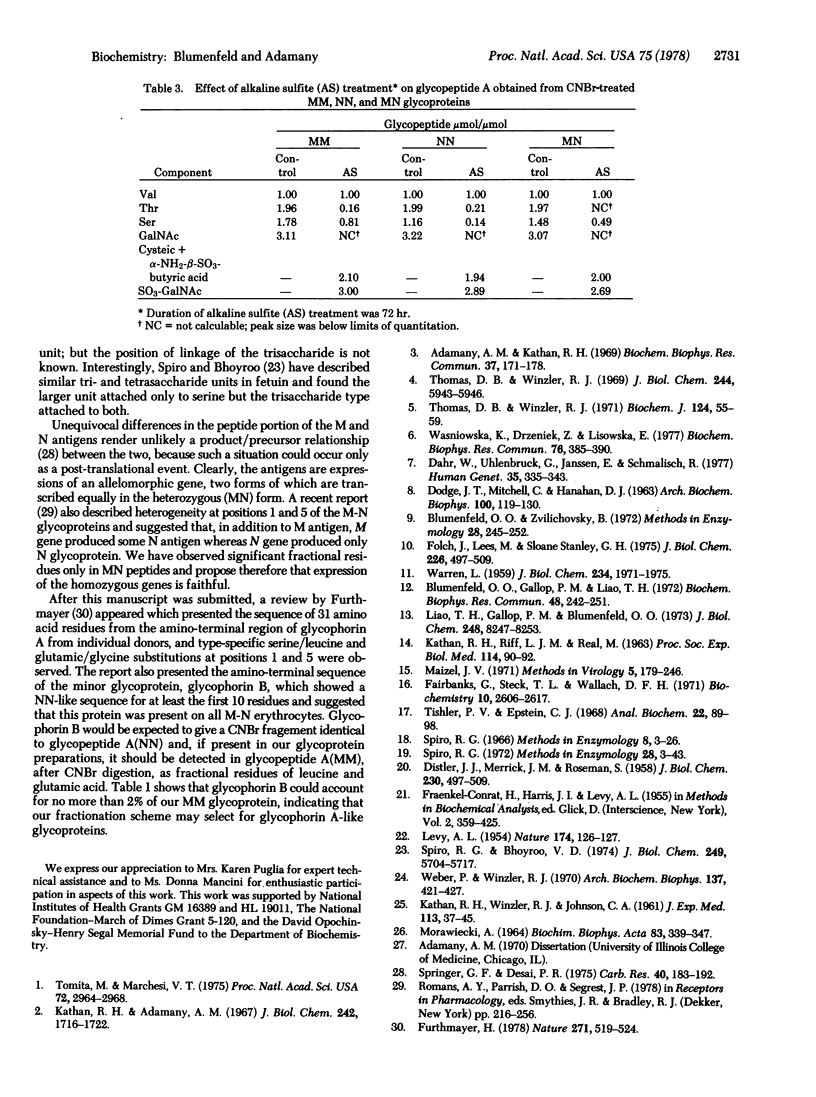
MM, NN, and MN glycoproteins of human erythrocytes from single donors were cleaved by cyanogen bromide into three fragments—A, B, and C—which, upon gel electrophoresis, appeared to be common to the three antigens. Phenol/aqueous urea partitioning and gel filtration were used to separate the peptides quantitatively. Peptide C lacked carbohydrate and homoserine and represented the carboxyl-terminal portion of the glycoproteins. Peptides A and B contained one homoserine each and accounted for all the carbohydrate of the glycoproteins. The peptide portion of glycopeptide A from MM, NN, or MN antigens consisted of eight amino acid residues, of which six were homologous and two varied according to blood type. The variants were serine and glycine in glycopeptide A(MM), leucine and glutamic acid in A(NN), and half-residues of serine, glycine, leucine, and glutamic acid in A(MN). Serine was the amino-terminal residue in A(MM), leucine in A(NN), and one half residue of serine and leucine in A(MN). Each glycopeptide carried two tetrasaccharides (2 NANA, 1 Gal, 1 GalNAc) and one trisaccharide (NANA, Gal, GalNAc) linked O-glycosidically to one serine and two threonines as determined by β-elimination and sulfite addition. The carbohydrate units were attached to serine and threonine located in the invariant region, because the amino-terminal serine residue could be oxidized by periodate. The M-N antigens are believed to be products of allelic genes which are expressed exclusively in homozygotes and equimolarly in heterozygotes.
