Abstract
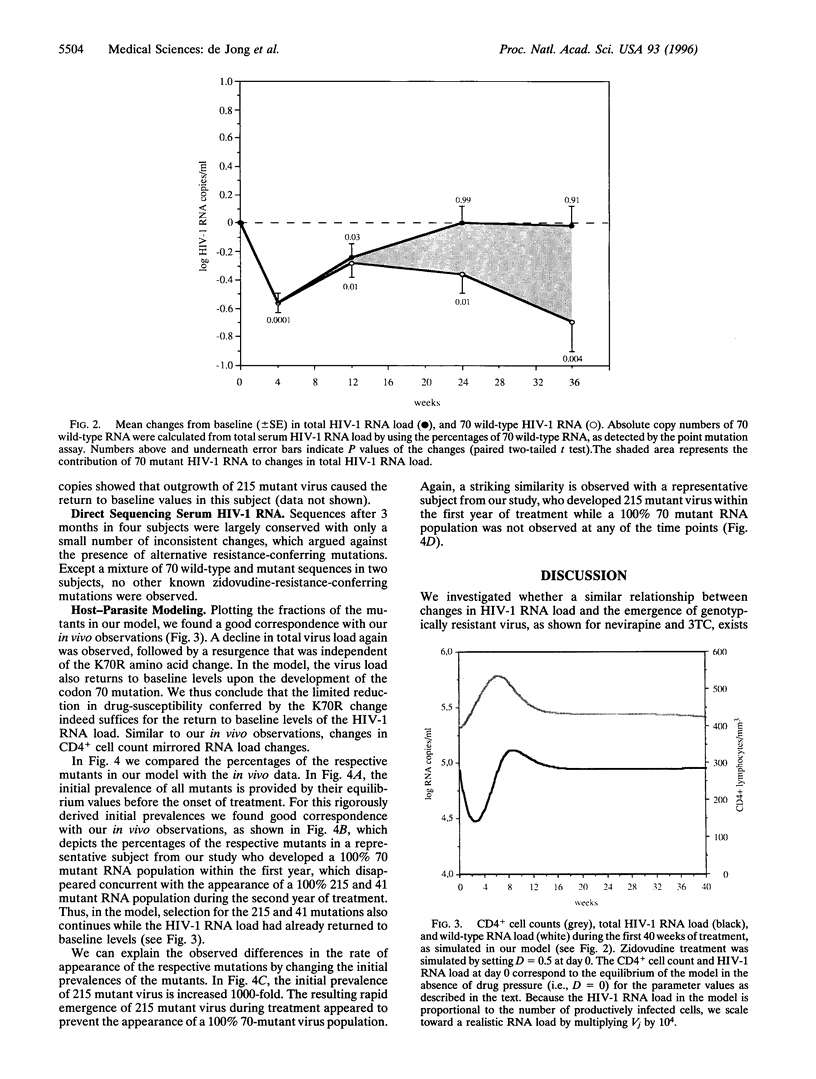
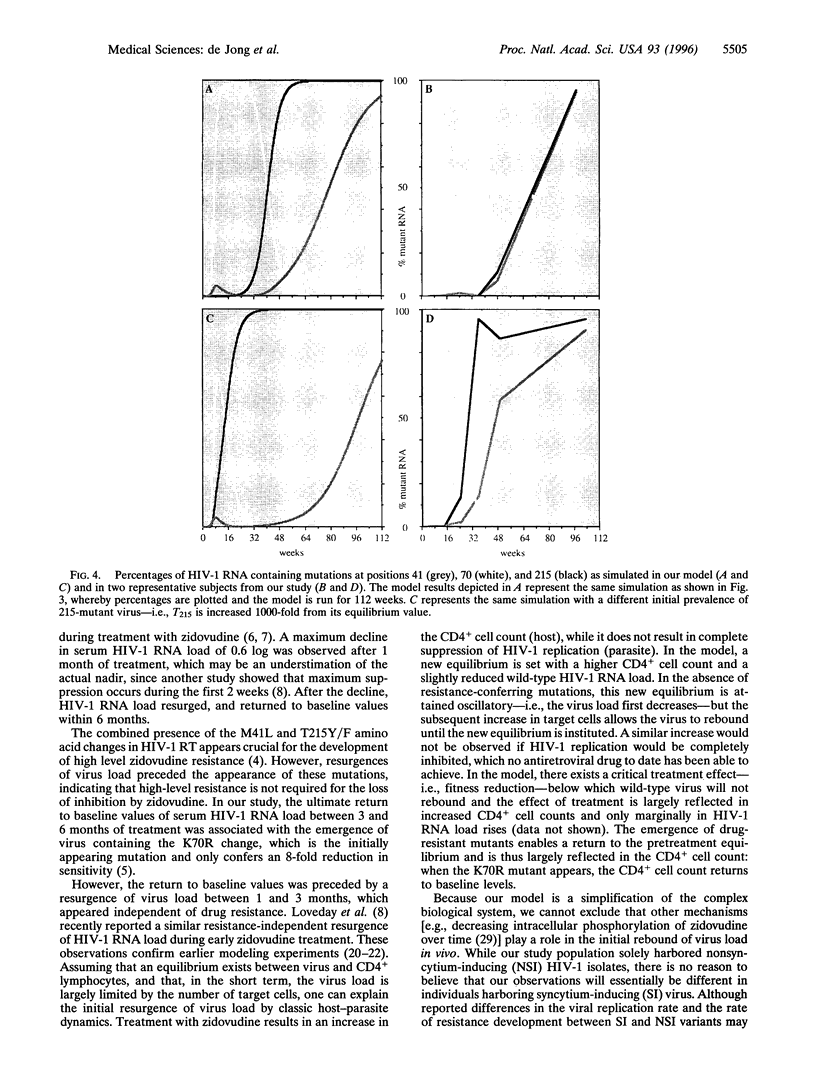
The association between human immunodeficiency virus type I (HIV-1) RNA load changes and the emergence of resistant virus variants was investigated in 24 HIV-1-infected asymptomatic persons during 2 years of treatment with zidovudine by sequentially measuring serum HIV-1 RNA load and the relative amounts of HIV-1 RNA containing mutations at reverse transcriptase (RT) codons 70 (K-->R), 41 (M-->L), and 215 (T-->Y/F). A mean maximum decline in RNA load occurred during the first month, followed by a resurgence between 1 and 3 months, which appeared independent of drug-resistance. Mathematical modeling suggests that this resurgence is caused by host-parasite dynamics, and thus reflects infection of the transiently increased numbers of CD4+ lymphocytes. Between 3 and 6 months of treatment, the RNA load returned to baseline values, which was associated with the emergence of virus containing a single lysine to arginine amino acid change at RT codon 70, only conferring an 8-fold reduction in susceptibility. Despite the relative loss of RNA load suppression, selection toward mutations at RT codons 215 and 41 continued. Identical patterns were observed in the mathematical model. While host-parasite dynamics and outgrowth of low-level resistant virus thus appear responsible for the loss of HIV-1 RNA load suppression, zidovudine continues to select for alternative mutations, conferring increasing levels of resistance.
Full text
PDF

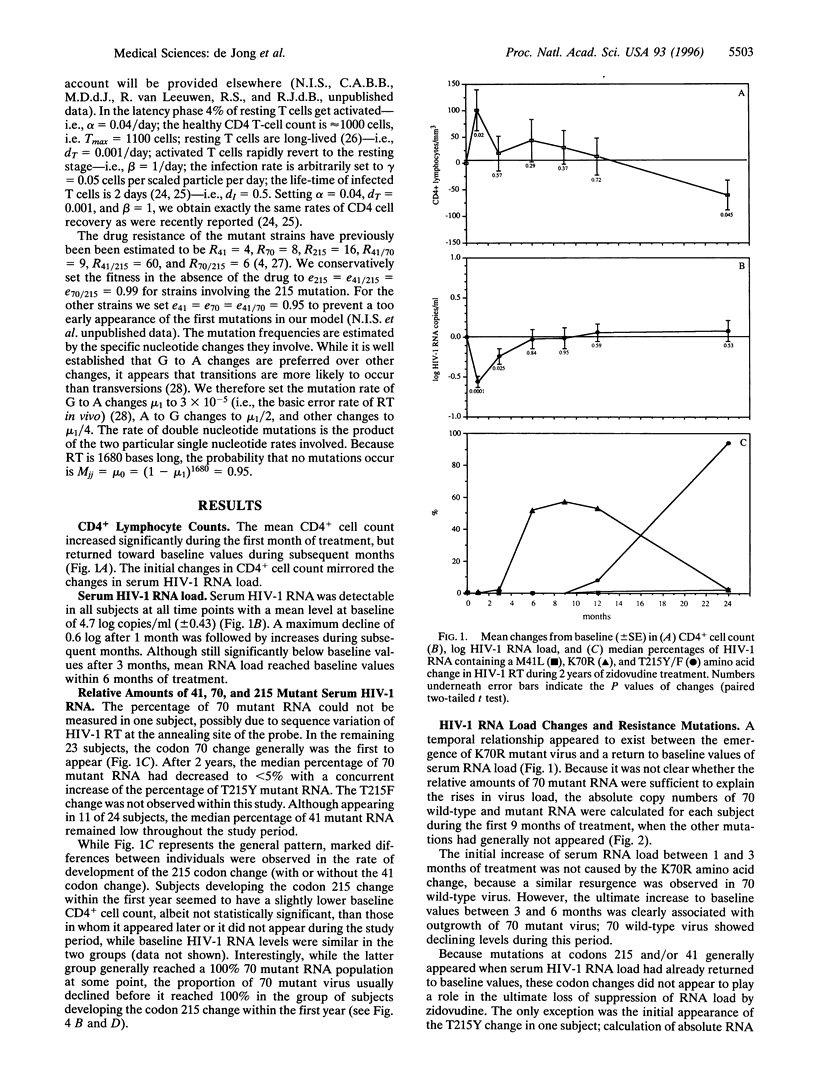

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boom R., Sol C. J., Salimans M. M., Jansen C. L., Wertheim-van Dillen P. M., van der Noordaa J. Rapid and simple method for purification of nucleic acids. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Mar;28(3):495–503. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.3.495-503.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boucher C. A., Lange J. M., Miedema F. F., Weverling G. J., Koot M., Mulder J. W., Goudsmit J., Kellam P., Larder B. A., Tersmette M. HIV-1 biological phenotype and the development of zidovudine resistance in relation to disease progression in asymptomatic individuals during treatment. AIDS. 1992 Nov;6(11):1259–1264. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199211000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boucher C. A., O'Sullivan E., Mulder J. W., Ramautarsing C., Kellam P., Darby G., Lange J. M., Goudsmit J., Larder B. A. Ordered appearance of zidovudine resistance mutations during treatment of 18 human immunodeficiency virus-positive subjects. J Infect Dis. 1992 Jan;165(1):105–110. doi: 10.1093/infdis/165.1.105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boucher C. A., Tersmette M., Lange J. M., Kellam P., de Goede R. E., Mulder J. W., Darby G., Goudsmit J., Larder B. A. Zidovudine sensitivity of human immunodeficiency viruses from high-risk, symptom-free individuals during therapy. Lancet. 