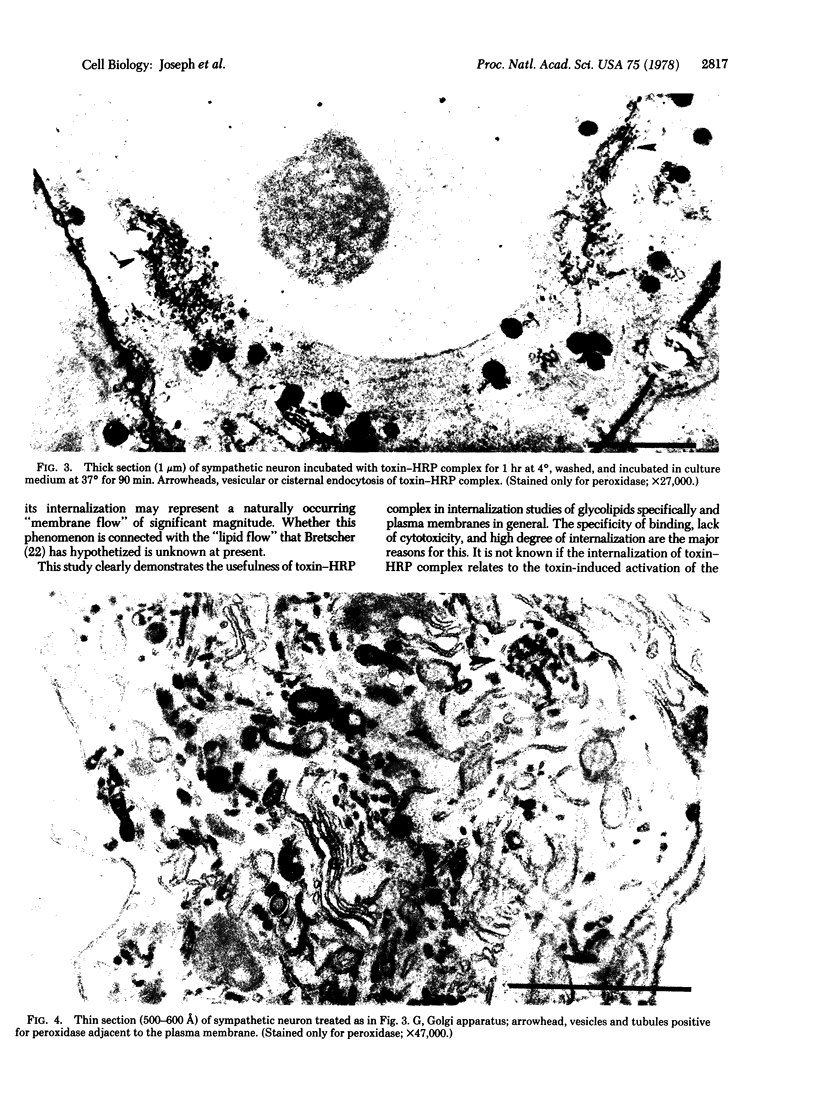
Abstract
Cholera toxin linked covalently by glutaraldehyde to horseradish peroxidase was incubated with cultured chicken sympathetic neurons at 4 degrees. Cells were washed and brought to 37 degrees to permit endocytosis of bound toxin on plasma membranes. Massive internalization of the ligand into vesicles and cisterns of the Golgi--endoplasmic reticulum--lysosome (GERL) system was demonstrated by the cytochemical reaction for the enzyme. Surface binding and subsequent endocytosis of the cholera toxin--enzyme conjugate was inhibited when conjugate and monosialoganglioside (GM1) were simultaneously applied to cells at 4 degrees. Cholera toxin is not toxic to neurons at the levels used. These results indicate that GERL is the primary site of endocytosis of presumed complexes of cholera toxin with its plasma membrane receptor (GM1 ganglioside-containing moieties). It is suggested that, in neurons, plasma-membrane bound ligands are taken up primarily into GERL.
