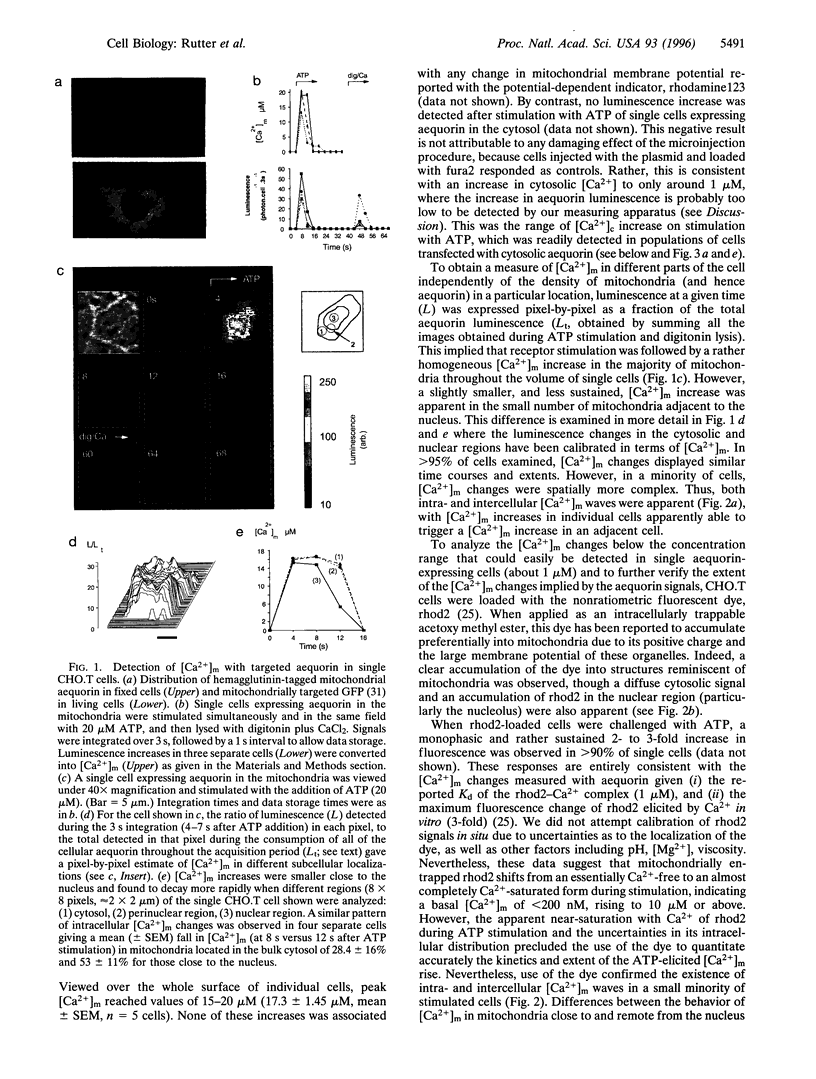
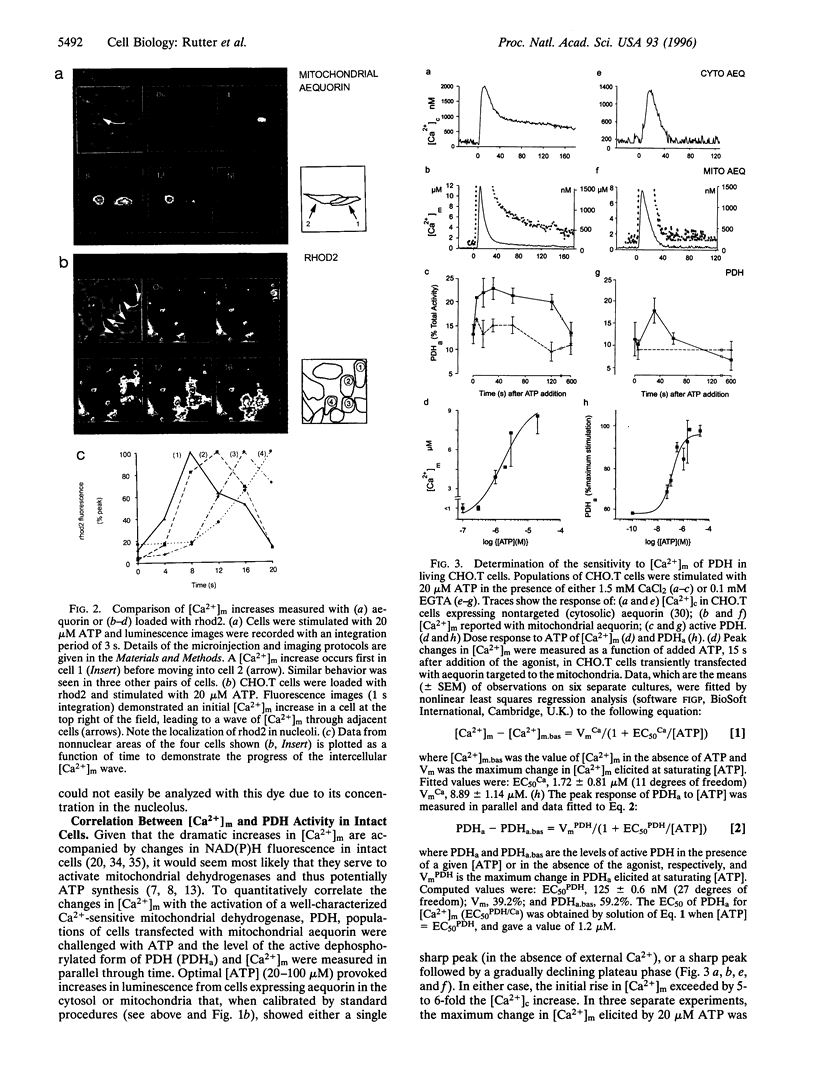
Abstract
Specific targeting of the recombinant, Ca2+ -sensitive photoprotein, aequorin to intracellular organelles has provided new insights into the mechanisms of intracellular Ca2+ homeostasis. When applied to small mammalian cells, a major limitation of this technique has been the need to average the signal over a large number of cells. This prevents the identification of inter- or intracellular heterogeneities. Here we describe the imaging in single mammalian cells (CHO.T) of [Ca2+] with recombinant chimeric aequorin targeted to mitochondria. This was achieved by optimizing expression of the protein through intranuclear injection of cDNA and through the use of a charge-coupled device camera fitted with a dual microchannel plate intensifier. This approach allows accurate quantitation of the kinetics and extent of the large changes in mitochondrial matrix [Ca2+] ([Ca2+](m)) that follow receptor stimulation and reveal different behaviors of mitochondrial populations within individual cells. The technique is compared with measurements of [Ca2+](m) using the fluorescent indicator, rhod2. Comparison of [Ca2+](m) with the activity of the Ca2+ -sensitive matrix enzyme, pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH), reveals that this enzyme is a target of the matrix [Ca2+] changes. Peak [Ca2+](m) values following receptor stimulation are in excess of those necessary for full activation of PDH in situ, but may be necessary for the activation of other mitochondrial dehydrogenases. Finally, the data suggest that the complex regulation of PDH activity by a phosphorylation-dephosphorylation cycle may provide a means by which changes in the frequency of cytosolic (and hence mitochondrial) [Ca2+] oscillations can be decoded by mitochondria.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Augustine G. J., Neher E. Calcium requirements for secretion in bovine chromaffin cells. J Physiol. 1992 May;450:247–271. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachs O., Agell N., Carafoli E. Calcium and calmodulin function in the cell nucleus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Aug 14;1113(2):259–270. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(92)90041-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and calcium signalling. Nature. 1993 Jan 28;361(6410):315–325. doi: 10.1038/361315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brini M., Marsault R., Bastianutto C., Alvarez J., Pozzan T., Rizzuto R. Transfected aequorin in the measurement of cytosolic Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]c). A critical evaluation. J Biol Chem. 1995 Apr 28;270(17):9896–9903. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.17.9896. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brini M., Marsault R., Bastianutto C., Alvarez J., Pozzan T., Rizzuto R. Transfected aequorin in the measurement of cytosolic Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]c). A critical evaluation. J Biol Chem. 1995 Apr 28;270(17):9896–9903. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.17.9896. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brini M., Marsault R., Bastianutto C., Pozzan T., Rizzuto R. Nuclear targeting of aequorin. A new approach for measuring nuclear Ca2+ concentration in intact cells. Cell Calcium. 