Abstract
Background:
Female pattern hair loss (FPHL) presents with visible patterns of hair loss, thus making a bedside diagnosis possible. However, there are cases of FPHL presenting without any visible hair thinning, making it necessary to subject them to a scalp biopsy to make a diagnosis.
Aim:
The aim of the following study is to determine if trichoscopy can be used as a bedside tool to diagnose Early FPHL in women presenting without any visible thinning of hair, using >20% hair diameter diversity – anisotrichosis, as the diagnostic criteria.
Materials and Methods:
Trichoscopy was performed on 20 cases of early FPHL (biopsy proven), 63 normal controls and 29 Grade 2 FPHL Controls.
Results and Discussion:
In the biopsy proven FPHL cases, 75% showed anisotrichosis on trichoscopy. This finding was significantly higher in FPHL Cases compared to normal controls. As expected, 93% of Grade 2 FPHL controls also showed the same finding. Trichoscopy was found to be 75% sensitive and 61.54% specific in diagnosing early FPHL. Thus, a negative result would be more indicative of absence of disease, however, a positive result would not always indicate the presence of disease.
Keywords: Anisotrichosis, female pattern hair loss, hair diameter diversity, trichoscopy
INTRODUCTION
The diagnosis of female pattern hair loss (FPHL) is largely made by standard clinical observations based on visible patterns of hair loss. Various global clinical scales have described these patterns such as those proposed by Ludwig,[1] Olsen,[2] Savin,[3] Biondo et al.[4] (Women's alopecia severity scale [WASS]). However, there is a set of women who present with the chronic hair loss without any discernible reduction in hair density over the crown. Such early forms are often overlooked and clinical evaluation may not be adequate to make the right diagnosis. In a study by Sinclair et al.,[5] it was observed that 56% (32/57) of women with a history of hair loss for >6 months duration, with a completely normal looking scalp, were actually diagnosed as FPHL on triple horizontal scalp biopsy. This diagnosis was based on histopathological terminal/vellus ratio of <4:1 (equivalent to >20% hair diameter diversity [HDD]).
On the other hand, trichoscopy[6,7] is a noninvasive method (vs. scalp biopsy) for diagnosis of hair loss, which uses videodermoscopy of hair and scalp at higher magnifications (×20 - ×70).[8,9,10] This allows a noninvasive measurement of HDD, which is a characteristic feature of FPHL, recently termed as “Anisotrichosis.”[11] Trichoscopy has been widely used as a diagnostic as well as a prognostic tool to measure anisotrichosis in cases of overt androgenetic alopecia (AGA) and FPHL.[8,12,13,14,15] Trichoscopy can thus also be used as a tool to diagnose FPHL in early cases. This could be made easier on the bed side by using a photographic scale to determine the presence of >20% anisotrichosis, rather than having to measure it.
The goal of our study was to determine if trichoscopy can be used as a reliable noninvasive tool to diagnose early FPHL in females presenting with diffuse hair loss of >6 months duration, without obvious scalp hair thinning, using a photographic diversity scale and possibly obviate the need for scalp biopsy in these patients. To the best of our knowledge, no such study has been performed to demonstrate the findings and validity of trichoscopy in early FPHL.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Written informed consent was obtained from all patients and the protocol was approved by the hospital-based ethics committee.
Subjects
Cases: 35 female cases with a complaint of progressive hair loss of gradual onset of >6 months duration, without obvious scalp midline widening were enrolled. These cases were graded as Grade 1 of Hair Loss as per the WASS. All relevant blood investigations were performed.
Patients with cicatricial alopecia, alopecia areata, trichotillomania, acute telogen effluvium or traction alopecia were excluded from the study.
Group 1 Controls: 63 healthy age- and sex-matched female volunteers with no history or findings suggestive of hair loss served as negative controls.
Group 2 Controls: 29 female patients with a complaint of progressive, gradual hair loss of >6 months duration, with obvious scalp midline widening, without thinning of hair on either side (Grade 2 hair loss - WASS) served as positive controls.
Procedure
Trichoscopy
All cases and controls were evaluated for HDD with a trichoscope at the midscalp. All the subjects were asked to shampoo their hair 1 day prior to the procedure. They were asked to avoid oiling or coloring their hair.
