Abstract
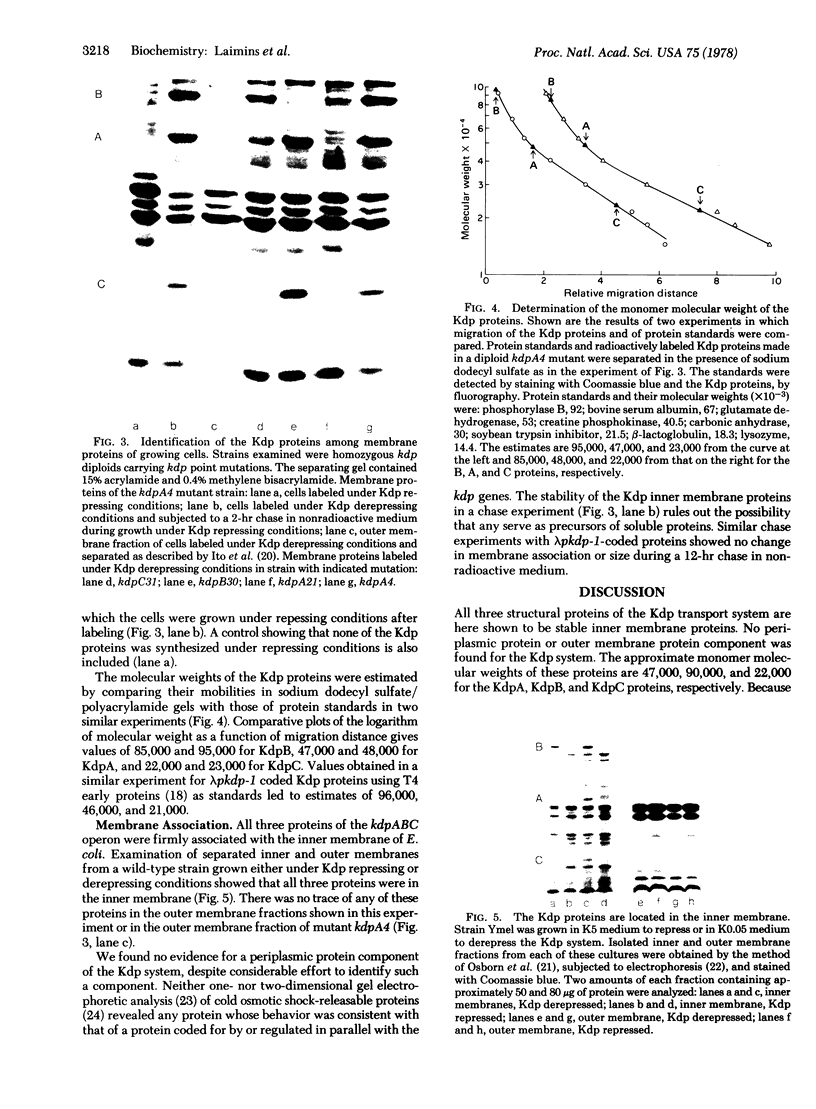
The three structural proteins of the ATP-driven Kdp potassium transport system of Escherichia coli [Rhoads, D. B., Waters, F. B. & Epstein, W. (1976) J. Gen. Physiol. 67, 325-341] have been identified and found to be located in the inner membrane. The high-affinity repressible Kdp system in one of four potassium transport systems in E. coli. The Kdp proteins were identified both in growing cells as well as in heavily UV-irradiated cells infected with transducing phages carrying the kdp operon. Although all previously identified ATP-driven transport systems of Gram-negative bacteria have been shown to contain a periplasmic protein component, no evidence was found for such a component or for an outer membrane component of the Kdp system. The molecular weights of the three inner membrane proteins, KdpA, KdpB, and KdpC, were determined to be 47,000, 90,000 and 22,000, respectively.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ames G. F., Lever J. Components of histidine transport: histidine-binding proteins and hisP protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Aug;66(4):1096–1103. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.4.1096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ames G. F., Spurich E. N. Protein-protein interaction in transport: periplasmic histidine-binding protein J interacts with P protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jun;73(6):1877–1881. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.6.1877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger E. A. Different mechanisms of energy coupling for the active transport of proline and glutamine in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 May;70(5):1514–1518. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.5.1514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger E. A., Heppel L. A. Different mechanisms of energy coupling for the shock-sensitive and shock-resistant amino acid permeases of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1974 Dec 25;249(24):7747–7755. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boos W. Bacterial transport. Annu Rev Biochem. 1974;43(0):123–146. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.43.070174.001011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boos W., Gordon A. S. Transport properties of the galactose-binding protein of Escherichia coli. Occurrence of two conformational states. J Biol Chem. 1971 Feb 10;246(3):621–628. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boos W., Hartig-Beecken I., Altendorf K. Purification and properties of a periplasmic protein related to sn-glycerol-3-phosphate transport in Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Feb;72(3):571–581. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11280.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowell J. L. Energetics of glycylglycine transport in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1974 Oct;120(1):139–146. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.1.139-146.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis S. J. Mechanism of energy coupling for transport of D-ribose in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1974 Oct;120(1):295–303. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.1.295-303.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein W., Davies M. Potassium-dependant mutants of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1970 Mar;101(3):836–843. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.3.836-843.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein W., Kim B. S. Potassium transport loci in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1971 Nov;108(2):639–644. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.2.639-644.