Abstract
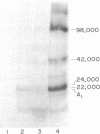
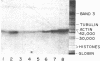
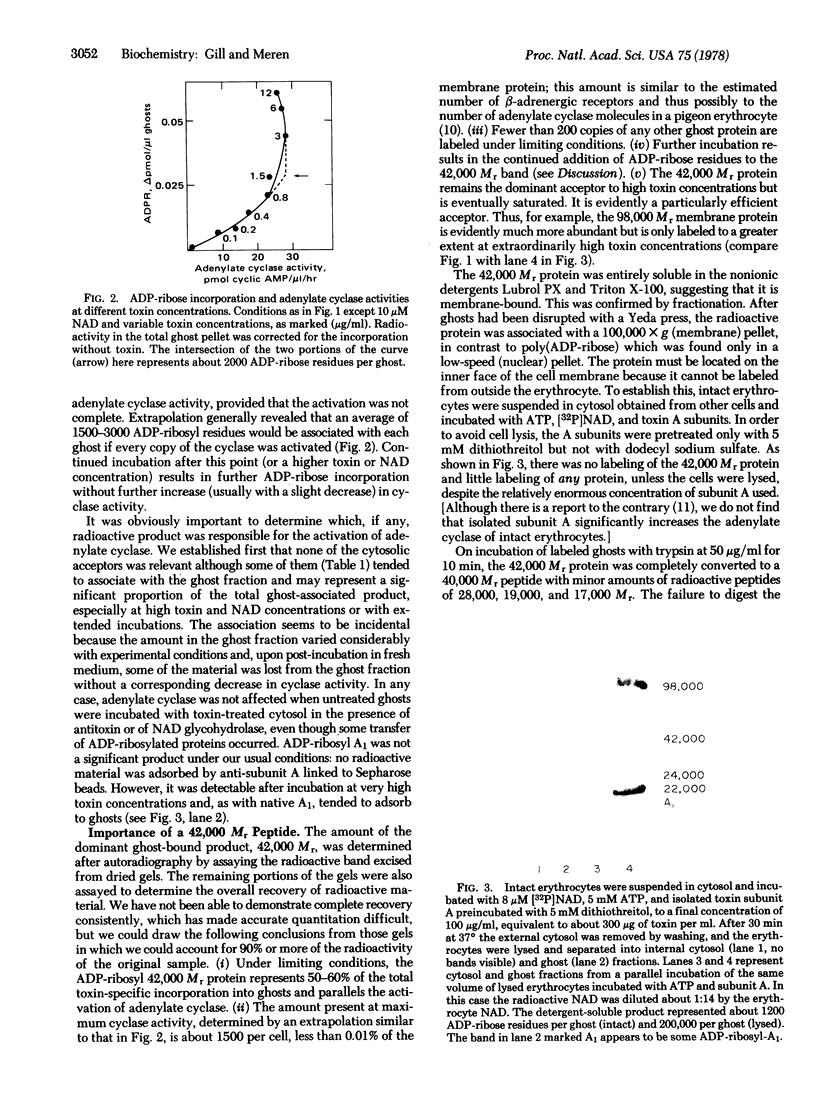
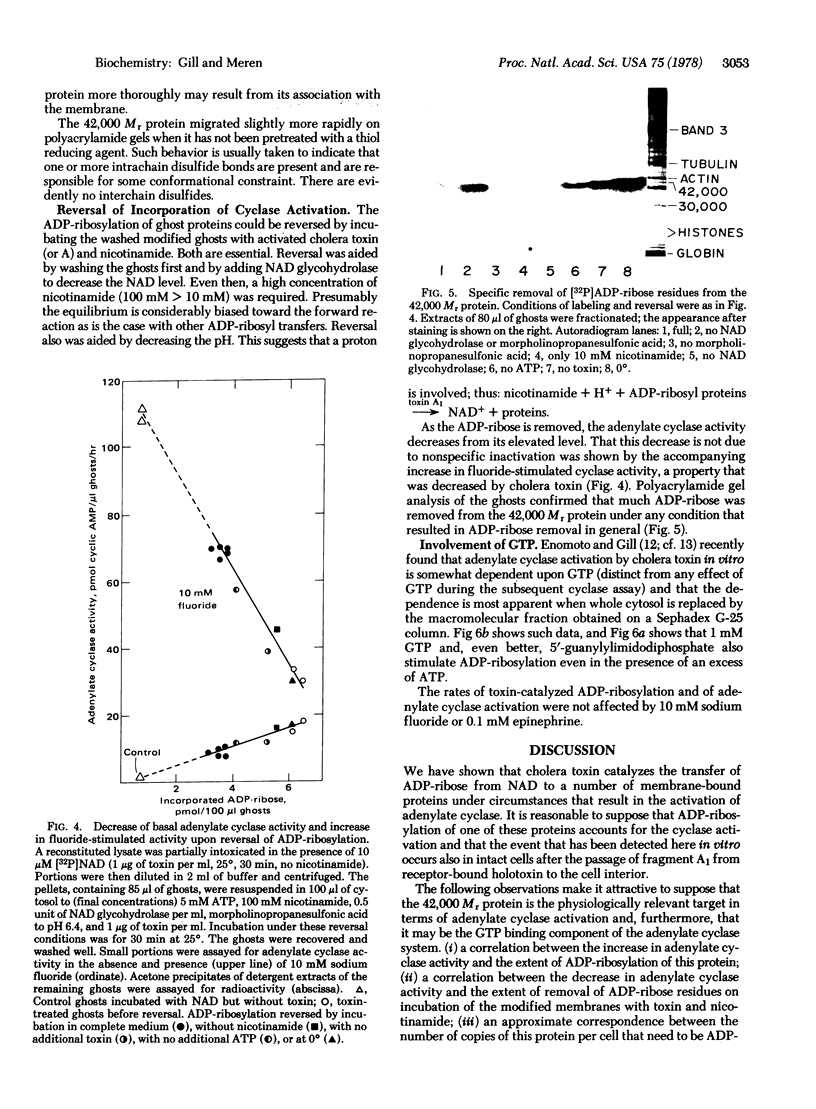
In the presence of ATP and a cytosolic factor, cholera toxin fragment A1 catalyzes the transfer of ADP-ribose from NAD to a number of soluble and membrane-bound proteins of the pigeon erythrocyte. Evidence is presented that suggests that the most readily modified membrane protein (Mr 42,000) is the adenylate cyclase-associated GTP-binding protein. Its modification by toxin is stimulated by guanine nucleotides. Adenylate cyclase activity increases in parallel with the addition of ADP-ribose to this protein and decreases in parallel with the subsequent reversal of ADP-ribosylation by toxin and nicotinamide. The protein is only accessible to toxin A subunits if the erythrocytes are lysed. When adenylate cyclase activity reaches a maximum, the number of ADP-ribose residues bound to this protein (about 1500 per cell) is similar to the reported number of beta-adrenergic receptors.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cassel D., Selinger Z. Mechanism of adenylate cyclase activation by cholera toxin: inhibition of GTP hydrolysis at the regulatory site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3307–3311. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores J., Sharp G. W. Effects of cholera toxin on adenylate cyclase. Studies with guanylylimidodiphosphate. J Clin Invest. 1975 Nov;56(5):1345–1349. doi: 10.1172/JCI108213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. M. Involvement of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide in the action of cholera toxin in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2064–2068. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2064. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. M., King C. A. The mechanism of action of cholera toxin in pigeon erythrocyte lysates. J Biol Chem. 1975 Aug 25;250(16):6424–6432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. M. The arrangement of subunits in cholera toxin. Biochemistry. 1976 Mar 23;15(6):1242–1248. doi: 10.1021/bi00651a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson G. L., Bourne H. R. Influence of cholera toxin on the regulation of adenylate cyclase by GTP. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Sep 23;78(2):792–798. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)90249-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lad P. M., Welton A. F., Rodbell M. Evidence for distinct guanine nucleotide sites in the regulation of the glucagon receptor and of adenylate cyclase activity. J Biol Chem. 1977 Sep 10;252(17):5942–5946. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinson S. L., Blume A. J. Altered guanine nucleotide hydrolysis as basis for increased adenylate cyclase activity after cholera toxin treatment. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jun 10;252(11):3766–3774. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss J., Manganiello V. C., Vaughan M. Hydrolysis of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide by choleragen and its A protomer: possible role in the activation of adenylate cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Dec;73(12):4424–4427. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.12.4424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss J., Vaughan M. Choleragen activation of solubilized adenylate cyclase: requirement for GTP and protein activator for demonstration of enzymatic activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4396–4400. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss J., Vaughan M. Mechanism of action of choleragen. Evidence for ADP-ribosyltransferase activity with arginine as an acceptor. J Biol Chem. 1977 Apr 10;252(7):2455–2457. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeuffer T. GTP-binding proteins in membranes and the control of adenylate cyclase activity. J Biol Chem. 1977 Oct 25;252(20):7224–7234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trepel J. B., Chuang D. M., Neff N. H. Transfer of ADP-ribose from NAD to choleragen: a subunit acts as catalyst and acceptor protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5440–5442. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Heyningen S., King C. A. Short communications. Subunit A from cholera toxin is an activator of adenylate cyclase in pigeon erythrocytes. Biochem J. 1975 Jan;146(1):269–271. doi: 10.1042/bj1460269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]