A clean midline was obtained at the midscalp with a fine toothed comb (kept constant throughout the study for all subjects). Isopropyl alcohol was used as the interface solution. Using the digital camera (Canon Powershot A640 10 MP, Keppal Bay Tower, Singapore) with its optical attachment pressing evenly against the scalp, trichoscopic images were taken at ×20 magnification at the midscalp – at the intersection between nose line and ear implantation line.
Images having features of scaling, white or colored hair, with an improper midline and backscattering effect were not accepted for analysis.
The optimal captured images were digitalized and displayed on a real time monitor and selected images were stored on a computer. The image was compared with a photographic scale for HDD and was rated as either,
Scale 1 – showing >20% HDD, suggestive of FPHL; or
Scale 2 – showing <20% HDD, not suggestive of FPHL. Thus, a trichoscopic diagnosis was established.
Scalp biopsy
All the cases were subjected to a triple horizontal scalp biopsy.
The biopsy was performed from the midscalp region – at the intersection between the nose line and ear implantation line, 1 cm away from the midline, to avoid a cosmetically disfiguring scar.
The hair over the above mentioned site was clipped short using a hair clipper (Moser Trichoscan edition hair clipper). The surrounding hair were secured away from the biopsy site with the help of sticking micropore tape. The skin was infiltrated with 2 ml of 2% lignocaine with 1:10000 adrenaline (AstraZeneca). After a waiting period of 10 min, a 4 mm disposable biopsy punch (Dermaindia) was used to take plugs of immediately adjacent skin in an anteroposterior line. Special care was taken to direct the punch in the direction of hair follicles. The wound was closed primarily with 2-0 nylon suture material (Ethicon), which was removed after 7-10 days.
The biopsy specimens were subjected to horizontal sectioning at the mid-isthmus level and were evaluated by a single observer. The histopathological diagnosis was made by counting the total no. of hair, total no. of terminal hair, total number of vellus hair and wherefore obtaining a terminal: vellus hair ratio. Follicles were classified as vellus-like using the criteria established by Whiting: The width of the inner root sheath equals or exceeds the diameter of the hair shaft or the hair shaft diameter is <30 μm.
Following diagnostic definitions were applied: (T - Terminal, V - Vellus)
T:V ratio ≤4:1 in one or more sections – FPHL
T:V ratio ≥8:1, with no section showing T:V ratio ≤4:1 – Chronic telogen effluvium (CTE)
T:V ratio between 4:1-8:1 – Indeterminate.
Final analysis
The trichoscopic diversity scale was compared with the histopathological diagnosis. The specificity and sensitivity of trichoscopy in cases and controls was computed using simple formulas. To obtain the statistical significance values, Chi-square test was used.
RESULTS
The mean ± SD ages of the female cases, Group 1 controls and Group 2 controls were comparable, the values being 29.12 ± 7.57, 28.32 ± 6.37 and 31.10 ± 6.11 years, respectively (P = 0.18).
Of the 35 women with Grade 1 hair loss (WASS), 20 had FPHL, 13 had CTE and 2 had indeterminate diagnosis on a triple horizontal scalp biopsy.
The trichoscopic findings of all cases and controls at the midscalp region are summarized in Tables 1 and 2.
Table 1.
Comparison of trichoscopic diagnosis with histopathologic diagnosis in cases
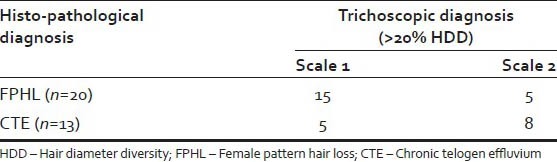
Table 2.
Trichoscopic diagnosis in Group 1 and Group 2 controls

Amongst the cases, 75% of FPHL cases showed >20% HDD on trichoscopy [Figure 1], and as one would expect, 93% of Group 2 controls showed >20% HDD [Figure 2]. >20% HDD was significantly higher in FPHL compared to Group 1 control [Figure 3] (31.75%, P < 0.006) and CTE cases (38.5%, P < 0.036).