1990 Sep 8;336(8715):585–590. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)93391-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bukrinsky M. I., Stanwick T. L., Dempsey M. P., Stevenson M. Quiescent T lymphocytes as an inducible virus reservoir in HIV-1 infection. Science. 1991 Oct 18;254(5030):423–427. doi: 10.1126/science.1925601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffin J. M. HIV population dynamics in vivo: implications for genetic variation, pathogenesis, and therapy. Science. 1995 Jan 27;267(5197):483–489. doi: 10.1126/science.7824947. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frost S. D., McLean A. R. Quasispecies dynamics and the emergence of drug resistance during zidovudine therapy of HIV infection. AIDS. 1994 Mar;8(3):323–332. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199403000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho D. D., Neumann A. U., Perelson A. S., Chen W., Leonard J. M., Markowitz M. Rapid turnover of plasma virions and CD4 lymphocytes in HIV-1 infection. Nature. 1995 Jan 12;373(6510):123–126. doi: 10.1038/373123a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaye S., Loveday C., Tedder R. S. A microtitre format point mutation assay: application to the detection of drug resistance in human immunodeficiency virus type-1 infected patients treated with zidovudine. J Med Virol. 1992 Aug;37(4):241–246. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890370402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellam P., Boucher C. A., Larder B. A. Fifth mutation in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase contributes to the development of high-level resistance to zidovudine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 1;89(5):1934–1938. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.5.1934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellam P., Boucher C. A., Tijnagel J. M., Larder B. A. Zidovudine treatment results in the selection of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 variants whose genotypes confer increasing levels of drug resistance. J Gen Virol. 1994 Feb;75(Pt 2):341–351. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-75-2-341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koot M., Schellekens P. T., Mulder J. W., Lange J. M., Roos M. T., Coutinho R. A., Tersmette M., Miedema F. Viral phenotype and T cell reactivity in human immunodeficiency virus type 1-infected asymptomatic men treated with zidovudine. J Infect Dis. 1993 Sep;168(3):733–736. doi: 10.1093/infdis/168.3.733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larder B. A., Darby G., Richman D. D. HIV with reduced sensitivity to zidovudine (AZT) isolated during prolonged therapy. Science. 1989 Mar 31;243(4899):1731–1734. doi: 10.1126/science.2467383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larder B. A., Kellam P., Kemp S. D. Zidovudine resistance predicted by direct detection of mutations in DNA from HIV-infected lymphocytes. AIDS. 1991 Feb;5(2):137–144. