Abstract
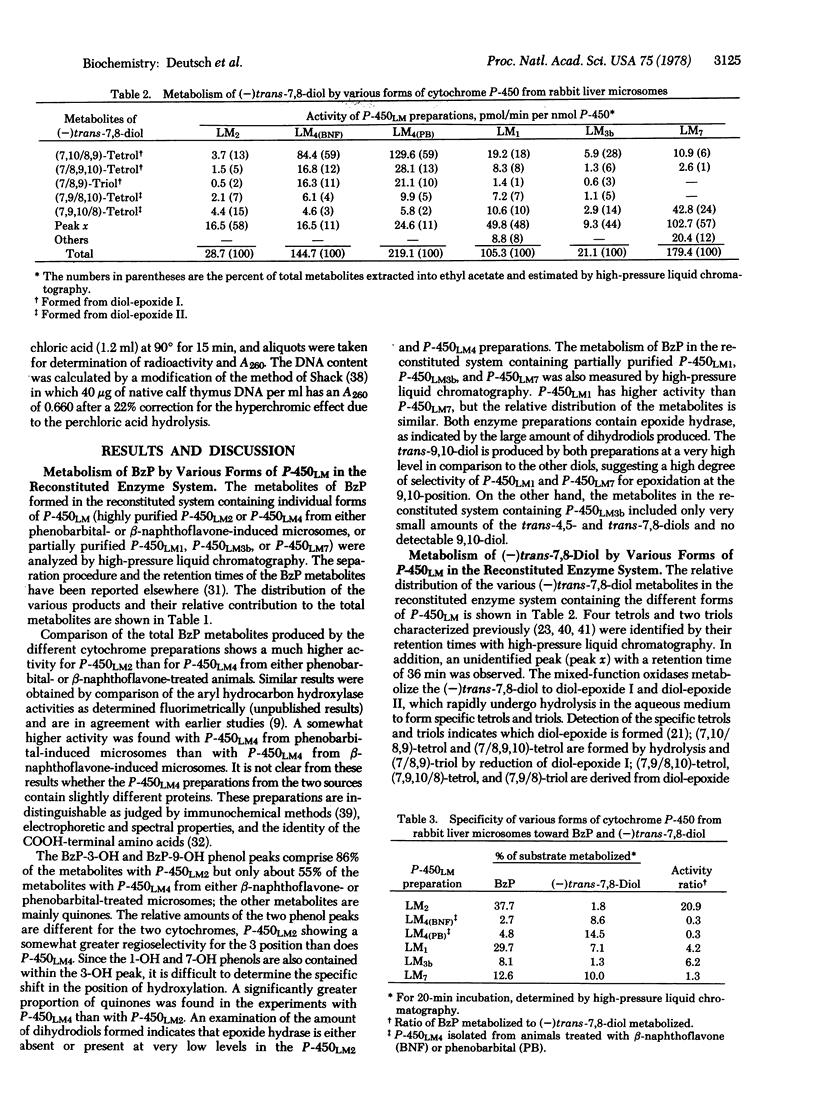
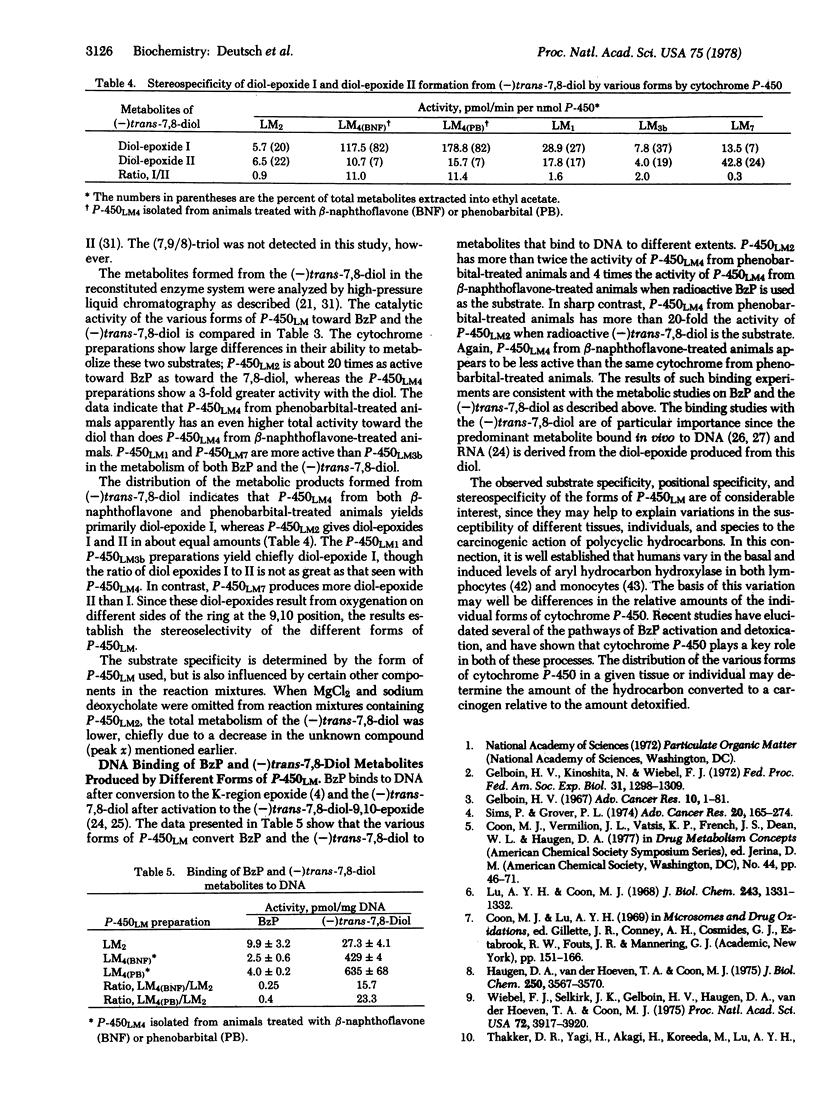
Highly purified cytochromes P-450LM2 and P-450LM4 and partially purified P-450LM1, P-450LM3b, and P-450LM7 from rabbit liver microsomes exhibit different catalytic activities in the metabolism of benzo[a]pyrene (BzP) and (-)-trans-7,8-dihydroxy-7,8-dihydrobenzo[a]pyrene [(-)trans-7,8-diol] in a reconstituted enzyme system. The two highly purified cytochromes also exhibit differences in the activation of BzP and (-)trans-7,8-diol to intermediates that bind to DNA, as well as in the stereoselective conversion of (-)trans-7,8-diol to the highly mutagenic and carcinogenic diol-epoxides r-7,t-8-dihydroxy-t-9,10-oxy-7,8,9,10- tetrahydrobenzo[a]pyrene (diol-epoxide I) and r - 7,t - 8 - dihydroxy - c - 9,10 - oxy - 7,8,9,10 - tetrahydrobenzo[a]pyrene (diol-epoxide II). P-450LM2 is more active than P-450LM4 in the metabolism of BzP and in its conversion to products that bind to DNA. In contrast, P-450LM4 is more active than P-450LM2 in the metabolism of (-)trans-7,8-diol and in its conversion to products that bind to DNA. The ratio of activity (percent substrate metabolized) with BzP relative to that with (-)trans-7,8-diol is 21 for P-450LM2 and 0.3 for P-450LM4; P-450LM1, P-450LM3b, and P-450LM7 gave intermediate ratios. Marked stereoselectivity in the oxygenation of the (-)trans-7,8-diol to the highly mutagenic and putatively carcinogenic diol-epoxides I and II was observed with P-450LM4, whereas the other preparations showed less selectivity. The ratio of diolepoxide I to diol-epoxide II ranges from 0.3 for P-450LM7 to 11 for P-450LM4. The substrate specificity and regio- and stereo-selectivity of the different forms of cytochrome P-450 may regulate the balance between activation and detoxification pathways of BzP and therefore determine the susceptibility of individual tissues, strains, and species to the carcinogenic action of BzP.