Figure 1.
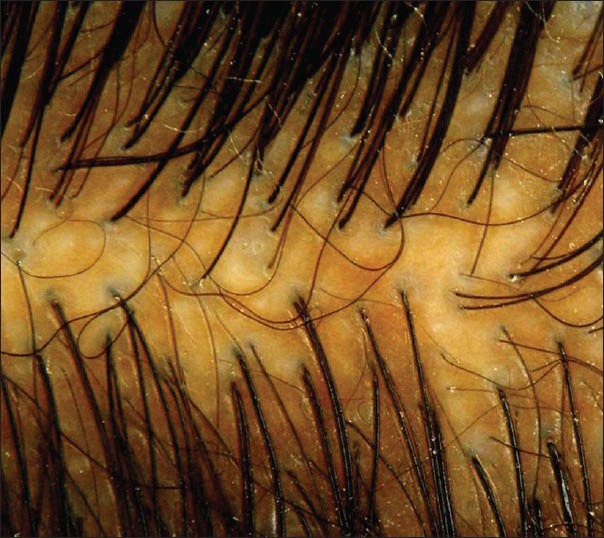
Case, Grade 1 female pattern hair loss showing anisotrichosis on trichoscopy
Figure 2.
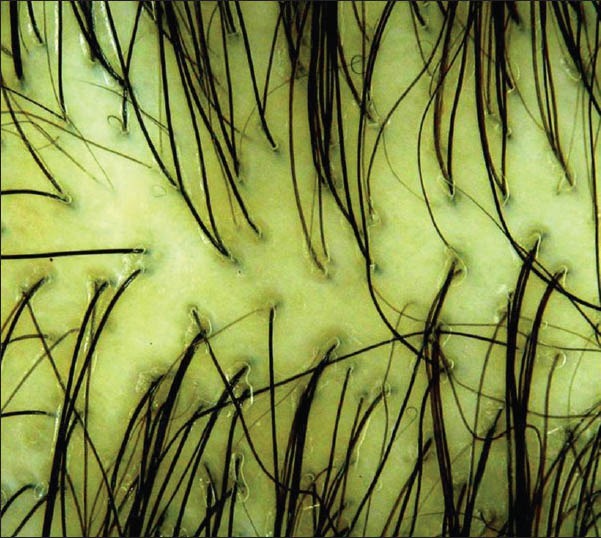
Group 2 control, Grade 2 female pattern hair loss, showing anisotrichosis on trichoscopy
Figure 3.
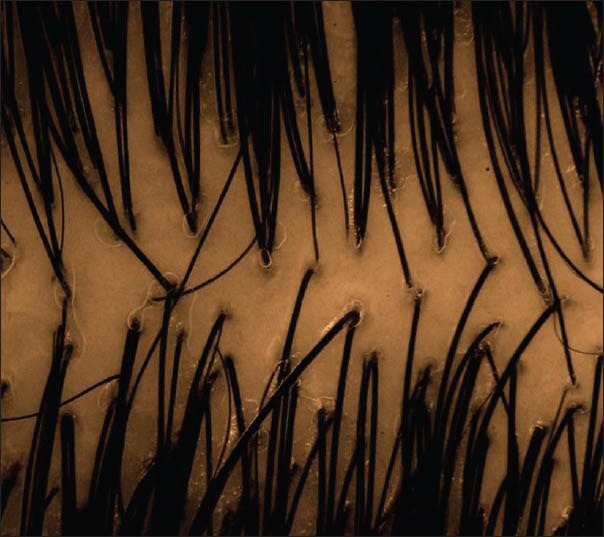
Group 1 control, normal, showing normal findings on trichoscopy
In the account of the above findings, trichoscopy in the midscalp region was found to be 75% sensitive and 61.54% specific in diagnosing early FPHL. The sensitivity of diagnosing Grade 2 FPHL increased to 93%.
DISCUSSION
The presence of hair with different caliber is typical of FPHL[16] and reflects progressive hair miniaturization due to the disease. In a study by Tosti et al. has postulated that a diversity of >20% is diagnostic of AGA.[17] This characteristic feature of FPHL is seen histopathologically as well as clinically. Trichoscopy aids in the better visualization of this feature, which may not always be visible to the naked eye.
