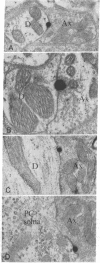
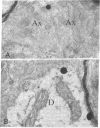
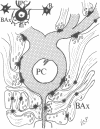
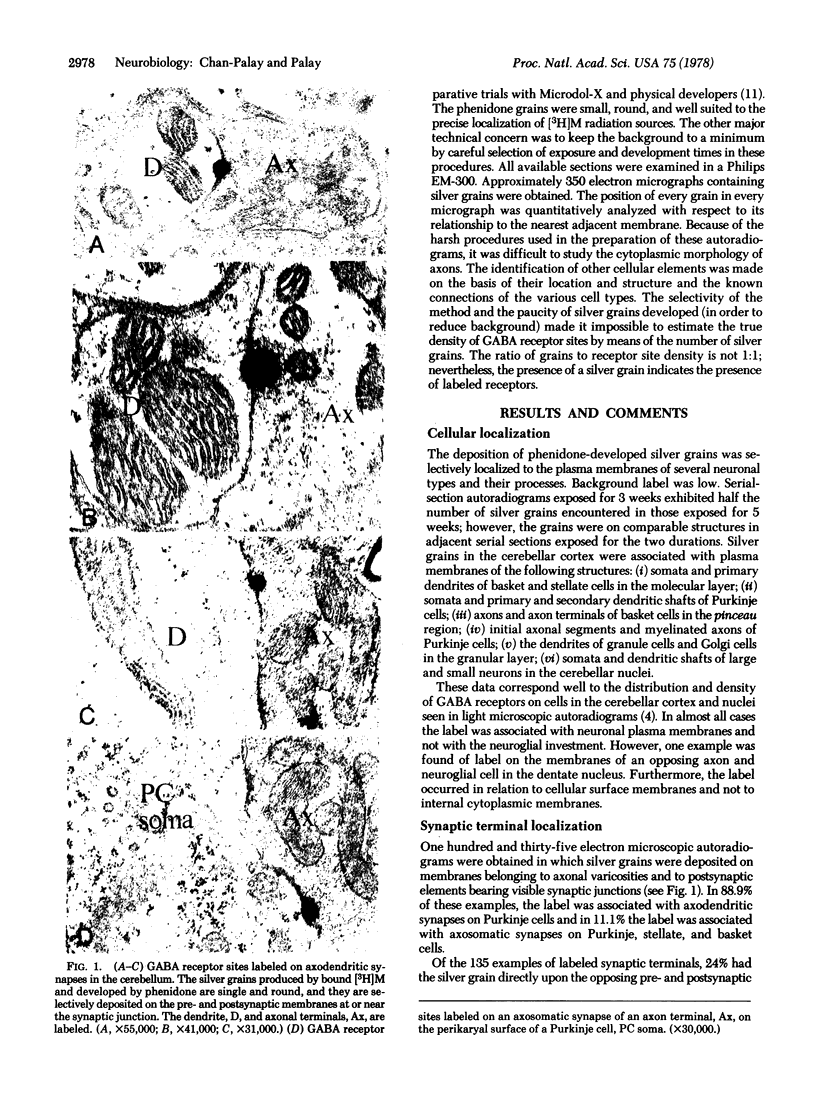
Abstract
This study utilizes tritiated muscimol binding and electron microscope autoradiography (Ilford L4 emulsion and phenidone development) to localize γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) receptor sites in the cerebellum of the rat. In the cerebellar cortex, silver grains were associated with somata and dendrites of basket and stellate cells in the molecular layer, with somata and primary and secondary dendritic shafts of Purkinje cells, axons and terminals of basket cells in the pinceau or basket, initial axonal segments and myelinated axons of Purkinje cells, and dendrites of granule and Golgi cells in the granular layer, and with somata and dendritic shafts of large and small cells in the cerebellar nuclei. These data correspond well to the light-microscope-autoradiographic observations in the cerebellum previously reported [Chan-Palay, V. (1978) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 75, 1024-1028]. Label over GABA receptor sites can be localized to the plasma membranes between pre- and postsynaptic elements at synaptic junctions, of which 88.9% of the samples are axodendritic and the remaining 11.1% are axosomatic. GABA receptor sites are also found along axonal membranes of the GABA-containing basket cell within the basket surrounding Purkinje cells, where true axo-axonal synapses are rare. It is speculated that GABA receptors in the basket may suggest a possibility of the basis for synchronization, either self-inhibition or facilitation within the basket formation, or presynaptic suppression of inhibitory action of basket cell on Purkinje cell.