1994 Oct;16(4):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(94)90089-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clapham D. E. Calcium signaling. Cell. 1995 Jan 27;80(2):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90408-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Combettes L., Tran D., Tordjmann T., Laurent M., Berthon B., Claret M. Ca(2+)-mobilizing hormones induce sequentially ordered Ca2+ signals in multicellular systems of rat hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1994 Dec 1;304(Pt 2):585–594. doi: 10.1042/bj3040585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dani J. W., Chernjavsky A., Smith S. J. Neuronal activity triggers calcium waves in hippocampal astrocyte networks. Neuron. 1992 Mar;8(3):429–440. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90271-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denton R. M., McCormack J. G. Ca2+ as a second messenger within mitochondria of the heart and other tissues. Annu Rev Physiol. 1990;52:451–466. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.52.030190.002315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denton R. M., McCormack J. G. On the role of the calcium transport cycle in heart and other mammalian mitochondria. FEBS Lett. 1980 Sep 22;119(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80986-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denton R. M., Randle P. J., Martin B. R. Stimulation by calcium ions of pyruvate dehydrogenase phosphate phosphatase. Biochem J. 1972 Jun;128(1):161–163. doi: 10.1042/bj1280161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denton R. M., Richards D. A., Chin J. G. Calcium ions and the regulation of NAD+-linked isocitrate dehydrogenase from the mitochondria of rat heart and other tissues. Biochem J. 1978 Dec 15;176(3):899–906. doi: 10.1042/bj1760899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubyak G. R., el-Moatassim C. Signal transduction via P2-purinergic receptors for extracellular ATP and other nucleotides. Am J Physiol. 1993 Sep;265(3 Pt 1):C577–C606. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1993.265.3.C577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hajnóczky G., Robb-Gaspers L. D., Seitz M. B., Thomas A. P. Decoding of cytosolic calcium oscillations in the mitochondria. Cell. 1995 Aug 11;82(3):415–424. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90430-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jouaville L. S., Ichas F., Holmuhamedov E. L., Camacho P., Lechleiter J. D. Synchronization of calcium waves by mitochondrial substrates in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Nature. 1995 Oct 5;377(6548):438–441. doi: 10.1038/377438a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight M. R., Read N. D., Campbell A. K., Trewavas A. J. Imaging calcium dynamics in living plants using semi-synthetic recombinant aequorins. J Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;121(1):83–90. doi: 10.1083/jcb.121.1.83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás R., Sugimori M., Silver R. B. Microdomains of high calcium concentration in a presynaptic terminal. Science. 