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins B. E., Wagner H., Jr, smith T. W. Sodium- and potassium-activated adenosine triphosphatase of the nasal salt gland of the duck (Anas platyrhynchos). Purification, characterization, and NH2-terminal amino acid sequence of the phosphorylating polypeptide. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jul 25;251(14):4365–4371. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito K., Sato T., Yura T. Synthesis and assembly of the membrane proteins in E. coli. Cell. 1977 Jul;11(3):551–559. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90073-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jean D. H., Albers R. W., Koval G. J. Sodium-potassium-activated adenosine triphosphatase of electrophorus electric organ. X. Immunochemical properties of the Lubrol-solubilized enzume and its constituent polypeptides. J Biol Chem. 1975 Feb 10;250(3):1035–1040. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi H., Van Brunt J., Harold F. M. ATP-linked calcium transport in cells and membrane vesicles of Streptococcus faecalis. J Biol Chem. 1978 Apr 10;253(7):2085–2092. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugtenberg B., Meijers J., Peters R., van der Hoek P., van Alphen L. Electrophoretic resolution of the "major outer membrane protein" of Escherichia coli K12 into four bands. FEBS Lett. 1975 Oct 15;58(1):254–258. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80272-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McEntee K., Hesse J. E., Epstein W. Identification and radiochemical purification of the recA protein of Escherichia coli K-12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):3979–3983. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.3979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. Z., Gold L. M., Huang W. M. The identification of prereplicative bacteriophage T4 proteins. J Biol Chem. 1973 Aug 10;248(15):5499–5501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POST R. L., MERRITT C. R., KINSOLVING C. R., ALBRIGHT C. D. Membrane adenosine triphosphatase as a participant in the active transport of sodium and potassium in the human erythrocyte. J Biol Chem. 1960 Jun;235:1796–1802. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piperno J. R., Oxender D. L. Amino-acid-binding protein released from Escherichia coli by osmotic shock. J Biol Chem. 1966 Dec 10;241(23):5732–5734. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M. ISOLATION OF THE lambda PHAGE REPRESSOR. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Feb;57(2):306–313. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.2.306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhoads D. B., Epstein W. Energy coupling to net K+ transport in Escherichia coli K-12. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 25;252(4):1394–1401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhoads D. B., Waters F. B., Epstein W. Cation transport in Escherichia coli. VIII. Potassium transport mutants. J Gen Physiol. 1976 Mar;67(3):325–341. doi: 10.1085/jgp.67.3.325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins A. R., Rotman B. Evidence for binding protein-independent substrate translocation by the methylgalactoside transport system of Escherichia coli K12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Feb;72(2):423–427. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.2.423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simoni R. D., Postma P. W. The energetics of bacterial active transport. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:523–554. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.002515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West I. C., Mitchell P. Proton/sodium ion antiport in Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1974 Oct;144(1):87–90. doi: 10.1042/bj1440087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]