Keywords: MN antigens, CNBr peptides
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adamany A. M., Kathan R. H. Isolation of a tetrasaccharide common to MM, NN and MN antigens. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Sep 24;37(1):171–178. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90896-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumenfeld O. O., Gallop P. M., Liao T. H. Modification and introduction of a specific radioactive label into the erythrocyte membrane sialoglycoproteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Jul 11;48(1):242–251. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90369-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DISTLER J. J., MERRICK J. M., ROSEMAN S. Glucosamine metabolism. III. Preparation and N-acetylation of crystalline D-glucosamine- and D-galactosamine-6-phosphoric acids. J Biol Chem. 1958 Jan;230(1):497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DODGE J. T., MITCHELL C., HANAHAN D. J. The preparation and chemical characteristics of hemoglobin-free ghosts of human erythrocytes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1963 Jan;100:119–130. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(63)90042-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahr W., Uhlenbruck G., Janssen E., Schmalisch R. Different N-terminal amino acids in the MN-glycoprotein from MM and NN erythrocytes. Hum Genet. 1977 Mar 14;35(3):335–343. doi: 10.1007/BF00446624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., LEES M., SLOANE STANLEY G. H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furthmayr H. Structural comparison of glycophorins and immunochemical analysis of genetic variants. Nature. 1978 Feb 9;271(5645):519–524. doi: 10.1038/271519a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATHAN R. H., RIFF L. J., REAL M. ASSOCIATION BETWEEN THE ERYTHROCYTE HEMAGGLUTINATION INHIBITOR AND THE M-N BLOOD GROUP SUBSTANCES. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1963 Oct;114:90–92. doi: 10.3181/00379727-114-28594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATHAN R. H., WINZLER R. J., JOHNSOM C. A. Preparation of an inhibitor of viral hemagglutination from human erythrocytes. J Exp Med. 1961 Jan 1;113:37–45. doi: 10.1084/jem.113.1.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kathan R. H., Adamany A. Comparison of human MM, NN, and MN blood group antigens. J Biol Chem. 1967 Apr 25;242(8):1716–1722. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVY A. L. A paper chromatographic method for the quantitative estimation of amino-acids. Nature. 1954 Jul 17;174(4420):126–127. doi: 10.1038/174126a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liao T. H., Gallop P. M., Blumenfeld O. O. Modification of sialyl residues of sialoglycoprotein(s) of the human erythrocyte surface. J Biol Chem. 1973 Dec 10;248(23):8247–8253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORAWIECKI A. DISSOCIATION OF M- AND N-GROUP MUCOPROTEINS INTO SUBUNITS IN DETERGENT SOLUTIONS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Nov 1;83:339–347. doi: 10.1016/0926-6526(64)90012-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiro R. G., Bhoyroo V. D. Structure of the O-glycosidically linked carbohydrate units of fetuin. J Biol Chem. 1974 Sep 25;249(18):5704–5717. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer G. F., Desai P. R. Human blood-group MN and precursor specificities: structural and biological aspects. Carbohydr Res. 1975 Mar;40(1):183–192. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6215(00)82680-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. B., Winzler R. J. Structural studies on human erythrocyte glycoproteins. Alkali-labile oligosaccharides. J Biol Chem. 1969 Nov 10;244(21):5943–5946. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. B., Winzler R. J. Structure of glycoproteins of human erythrocytes. Alkali-stable oligosaccharides. Biochem J. 1971 Aug;124(1):55–59. doi: 10.1042/bj1240055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tishler P. V., Epstein C. J. A convenient method of preparing polyacrylamide gels for liquid scintillation spectrometry. Anal Biochem. 1968 Jan;22(1):89–98. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(68)90262-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomita M., Marchesi V. T. Amino-acid sequence and oligosaccharide attachment sites of human erythrocyte glycophorin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):2964–2968. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.2964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARREN L. The thiobarbituric acid assay of sialic acids. J Biol Chem. 1959 Aug;234(8):1971–1975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waśniowska K., Drzeniek Z., Lisowska E. The amino acids of M and N blood group glycopeptides are different. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 May 23;76(2):385–390. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)90736-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber P., Winzler R. J. Sulfonated amino sugars derived from alkaline sulfite-treated glycoproteins. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1970 Apr;137(2):421–427. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(70)90458-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]