The use of trichoscopy dates back to the early 1990's[18] and since then it has been used for the diagnosis of various hair and scalp disorders like AGA,[8,12,13,14] alopecia areata,[8,19,20] cicatricial alopecia,[18,21] hair shaft disorders,[22,23,24] microsporiasis.[25]
Via trichoscopy, AGA has been characterized by increased percentage of thin hairs, increased hair shaft diameter diversity, increased percentage of single hair units, presence of yellow dots, perifollicular hyperpigmentation.[7,8,12,15] However, these have been studied in white subjects. A study done on Asian population showed that perifollicular pigmentation was less appreciated on the Asian scalp compared to the white population.[14] Even amongst the white population, the number of yellow dots observed in FPHL cases were 20% higher on ×70 magnification versus ×20 magnification,[12] making it a relatively unreliable finding. Presence of yellow dots is a finding present in alopecia areata, trichotillomania, in addition to AGA;[9] wherein, in a recent study it was found to be significantly higher in alopecia areata.[26] The same study showed that HDD was present in all cases of AGA and was significantly higher than in other forms of hair loss. Inui[14] postulated that >20% HDD is an essential feature to diagnose AGA and FPHL. More so, according to de Lacharrière et al.,[13] diversity in hair diameter was the main and most accurate clinical parameter linked to follicle miniaturization.
Hence, in our study HDD was considered as sole diagnostic criteria for FPHL, using a photographic scale for bedside use.
Using >20% HDD as a diagnostic parameter, trichoscopy could diagnose 75% of Grade 1 FPHL and 93% of Grade 2 FPHL. This increase in detection from Grade 1 to Grade 2 could be due to the increasing miniaturization with increasing grade of FPHL, further signifying the correlation between HDD and follicle miniaturization.[13]
Trichoscopy is found to be 75% sensitive and 61.54% specific in diagnosing early FPHL. In view of the high sensitivity, a negative result would be more indicative of absence of disease, however, due to the low specificity, a positive result would not always indicate the presence of disease.
Since >20% HDD is also a finding observed in a small proportion of normal controls, this occurrence in the normal population should be further elucidated. If possible these normal women should be biopsied to look for an underlying androgenetic process. If not, a long-term follow-up of such patients for the development of FPHL should be attempted.
CONCLUSION
Based on the above study it can be concluded that trichoscopy is a sensitive, non-invasive tool for preliminary evaluation of females with early diffuse hair loss. It is easy to use and interpret a time-saving and relatively inexpensive tool. One can consider using trichoscopy as an aid for screening of such females and avoid the patient feared scalp biopsy to some extent. A negative result would help in ruling out FPHL; however a positive one still does not obviate the need for a scalp biopsy.
Footnotes
Source of Support: Nil
Conflict of Interest: None declared.