Keywords: cerebellar cortex, nuclei, electron microscope autoradiography
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chan-Palay V. Autoradiographic localization of gamma-aminobutyric acid receptors in the rat central nervous system by using [3H]muscimol. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Feb;75(2):1024–1028. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.2.1024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan-Palay V. Fine structure of labelled axons in the cerebellar cortex and nuclei of rodents and primates after intraventricular infusions with tritiated serotonin. Anat Embryol (Berl) 1975 Dec 31;148(3):235–265. doi: 10.1007/BF00319846. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan-Palay V. Quantitative visualization of gamma-aminobutyric acid receptors in hippocampus and area dentata demonstrated by [3H]muscimol autoradiography. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2516–2520. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eccles J. C., Llinás R., Sasaki K. The inhibitory interneurones within the cerebellar cortex. Exp Brain Res. 1966;1(1):1–16. doi: 10.1007/BF00235206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enna S. J., Collins J. F., Snyder S. H. Stereospecificity and structure--activity requirements of GABA receptor binding in rat brain. Brain Res. 1977 Mar 18;124(1):185–190. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90878-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eugster C. H. Chemie der Wirkstoffe aus dem Fliegenpilz (Amanita muscaria) Fortschr Chem Org Naturst. 1969;27:261–321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fertuck H. C., Salpeter M. M. Quantitation of junctional and extrajunctional acetylcholine receptors by electron microscope autoradiography after 125I-alpha-bungarotoxin binding at mouse neuromuscular junctions. J Cell Biol. 1976 Apr;69(1):144–158. doi: 10.1083/jcb.69.1.144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gobel S. Axo-axonic septate junctions in the basket formations of the cat cerebellar cortex. J Cell Biol. 1971 Oct;51(1):328–333. doi: 10.1083/jcb.51.1.328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hökfelt T., Ljungdahl A. Cellular localization of labeled gamma-aminobutyric acid (3H-GABA) in rat cerebellar cortex: an autoradiographic study. Brain Res. 1970 Sep 16;22(3):391–396. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(70)90480-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston G. A., Krogsgaard-Larsen P., Stephanson A. L., Twitchin B. Inhibition of the uptake of GABA and related amino acids in rat brain slices by the optical isomers of nipecotic acid. J Neurochem. 1976 May;26(5):1029–1032. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1976.tb06488.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krogsgaard-Larsen P., Johnston G. A., Curtis D. R., Game C. J., McCulloch R. M. Structure and biological activity of a series of conformationally restricted analogues of GABA. J Neurochem. 1975 Dec;25(6):803–809. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1975.tb04411.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lettré H., Paweletz N. Probleme der elektronenmikroskopischen Autoradiographie. Naturwissenschaften. 1966 Jun;53(11):268–271. doi: 10.1007/BF00621640. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin B. J., Wood J. G., Saito K., Barber R., Vaughn J. E., Roberts E., Wu J. Y. The fine structural localization of glutamate decarboxylase in synaptic terminals of rodent cerebellum. Brain Res. 1974 Aug 23;76(3):377–391. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)90815-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sotelo C., Llinás R. Specialized membrane junctions between neurons in the vertebrate cerebellar cortex. J Cell Biol. 1972 May;53(2):271–289. doi: 10.1083/jcb.53.2.271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]