Full text
PDF


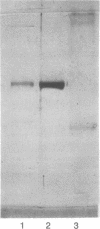
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antoine J. C., Avrameas S., Gonatas N. K., Stieber A., Gonatas J. O. Plasma membrane and internalized immunoglobulins of lymph node cells studied with conjugates of antibody or its Fab fragments with horseradish peroxidase. J Cell Biol. 1974 Oct;63(1):12–23. doi: 10.1083/jcb.63.1.12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avrameas S., Ternynck T. Peroxidase labelled antibody and Fab conjugates with enhanced intracellular penetration. Immunochemistry. 1971 Dec;8(12):1175–1179. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(71)90395-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett V., O'Keefe E., Cuatrecasaş P. Mechanism of action of cholera toxin and the mobile receptor theory of hormone receptor-adenylate cyclase interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jan;72(1):33–37. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.1.33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretscher M. S. Directed lipid flow in cell membranes. Nature. 1976 Mar 4;260(5546):21–23. doi: 10.1038/260021a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang K. J., Bennett V., Cuatrecasas P. Membrane receptors as general markers for plasma membrane isolation procedures. The use of 125-I-labeled wheat germ agglutinin, insulin, and cholera toxin. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jan 25;250(2):488–500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Interaction of Vibrio cholerae enterotoxin with cell membranes. Biochemistry. 1973 Aug 28;12(18):3547–3558. doi: 10.1021/bi00742a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Essner E., Haimes H. Ultrastructural study of GERL in beige mouse alveolar macrophages. J Cell Biol. 1977 Nov;75(2 Pt 1):381–387. doi: 10.1083/jcb.75.2.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein R. A., Boesman M., Neoh S. H., LaRue M. K., Delaney R. Dissociation and recombination of the subunits of the cholera enterotoxin (choleragen). J Immunol. 1974 Jul;113(1):145–150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonatas N. K., Avrameas S. Detection of carbohydrates with lectin-peroxidase conjugates. Methods Cell Biol. 1977;15:387–406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonatas N. K., Kim S. U., Stieber A., Avrameas S. Internalization of lectins in neuronal GERL. J Cell Biol. 1977 Apr;73(1):1–13. doi: 10.1083/jcb.73.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonatas N. K., Steiber A., Kim S. U., Graham D. I., Avrameas S. Internalization of neuronal plasma membrane ricin receptors into the Golgi apparatus. Exp Cell Res. 1975 Sep;94(2):426–431. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(75)90508-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herzog V., Farquhar M. G. Luminal membrane retrieved after exocytosis reaches most golgi cisternae in secretory cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):5073–5077. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.5073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holtzman E. The origin and fate of secretory packages, especially synaptic vesicles. Neuroscience. 1977;2(3):327–355. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(77)90001-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S. U., Munkacsi I. Morphological and cytochemical characteristics of neurons in cultures of mouse sympathetic ganglia. Exp Neurol. 1974 Oct;45(1):94–103. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(74)90103-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lospalluto J. J., Finkelstein R. A. Chemical and physical properties of cholera exo-enterotoxin (choleragen) and its spontaneously formed toxoid (choleragenoid). Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jan 26;257(1):158–166. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(72)90265-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manuelidis L., Manuelidis E. E. Cholera toxin-peroxidase: changes in surface labeling of glioblastoma cells with increased time in tissue culture. Science. 1976 Aug 13;193(4253):588–590. doi: 10.1126/science.959818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masurovsky E. B., Bunge R. P. Fluoroplastic coverslips for long-term nerve tissue culture. Stain Technol. 1968 May;43(3):161–165. doi: 10.3109/10520296809115061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novikoff A. B. The endoplasmic reticulum: a cytochemist's view (a review). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Aug;73(8):2781–2787. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.8.2781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverstein S. C., Steinman R. M., Cohn Z. A. Endocytosis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:669–722. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.003321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TRAMS E. G., LAUTER C. J. On the isolation and characterization of gangliosides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Jul 2;60:350–358. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90410-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unanue E. R. Cellular events folowing binding of antigen to lymphocytes. Am J Pathol. 1974 Oct;77(1):2–22. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weldon P. R. Pinocytotic uptake and intracellular distribution of colloidal thorium dioxide by cultured sensory neurites. J Neurocytol. 1975 Jun;4(3):341–356. doi: 10.1007/BF01102117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]