Keywords: chemical carcinogenesis, detoxification, hydroxylases, diol-epoxides, benzo[a]pyrene activation
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bast R. C., Jr, Okuda T., Plotkin E., Tarone R., Rapp H. J., Gelboin H. V. Development of an assay for aryl hydrocarbon (benzo(a)pyrene) hydroxylase in human peripheral blood monocytes. Cancer Res. 1976 Jun;36(6):1967–1974. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CONNEY A. H., MILLER E. C., MILLER J. A. Substrate-induced synthesis and other properties of benzpyrene hydroxylase in rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1957 Oct;228(2):753–766. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen G. M., Moore B. P., Bridges J. W. Organic solvent soluble sulphate ester conjugates of monohydroxybenzo(a)pyrenes. Biochem Pharmacol. 1977 Mar 15;26(6):551–553. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(77)90335-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daudel P., Duquesne M., Vigny P., Grover P. L., Sims P. Fluorescence spectral evidence that benzo(a)pyrene-DNA products in mouse skin arise from diol-epoxides. FEBS Lett. 1975 Oct 1;57(3):250–253. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80310-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean W. L., Coon M. J. Immunochemical studies on two electrophoretically homogeneous forms of rabbit liver microsomal cytochrome P-450: P-450LM2 and P-450LM4. J Biol Chem. 1977 May 25;252(10):3255–3261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelboin H. V. A microsome-dependent binding of benzo[a]pyrene to DNA. Cancer Res. 1969 Jun;29(6):1272–1276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelboin H. V. Carcinogens, enzyme induction, and gene action. Adv Cancer Res. 1967;10:1–81. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60076-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelboin H. V., Kinoshita N., Wiebel F. J. Microsomal hydroxylases: induction and role in polycyclic hydrocarbon carcinogenesis and toxicity. Fed Proc. 1972 Jul-Aug;31(4):1298–1309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haugen D. A., Coon M. J. Properties of electrophoretically homogeneous phenobarbital-inducible and beta-naphthoflavone-inducible forms of liver microsomal cytochrome P-450. J Biol Chem. 1976 Dec 25;251(24):7929–7939. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haugen D. A., van der Hoeven T. A., Coon M. J. Purified liver microsomal cytochrome P-450. Separation and characterization of multiple forms. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 10;250(9):3567–3570. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holder G., Yagi H., Dansette P., Jerina D. M., Levin W., Lu A. Y., Conney A. H. Effects of inducers and epoxide hydrase on the metabolism of benzo(a)pyrene by liver microsomes and a reconstituted system: analysis by high pressure liquid chromatography. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Nov;71(11):4356–4360. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.11.4356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huberman E., Sachs L., Yang S. K., Gelboin V. Identification of mutagenic metabolites of benzo(a)pyrene in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):607–611. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIRBY K. S. A new method for the isolation of deoxyribonucleic acids; evidence on the nature of bonds between deoxyribonucleic acid and protein. Biochem J. 1957 Jul;66(3):495–504. doi: 10.1042/bj0660495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellermann G., Luyten-Kellermann M., Shaw C. R. Genetic variation of aryl hydrocarbon hydroxylase in human lymphocytes. Am J Hum Genet. 1973 May;25(3):327–331. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King H. W., Osborne M. R., Beland F. A., Harvey R. G., Brookes P. (+/-)-7alpha,8beta-dihydroxy-9beta,10beta-epoxy-7,8,9,10-tetrahydrobenzo(a)-pyrene is an intermediate in the metabolism and binding to DNA of benzo(a)pyrene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Aug;73(8):2679–2681. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.8.2679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinoshita N., Shears B., Gelboin H. V. K-region and non-K-region metabolism of benzo(a)pyrene by rat liver microsomes. Cancer Res. 1973 Aug;33(8):1937–1944. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leutz J. C., Gelboin H. V. Benzo(a)pyrene-4,5-oxide hydratase: assay, properties, and induction. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Jun;168(2):722–725. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90307-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu A. Y., Coon M. J. Role of hemoprotein P-450 in fatty acid omega-hydroxylation in a soluble enzyme system from liver microsomes. J Biol Chem. 1968 Mar 25;243(6):1331–1332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nebert D. W., Gelboin H. V. Substrate-inducible microsomal aryl hydroxylase in mammalian cell culture. I. Assay and properties of induced enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1968 Dec 10;243(23):6242–6249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemoto N., Gelboin H. V. Enzymatic conjugation of benzo (a) pyrene oxides, phenols and dihydrodiols with UDP-glucuronic acid. Biochem Pharmacol. 