Abstract
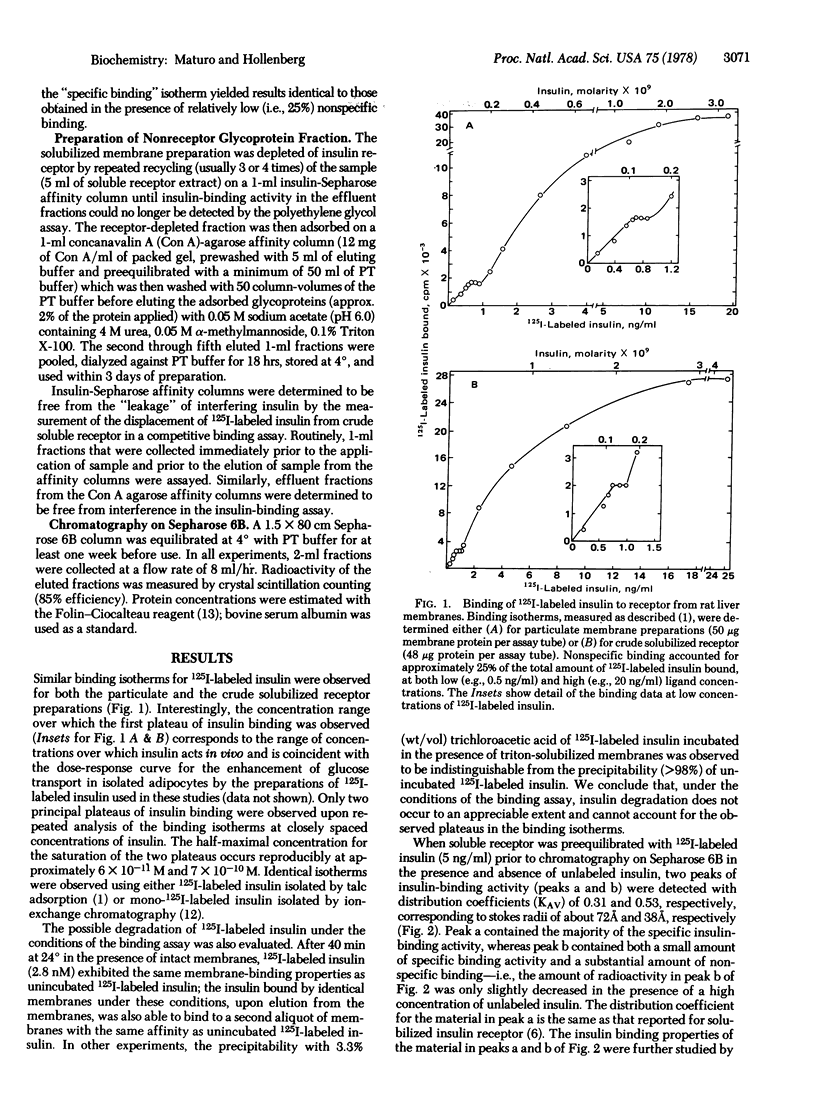
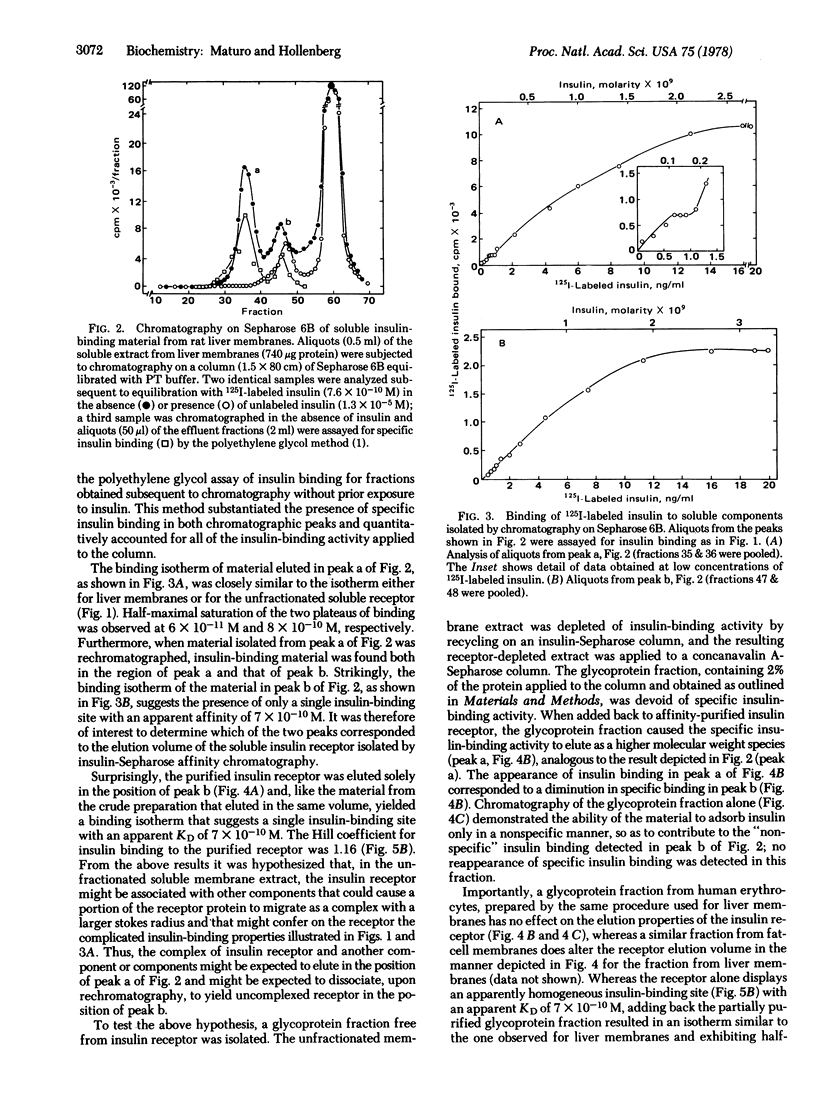
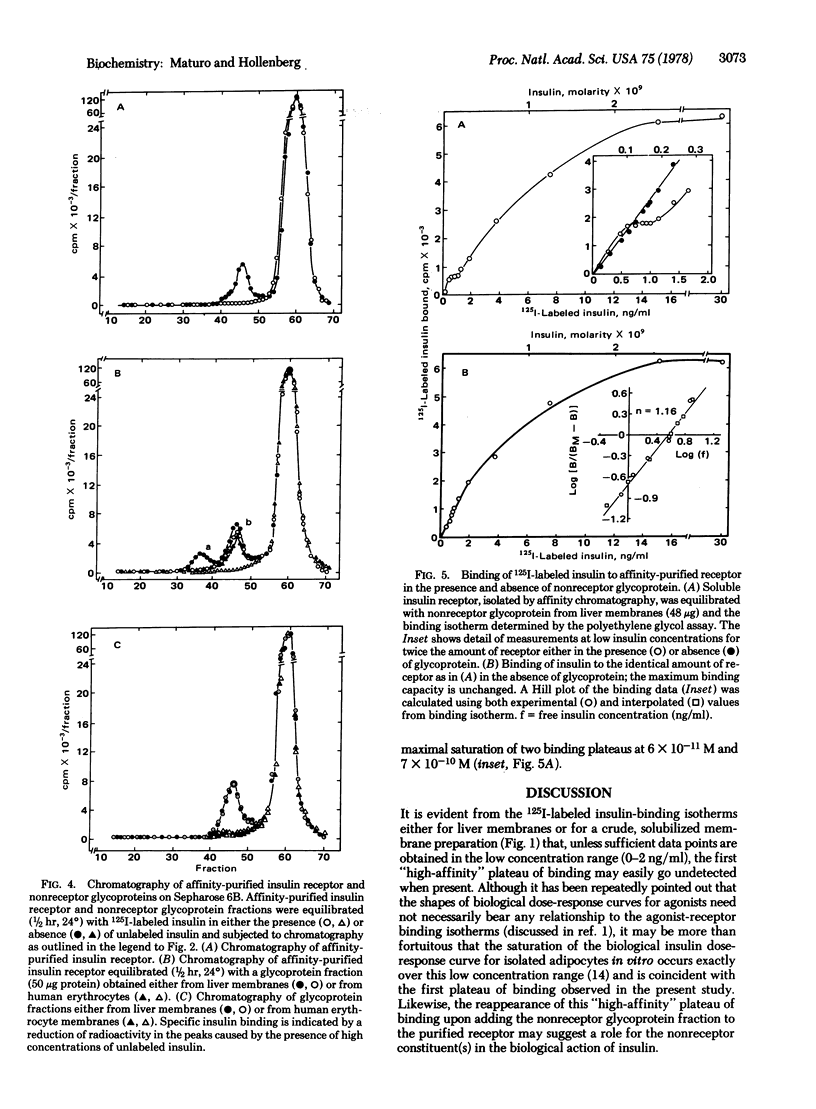
In crude receptor preparations (either particulate or soluble) of rat liver membranes, the insulin receptor exhibits complicated binding kinetics (two binding plateaus, half-saturated at approximately 60 pM and 700 pM insulin) and an apparent chromatographic heterogeneity, suggested by the presence of two detectable, soluble insulin-binding components with apparent Stokes radii of 72 Å and 38 Å. In contrast, the insulin receptor isolated by affinity chromatography exhibits a simple binding isotherm (half-maximal saturation of binding at 700 pM insulin) without evidence for negative cooperativity and behaves as a single component (apparent Stokes radius of 38 Å) upon chromatography on Sepharose 6B. The apparent discrepancies between the properties of the unpurified insulin receptor and the affinity-purified receptor can be attributed to the presence in crude preparations of a nonreceptor constituent(s) having properties consistent with those of a membrane glycoprotein. A glycoprotein fraction from such crude soluble membrane preparations, freed from insulin receptor and subsequently partially purified using concanavalin-A-agarose, when combined with affinity-purified insulin receptor, causes both a reappearance of the complicated binding kinetics and an increase in the receptor's apparent Stokes radius from 38 Å to 72 Å. Similar results are observed for a glycoprotein fraction obtained from rat adipocyte membranes but are not observed for an identical fraction isolated from human erythrocyte membranes. We conclude that the insulin receptor in rat liver membranes can interact with another nonreceptor membrane glycoprotein that may represent either a nonrecognition moiety of the receptor oligomer or an effector molecule to the biological action of insulin.
Keywords: affinity chromatography, receptor cooperativity, mobile receptor hypothesis