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199102000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larder B. A., Kemp S. D. Multiple mutations in HIV-1 reverse transcriptase confer high-level resistance to zidovudine (AZT). Science. 1989 Dec 1;246(4934):1155–1158. doi: 10.1126/science.2479983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loveday C., Kaye S., Tenant-Flowers M., Semple M., Ayliffe U., Weller I. V., Tedder R. S. HIV-1 RNA serum-load and resistant viral genotypes during early zidovudine therapy. Lancet. 1995 Apr 1;345(8953):820–824. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(95)92963-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansky L. M., Temin H. M. Lower in vivo mutation rate of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 than that predicted from the fidelity of purified reverse transcriptase. J Virol. 1995 Aug;69(8):5087–5094. doi: 10.1128/jvi.69.8.5087-5094.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean A. R., Emery V. C., Webster A., Griffiths P. D. Population dynamics of HIV within an individual after treatment with zidovudine. AIDS. 1991 May;5(5):485–489. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199105000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean A. R., Nowak M. A. Competition between zidovudine-sensitive and zidovudine-resistant strains of HIV. AIDS. 1992 Jan;6(1):71–79. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199201000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mclean A. R., Michie C. A. In vivo estimates of division and death rates of human T lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Apr 25;92(9):3707–3711. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.9.3707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulder J. W., Cooper D. A., Mathiesen L., Sandström E., Clumeck N., Gatell J. M., French M., Donovan B., Gray F., Yeo J. M. Zidovudine twice daily in asymptomatic subjects with HIV infection and a high risk of progression to AIDS: a randomized, double-blind placebo-controlled study. The European-Australian Collaborative Group (Study 017) AIDS. 1994 Mar;8(3):313–321. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199403000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulder J., McKinney N., Christopherson C., Sninsky J., Greenfield L., Kwok S. Rapid and simple PCR assay for quantitation of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 RNA in plasma: application to acute retroviral infection. J Clin Microbiol. 1994 Feb;32(2):292–300. doi: 10.1128/jcm.32.2.292-300.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nijhuis M., Boucher C. A., Schuurman R. Sensitive procedure for the amplification of HIV-1 RNA using a combined reverse-transcription and amplification reaction. Biotechniques. 1995 Aug;19(2):178-80, 182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richman D. D., Havlir D., Corbeil J., Looney D., Ignacio C., Spector S. A., Sullivan J., Cheeseman S., Barringer K., Pauletti D. Nevirapine resistance mutations of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 selected during therapy. J Virol. 