1976 May 15;25(10):1221–1226. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(76)90373-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemoto N., Gelboin H. V., Habig W. H., Ketley J. N., Jakoby W. B. K region benzo (alpha) pyrene-4,5-oxide is conjugated by homogeneous gluthathione S-transferases. Nature. 1975 Jun 5;255(5508):512–512. doi: 10.1038/255512a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHACK J. On the recognition and estimation of denatured deoxyribonucleate. J Biol Chem. 1958 Sep;233(3):677–680. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selkirk J. K., Croy R. G., Gelboin H. V. Isolation by high pressure liquid chromatography and characterization of benzo(a)pyrene-4'5-epoxide as a metobolite of benzoapyrene. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 May;168(1):322–326. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90256-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sims P., Grover P. L. Epoxides in polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon metabolism and carcinogenesis. Adv Cancer Res. 1974;20:165–274. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60111-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sims P., Grover P. L., Swaisland A., Pal K., Hewer A. Metabolic activation of benzo(a)pyrene proceeds by a diol-epoxide. Nature. 1974 Nov 22;252(5481):326–328. doi: 10.1038/252326a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sims P. Qualitative and quantitative studies on the metabolism of a series of aromatic hydrocarbons by rat-liver preparations. Biochem Pharmacol. 1970 Mar;19(3):795–818. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(70)90243-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thakker D. R., Yagi H., Akagi H., Koreeda M., Lu A. H., Levin W., Wood A. W., Conney A. H., Jerina D. M. Metabolism of benzo[a]pyrene. VI. Stereoselective metabolism of benzo[a]pyrene and benzo[a]pyrene 7,8-dihydrodiol to diol epoxides. Chem Biol Interact. 1977 Mar;16(3):281–300. doi: 10.1016/0009-2797(77)90108-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein I. B., Jeffrey A. M., Jennette K. W., Blobstein S. H., Harvey R. G., Harris C., Autrup H., Kasai H., Nakanishi K. Benzo(a)pyrene diol epoxides as intermediates in nucleic acid binding in vitro and in vivo. Science. 1976 Aug 13;193(4253):592–595. doi: 10.1126/science.959820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiebel F. J., Selkirk J. K., Gelboin H. V., Haugen D. A., van der Hoeven T. A., Coon M. J. Position-specific oxygenation of benzo(a)pyrene by different forms of purified cytochrome P-450 from rabbit liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3917–3920. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang S. K., Gelboin H. V. Microsomal mixed-function oxidases and epoxide hydratase convert benzo(a)pyrene stereospecifically to optically active dihydroxydihydrobenzo(a)pyrenes. Biochem Pharmacol. 1976 Oct 1;25(19):2221–2225. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(76)90138-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang S. K., Gelboin H. V. Nonenzymatic reduction of benzo(a)pyrene diol-epoxides to trihydroxypentahydrobenzo(a)pyrenes by reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate. Cancer Res. 1976 Nov;36(11 Pt 1):4185–4189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang S. K., Gelboin H. V., Weber J. D., Sankaran V., Fischer D. L., Engel J. F. Resolution of optical isomers by high-pressure liquid chromatography. The separation of benzo[a]pyrene trans-diol derivatives. Anal Biochem. 1977 Apr;78(2):520–526. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90112-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang S. K., McCourt D. W., Gelboin H. V., Miller J. R., Roller P. P. Stereochemistry of the hydrolysis products and their acetonides of two stereoisomeric benzo[a]pyrene 7,8-diol 9,10-epoxides. J Am Chem Soc. 1977 Jul 20;99(15):5124–5130. doi: 10.1021/ja00457a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang S. K., McCourt D. W., Roller P. P., Gelboin H. V. Enzymatic conversion of benzo(a)pyrene leading predominantly to the diol-epoxide r-7,t-8-dihydroxy-t-9,10-oxy-7,8,9,10-tetrahydrobenzo(a)pyrene through a single enantiomer of r-7, t-8-dihydroxy-7,8-dihydrobenzo(a)pyrene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Aug;73(8):2594–2598. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.8.2594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang S. K., Roller P. P., Gelboin H. V. Enzymatic mechanism of benzo[a]pyrene conversion to phenols and diols and an improved high-pressure liquid chromatographic separation of benzo[a]pyrene derivatives. Biochemistry. 1977 Aug 9;16(16):3680–3687. doi: 10.1021/bi00635a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Hoeven T. A., Coon M. J. Preparation and properties of partially purified cytochrome P-450 and reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate-cytochrome P-450 reductase from rabbit liver microsomes. J Biol Chem. 1974 Oct 10;249(19):6302–6310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