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennett V., O'Keefe E., Cuatrecasaş P. Mechanism of action of cholera toxin and the mobile receptor theory of hormone receptor-adenylate cyclase interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jan;72(1):33–37. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.1.33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Affinity chromatography and purification of the insulin receptor of liver cell membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 May;69(5):1277–1281. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.5.1277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Affinity chromatography and purification of the insulin receptor of liver cell membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 May;69(5):1277–1281. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.5.1277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P., Hollenberg M. D. Membrane receptors and hormone action. Adv Protein Chem. 1976;30:251–451. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60481-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Insulin--receptor interactions in adipose tissue cells: direct measurement and properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jun;68(6):1264–1268. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.6.1264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Isolation of the insulin receptor of liver and fat-cell membranes (detergent-solubilized-( 125 I)insulin-polyethylene glycol precipitation-sephadex). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Feb;69(2):318–322. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.2.318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Membrane receptors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1974;43(0):169–214. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.43.070174.001125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Properties of the insulin receptor isolated from liver and fat cell membranes. J Biol Chem. 1972 Apr 10;247(7):1980–1991. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeMeyts P., Bainco A. R., Roth J. Site-site interactions among insulin receptors. Characterization of the negative cooperativity. J Biol Chem. 1976 Apr 10;251(7):1877–1888. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desbuquois B., Krug F., Cuatrecasas P. Inhibitors of glucagon inactivation. Effect on glucagon--receptor interactions and glucagon-stimulated adenylate cyclase activity in liver cell membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Mar 20;343(1):101–120. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(74)90242-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freychet P., Roth J., Neville D. M., Jr Monoiodoinsulin: demonstration of its biological activity and binding to fat cells and liver membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Apr 16;43(2):400–408. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90767-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsberg B. H., Kahn C. R., Roth J., De Meyts P. Insulin-induced dissociation of its receptor into subunits: possible molecular concomitant of negative cooperativity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Dec 20;73(4):1068–1074. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90232-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsberg B. H., Kahn C. R., Roth J., De Meyts P. Insulin-induced dissociation of its receptor into subunits: possible molecular concomitant of negative cooperativity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Dec 20;73(4):1068–1074. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90232-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs S., Cuatrecasas P. The mobile receptor hypothesis and "cooperativity" of hormone binding. Application to insulin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 May 21;433(3):482–495. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90275-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn C. R., Freychet P., Roth J., Neville D. M., Jr Quantitative aspects of the insulin-receptor interaction in liver plasma membranes. J Biol Chem. 1974 Apr 10;249(7):2249–2257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollet R. J., Standaert M. L., Haase B. A. Insulin binding to the human lymphocyte receptor. Evaluation of the negative cooperativity model. J Biol Chem. 1977 Aug 25;252(16):5828–5834. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Haën C. The non-stoichiometric floating receptor model for hormone sensitive adenylyl cyclase. J Theor Biol. 1976 May 21;58(2):383–400. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5193(76)80126-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


