Abstract
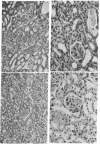
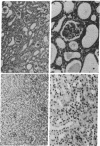
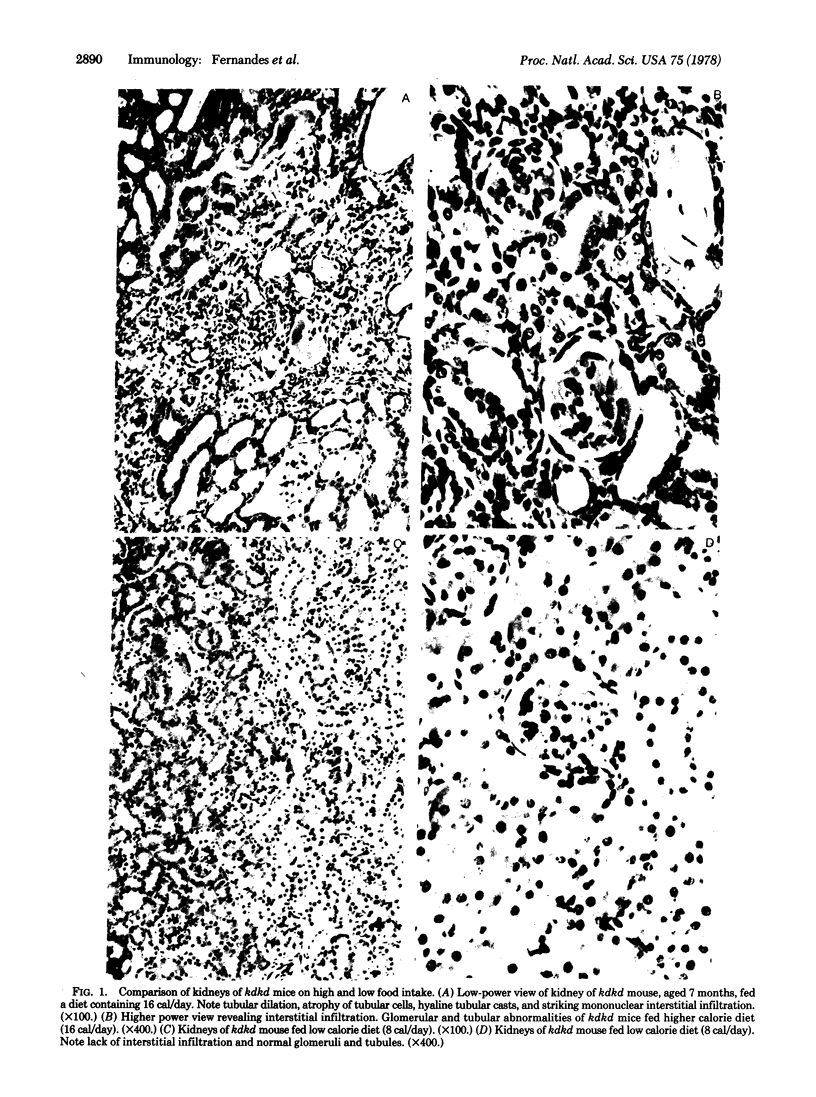
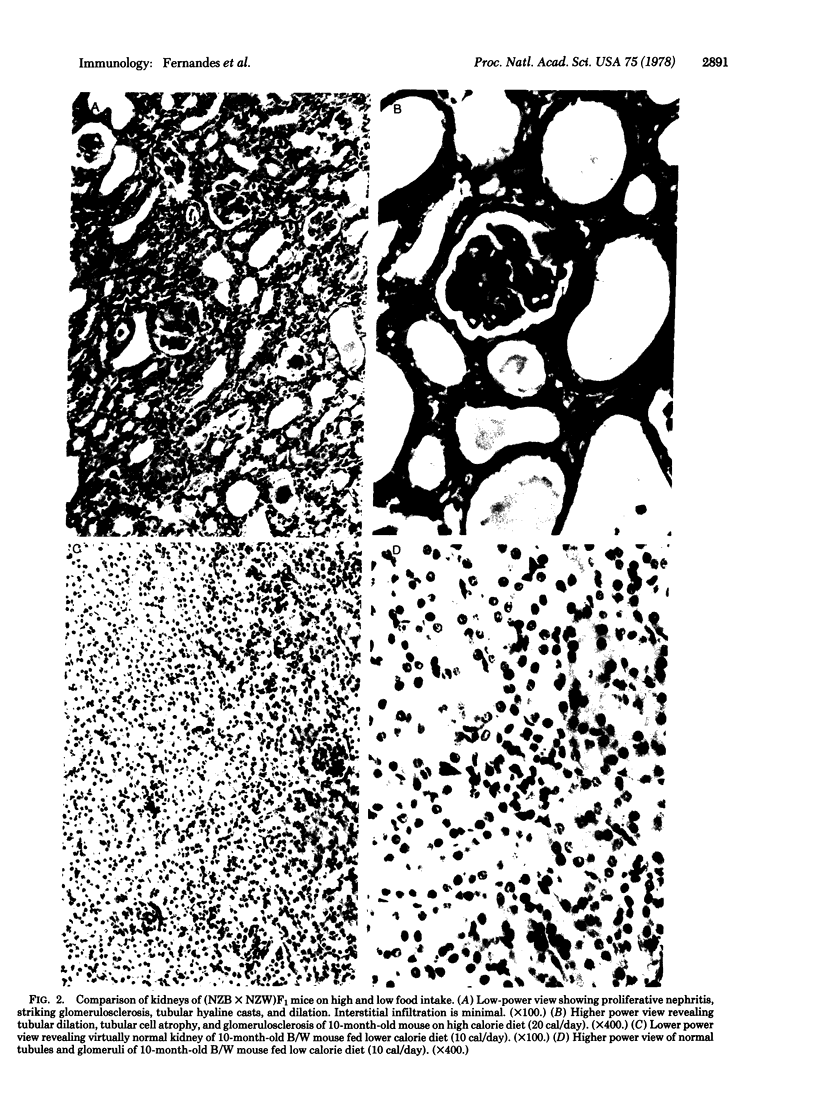
Striking inhibition of development of renal disease and prolongation of lifespan have been achieved in kdkd mice by restricting their daily food intake. Restricting protein intake alone did not prolong life nor did it inhibit development of kidney disease. The kdkd nephronophthisis, although very different histologically from the renal disease of B/W mice, may also have immunological components. Like the immunologically based renal disease of B/W mice, renal disease in kdkd mice is decreased or eliminated histologically by dietary restriction, which inhibits development of autoimmunity directed toward the erythrocytes of these mice. Further analysis will be needed to elucidate the cause of progressive renal disease in both the kdkd and B/W models and to permit understanding of the profound influence of restriction of food intake on development and progression of these very different renal diseases.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dubois E. L., Strain L. Effect of diet on survival and nephropathy of NZB-NZW hybrid mice. Biochem Med. 1973 Apr;7(2):336–342. doi: 10.1016/0006-2944(73)90091-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandes G., Friend P., Yunis E. J., Good R. A. Influence of dietary restriction on immunologic function and renal disease in (NZB x NZW) F1 mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1500–1504. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandes G., Halberg F., Yunis E. J., Good R. A. Circadian rhythmic plaque-forming cell response of spleens from mice immunized with SRBC. J Immunol. 1976 Sep;117(3):962–966. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandes G., Yunis E. J., Good R. A. Influence of diet on survival of mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Apr;73(4):1279–1283. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.4.1279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandes G., Yunis E. J., Good R. A. Influence of protein restriction on immune functions in NZB mice. J Immunol. 1976 Mar;116(3):782–790. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandes G., Yunis E. J., Good R. A. Suppression of adenocarcinoma by the immunological consequences of calorie restriction. Nature. 1976 Oct 7;263(5577):504–507. doi: 10.1038/263504b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandes G., Yunis E. J., Smith J., Good R. A. Dietary influence on breeding behavior, hemolytic anemia, and longevity in NZB mice. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1972 Apr;139(4):1189–1196. doi: 10.3181/00379727-139-36327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner M. B., Ihle J. N., Pillarisetty R. J., Talal N., Dubois E. L., Levy J. A. Type C virus expression and host response in diet-cured NZB/W mice. Nature. 1977 Jul 28;268(5618):341–344. doi: 10.1038/268341a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerbase-DeLima M., Liu R. K., Cheney K. E., Mickey R., Walford R. L. Immune function and survival in a long-lived mouse strain subjected to undernutrition. Gerontologia. 1975;21(4):184–202. doi: 10.1159/000212044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert P. H., Dixon F. J. Pathogenesis of the glomerulonephritis of NZB/W mice. J Exp Med. 1968 Mar 1;127(3):507–522. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.3.507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyon M. F., Hulse E. V. An inherited kidney disease of mice resembling human nephronophthisis. J Med Genet. 1971 Mar;8(1):41–48. doi: 10.1136/jmg.8.1.41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross M. H. Aging, nutrition and hepatic enzyme activity patterns in the rat. J Nutr. 1969 Apr;97(4 Suppl):565+–565+. doi: 10.1093/jn/97.suppl_4.565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucker S. M., Mason R. L., Beauchene R. E. Influence of diet and feed restriction on kidney function of aging male rats. J Gerontol. 1976 May;31(3):264–270. doi: 10.1093/geronj/31.3.264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walford R. L., Liu R. K., Gerbase-Delima M., Mathies M., Smith G. S. Longterm dietary restriction and immune function in mice: response to sheep red blood cells and to mitogenic agents. Mech Ageing Dev. 1973 Dec;2(6):447–454. doi: 10.1016/0047-6374(73)90035-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]