REFERENCES
- 1.Ludwig E. Classification of the types of androgenetic alopecia (common baldness) occurring in the female sex. Br J Dermatol. 1977;97:247–54. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1977.tb15179.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Olsen EA. Current and novel methods for assessing efficacy of hair growth promoters in pattern hair loss. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003;48:253–62. doi: 10.1067/mjd.2003.81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Savin RC. A method for visually describing and quantitating hair loss in male pattern baldness (abstract) J Invest Dermatol. 1992;98:604. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Biondo S, Goble D, Sinclair R. Women who present with female pattern hair loss tend to underestimate the severity of their hair loss. Br J Dermatol. 2004;150:750–2. doi: 10.1046/j.0007-0963.2003.05809.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Sinclair R, Jolley D, Mallari R, Magee J. The reliability of horizontally sectioned scalp biopsies in the diagnosis of chronic diffuse telogen hair loss in women. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;51:189–99. doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622(03)00045-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Olszewska M, Rudnicka L, Rakowska A, Kowalska-Oledzka E, Slowinska M. Trichoscopy. Arch Dermatol. 2008;144:1007. doi: 10.1001/archderm.144.8.1007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Rudnicka L, Olszewska M, Majsterek M. Presence and future of dermoscopy. Expert Rev Dermatol. 2006;1:769–72. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Lacarrubba F, Dall’Oglio F, Rita Nasca M, Micali G. Videodermatoscopy enhances diagnostic capability in some forms of hair loss. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2004;5:205–8. doi: 10.2165/00128071-200405030-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Ross EK, Vincenzi C, Tosti A. Videodermoscopy in the evaluation of hair and scalp disorders. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006;55:799–806. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2006.04.058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Rudnicka L, Olszewska M, Rakowska A, Kowalska-Oledzka E, Slowinska M. Trichoscopy: A new method for diagnosing hair loss. J Drugs Dermatol. 2008;7:651–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Sewell LD, Elston DM, Dorion RP. “Anisotrichosis”: A novel term to describe pattern alopecia. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2007;56:856. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2007.01.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Rakowska A, Slowinska M, Kowalska-Oledzka E, Olszewska M, Rudnicka L. Dermoscopy in female androgenic alopecia: Method standardization and diagnostic criteria. Int J Trichology. 2009;1:123–30. doi: 10.4103/0974-7753.58555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.de Lacharrière O, Deloche C, Misciali C, Piraccini BM, Vincenzi C, Bastien P, et al. Hair diameter diversity: A clinical sign reflecting the follicle miniaturization. Arch Dermatol. 2001;137:641–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Inui S, Nakajima T, Itami S. Scalp dermoscopy of androgenetic alopecia in Asian people. J Dermatol. 2009;36:82–5. doi: 10.1111/j.1346-8138.2009.00593.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Olszewska M, Rudnicka L. Effective treatment of female androgenic alopecia with dutasteride. J Drugs Dermatol. 2005;4:637–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Whiting DA. Scalp biopsy as a diagnostic and prognostic tool in androgenetic alopecia. Dermatol Ther. 1998;8:24–33. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Tosti A. Androgenetic alopecia. In: Tosti A, editor. Dermocopy of Hair and Calp Disorders with Clinical and Pathological Correlations. Vol. 2. UK: Informa Healthcare; 2007. pp. 15–25. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Kossard S, Zagarella S. Spotted cicatricial alopecia in dark skin. A dermoscopic clue to fibrous tracts. Australas J Dermatol. 1993;34:49–51. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-0960.1993.tb00856.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Inui S, Nakajima T, Itami S. Dry dermoscopy in clinical treatment of alopecia areata. J Dermatol. 2007;34:635–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1346-8138.2007.00345.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Tosti A, Whiting D, Iorizzo M, Pazzaglia M, Misciali C, Vincenzi C, et al. The role of scalp dermoscopy in the diagnosis of alopecia areata incognita. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;59:64–7. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2008.03.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Tosti A, Torres F, Misciali C, Vincenzi C, Starace M, Miteva M, et al. Follicular red dots: A novel dermoscopic pattern observed in scalp discoid lupus erythematosus. Arch Dermatol. 2009;145:1406–9. doi: 10.1001/archdermatol.2009.277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Rakowska A, Slowinska M, Czuwara J, Olszewska M, Rudnicka L. Dermoscopy as a tool for rapid diagnosis of monilethrix. J Drugs Dermatol. 2007;6:222–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Rakowska A, Slowinska M, Kowalska-Oledzka E, Rudnicka L. Trichoscopy in genetic hair shaft abnormalities. J Dermatol Case Rep. 2008;2:14–20. doi: 10.3315/jdcr.2008.1009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Rakowska A, Kowalska-Oledzka E, Slowinska M, Rosinska D, Rudnicka L. Hair shaft videodermoscopy in netherton syndrome. Pediatr Dermatol. 2009;26:320–2. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1470.2008.00778.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Slowinska M, Rudnicka L, Schwartz RA, Kowalska-Oledzka E, Rakowska A, Sicinska J, et al. Comma hairs: A dermatoscopic marker for tinea capitis: A rapid diagnostic method. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;59:S77–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2008.07.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Karadağ Köse Ö, Güleç AT. Clinical evaluation of alopecias using a handheld dermatoscope. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;67:206–14. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2011.08.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