1994 Mar;68(3):1660–1666. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.3.1660-1666.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richman D., Shih C. K., Lowy I., Rose J., Prodanovich P., Goff S., Griffin J. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 mutants resistant to nonnucleoside inhibitors of reverse transcriptase arise in tissue culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11241–11245. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roos M. T., Miedema F., Eeftinck Schattenkerk J. K., de Wolf F., Goudsmit J., Lange J. M., Danner S. A., Out T. A., Schellekens P. T. Cellular and humoral immunity in various cohorts of male homosexuals in relation to infection with human immunodeficiency virus. Neth J Med. 1989 Apr;34(3-4):132–141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuurman R., Keulen W. Modified protocol for DNA sequence analysis using Sequenase 2.0. Biotechniques. 1991 Feb;10(2):185–185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuurman R., Nijhuis M., van Leeuwen R., Schipper P., de Jong D., Collis P., Danner S. A., Mulder J., Loveday C., Christopherson C. Rapid changes in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 RNA load and appearance of drug-resistant virus populations in persons treated with lamivudine (3TC). J Infect Dis. 1995 Jun;171(6):1411–1419. doi: 10.1093/infdis/171.6.1411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stretcher B. N., Pesce A. J., Frame P. T., Stein D. S. Pharmacokinetics of zidovudine phosphorylation in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients infected with human immunodeficiency virus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1994 Jul;38(7):1541–1547. doi: 10.1128/aac.38.7.1541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tisdale M., Kemp S. D., Parry N. R., Larder B. A. Rapid in vitro selection of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 resistant to 3'-thiacytidine inhibitors due to a mutation in the YMDD region of reverse transcriptase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 15;90(12):5653–5656. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.12.5653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei X., Ghosh S. K., Taylor M. E., Johnson V. A., Emini E. A., Deutsch P., Lifson J. D., Bonhoeffer S., Nowak M. A., Hahn B. H. Viral dynamics in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection. Nature. 1995 Jan 12;373(6510):117–122. doi: 10.1038/373117a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Wolf F., Lange J. M., Goudsmit J., Cload P., de Gans J., Schellekens P. T., Coutinho R. A., Fiddian A. P., van der Noordaa J. Effect of zidovudine on serum human immunodeficiency virus antigen levels in symptom-free subjects. Lancet. 1988 Feb 20;1(8582):373–376. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)91179-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]