1992 May 1;256(5057):677–679. doi: 10.1126/science.1350109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormack J. G., Denton R. M. The effects of calcium ions and adenine nucleotides on the activity of pig heart 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase complex. Biochem J. 1979 Jun 15;180(3):533–544. doi: 10.1042/bj1800533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormack J. G., Halestrap A. P., Denton R. M. Role of calcium ions in regulation of mammalian intramitochondrial metabolism. Physiol Rev. 1990 Apr;70(2):391–425. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1990.70.2.391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormack J. G. Studies on the activation of rat liver pyruvate dehydrogenase and 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase by adrenaline and glucagon. Role of increases in intramitochondrial Ca2+ concentration. Biochem J. 1985 Nov 1;231(3):597–608. doi: 10.1042/bj2310597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller B., Chauhan A., Jaffe L. F., Miller A. L. Oscillations in free [Ca2+]i during early cell division cycles in Xenopus laevis embryos. Biol Bull. 1994 Oct;187(2):239–240. doi: 10.1086/BBLv187n2p239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minta A., Kao J. P., Tsien R. Y. Fluorescent indicators for cytosolic calcium based on rhodamine and fluorescein chromophores. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 15;264(14):8171–8178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyata H., Silverman H. S., Sollott S. J., Lakatta E. G., Stern M. D., Hansford R. G. Measurement of mitochondrial free Ca2+ concentration in living single rat cardiac myocytes. Am J Physiol. 1991 Oct;261(4 Pt 2):H1123–H1134. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1991.261.4.H1123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musil L. S., Goodenough D. A. Multisubunit assembly of an integral plasma membrane channel protein, gap junction connexin43, occurs after exit from the ER. Cell. 1993 Sep 24;74(6):1065–1077. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90728-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nedergaard M. Direct signaling from astrocytes to neurons in cultures of mammalian brain cells. Science. 1994 Mar 25;263(5154):1768–1771. doi: 10.1126/science.8134839. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls D., Akerman K. Mitochondrial calcium transport. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Sep 1;683(1):57–88. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(82)90013-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pralong W. F., Spät A., Wollheim C. B. Dynamic pacing of cell metabolism by intracellular Ca2+ transients. J Biol Chem. 1994 Nov 4;269(44):27310–27314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rizzuto R., Bastianutto C., Brini M., Murgia M., Pozzan T. Mitochondrial Ca2+ homeostasis in intact cells. J Cell Biol. 1994 Sep;126(5):1183–1194. doi: 10.1083/jcb.126.5.1183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rizzuto R., Brini M., Murgia M., Pozzan T. Microdomains with high Ca2+ close to IP3-sensitive channels that are sensed by neighboring mitochondria. Science. 1993 Oct 29;262(5134):744–747. doi: 10.1126/science.8235595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rizzuto R., Brini M., Pizzo P., Murgia M., Pozzan T. Chimeric green fluorescent protein as a tool for visualizing subcellular organelles in living cells. Curr Biol. 1995 Jun 1;5(6):635–642. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(95)00128-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rizzuto R., Simpson A. W., Brini M., Pozzan T. Rapid changes of mitochondrial Ca2+ revealed by specifically targeted recombinant aequorin. Nature. 1992 Jul 23;358(6384):325–327. doi: 10.1038/358325a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robb-Gaspers L. D., Thomas A. P. Coordination of Ca2+ signaling by intercellular propagation of Ca2+ waves in the intact liver. J Biol Chem. 1995 Apr 7;270(14):8102–8107. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.14.8102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutter G. A. Ca2(+)-binding to citrate cycle dehydrogenases. Int J Biochem. 1990;22(10):1081–1088. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(90)90105-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutter G. A., Denton R. M. Regulation of NAD+-linked isocitrate dehydrogenase and 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase by Ca2+ ions within toluene-permeabilized rat heart mitochondria. Interactions with regulation by adenine nucleotides and NADH/NAD+ ratios. Biochem J. 1988 May 15;252(1):181–189. doi: 10.1042/bj2520181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutter G. A., Midgley P. J., Denton R. M. Regulation of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex by Ca2+ within toluene-permeabilized heart mitochondria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Dec 14;1014(3):263–270. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(89)90222-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutter G. A., Theler J. M., Murgia M., Wollheim C. B., Pozzan T., Rizzuto R. Stimulated Ca2+ influx raises mitochondrial free Ca2+ to supramicromolar levels in a pancreatic beta-cell line. Possible role in glucose and agonist-induced insulin secretion. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 25;268(30):22385–22390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutter G. A., White M. R., Tavaré J. M. Involvement of MAP kinase in insulin signalling revealed by non-invasive imaging of luciferase gene expression in single living cells. Curr Biol. 1995 Aug 1;5(8):890–899. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(95)00179-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. Y., Pozzan T., Rink T. J. Calcium homeostasis in intact lymphocytes: cytoplasmic free calcium monitored with a new, intracellularly trapped fluorescent indicator. J Cell Biol. 1982 Aug;94(2):325–334. doi: 10.1083/jcb.94.2.325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollheim C. B., Biden T. J. Signal transduction in insulin secretion: comparison between fuel stimuli and receptor agonists. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1986;488:317–333. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1986.tb46568.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods N. M., Cuthbertson K. S., Cobbold P. H. Repetitive transient rises in cytoplasmic free calcium in hormone-stimulated hepatocytes. Nature. 1986 Feb 13;319(6054):600–602. doi: 10.1038/319600a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





