Abstract
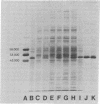
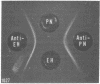
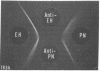
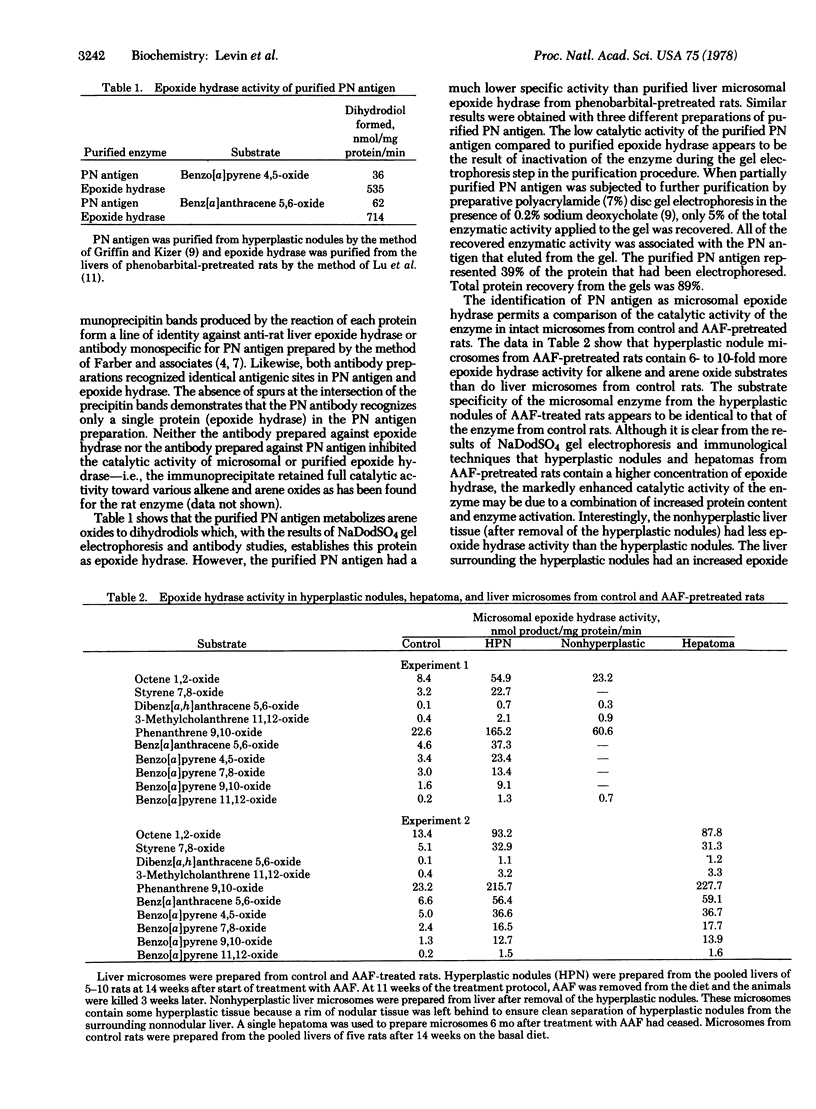
A liver microsomal protein, previously referred to as preneoplastic antigen, from hyperplastic nodules of rats fed a diet containing 2-acetylaminofluorene has been identified as the enzyme epoxide hydrase [glycol hydro-lyase (epoxideforming), EC 4.2.1.63]. Purified preneoplastic antigen from hyperplastic nodules and purified rat liver microsomal epoxide hydrase are immunochemically identical on the basis of Ouchterlony double-diffusion analysis. In addition, the purified proteins have identical minimum molecular weights in sodium dodecyl sulfate/polyacrylamide gels, and both proteins catalyze the hydration of arene oxides to dihydrodiols. Chronic feeding of 2-acetylaminofluorene to rats results in a 5- to 7-fold increase in epoxide hydrase activity in rat liver. The induced level of the enzyme is maintained in developing hyperplastic nodules and hepatomas but not in the nontumor tissue after removal of the carcinogen from the diet.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BERMAN C. Primary carcinoma of the liver. Adv Cancer Res. 1958;5:55–96. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60409-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron R., Sweeney G. D., Jones K., Lee G., Farber E. A relative deficiency of cytochrome P-450 and aryl hydrocarbon [benzo(a)pyrene] hydroxylase in hyperplastic nodules induced by 2-acetylaminofluorene in rat liver. Cancer Res. 1976 Nov;36(11 Pt 1):3888–3893. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conney A. H. Pharmacological implications of microsomal enzyme induction. Pharmacol Rev. 1967 Sep;19(3):317–366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein S. M., McNary J., Bartus B., Farber E. Chemical carcinogenesis: persistence of bound forms of 2-fluorenylacetamide. Science. 1968 Nov 22;162(3856):907–908. doi: 10.1126/science.162.3856.907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein S., Ito N., Merkow L., Farber E. Cellular analysis of liver carcinogenesis: the induction of large hyperplastic nodules in the liver with 2-fluorenylacetamide or ethionine and some aspects of their morphology and glycogen metabolism. Cancer Res. 1967 Sep;27(9):1702–1711. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin M. J., Kizer D. E. Purification and quantitation of preneoplastic antigen from hyperplastic nodules and normal liver. Cancer Res. 1978 Apr;38(4):1136–1141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higginson J., Svoboda D. J. Primary carcinoma of the liver as a pathologist's problem. Pathol Annu. 1970;5:61–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerina D. M., Daly J. W. Arene oxides: a new aspect of drug metabolism. Science. 1974 Aug 16;185(4151):573–582. doi: 10.1126/science.185.4151.573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerina D. M., Dansette P. M. Hepatic microsomal epoxide hydrase: a sensitive radiometric assay for hydration of arene oxides of carcinogenic aromatic hydrocarbons. Mol Pharmacol. 1977 Mar;13(2):342–351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin J. C., Hiasa Y., Farber E. Preneoplastic antigen as a marker for endoplasmic reticulum of putative premalignant hepatocytes during liver carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 1977 Jul;37(7 Pt 1):1972–1981. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu A. Y., Ryan D., Jerina D. M., Daly J. W., Levin W. Liver microsomal expoxide hydrase. Solubilization, purification, and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1975 Oct 25;250(20):8283–8288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEDES G., FRIEDMANN B., WEINHOUSE S. Fatty acid metabolism. VIII. Acetate metabolism in vitro during hepatocarcinogenesis by p-dimethylaminoazobenzene. Cancer Res. 1956 Jan;16(1):57–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. A. Carcinogenesis by chemicals: an overview--G. H. A. Clowes memorial lecture. Cancer Res. 1970 Mar;30(3):559–576. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyake Y., Gaylor J. L., Morris H. P. Abnormal microsomal cytochromes and electron transport in Morris hepatomas. J Biol Chem. 1974 Mar 25;249(6):1980–1987. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okita K., Kligman L. H., Farber E. A new common marker for premalignant and malignant hepatocytes induced in the rat by chemical carcinogens. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1975 Jan;54(1):199–202. doi: 10.1093/jnci/54.1.199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saine S. E., Strobel H. W. Drug metabolism in liver tumors. Resolution of components and reconstitution of activity. Mol Pharmacol. 1976 Jul;12(4):649–657. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sims P., Grover P. L. Epoxides in polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon metabolism and carcinogenesis. Adv Cancer Res. 1974;20:165–274. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60111-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]