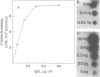
Abstract
We describe a very sensitive method to detect as antigens the presence of specific proteins within phage plaques or bacterial colonies. We coat plastic sheets with antibody molecules, expose the sheet to lysed bacteria so that a released antigen can bind, and then label the immobilized antigen with radioiodinated antibodies. Thus, the antigen is sandwiched between the antibodies attached to the plastic sheet and those carrying the radioactive label. Autoradiography then shows the positions of antigen-containing colonies or phage plaques. A few molecules of antigen released from each bacterial cell generatean adequate signal.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Catt K., Tregear G. W. Solid-phase radioimmunoassay in antibody-coated tubes. Science. 1967 Dec 22;158(3808):1570–1572. doi: 10.1126/science.158.3808.1570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowler A. V. High-level production of -galactosidase by Escherichia coli merodiploids. J Bacteriol. 1972 Nov;112(2):856–860. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.2.856-860.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Mills A. D. Enhanced autoradiographic detection of 32P and 125I using intensifying screens and hypersensitized film. FEBS Lett. 1977 Oct 15;82(2):314–316. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80609-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livingston D. M. Immunoaffinity chromatography of proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1974;34:723–731. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(74)34094-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skalka A., Shapiro L. In situ immunoassays for gene translation products in phage plaques and bacterial colonies. Gene. 1976;1(1):65–79. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(76)90007-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]