Abstract
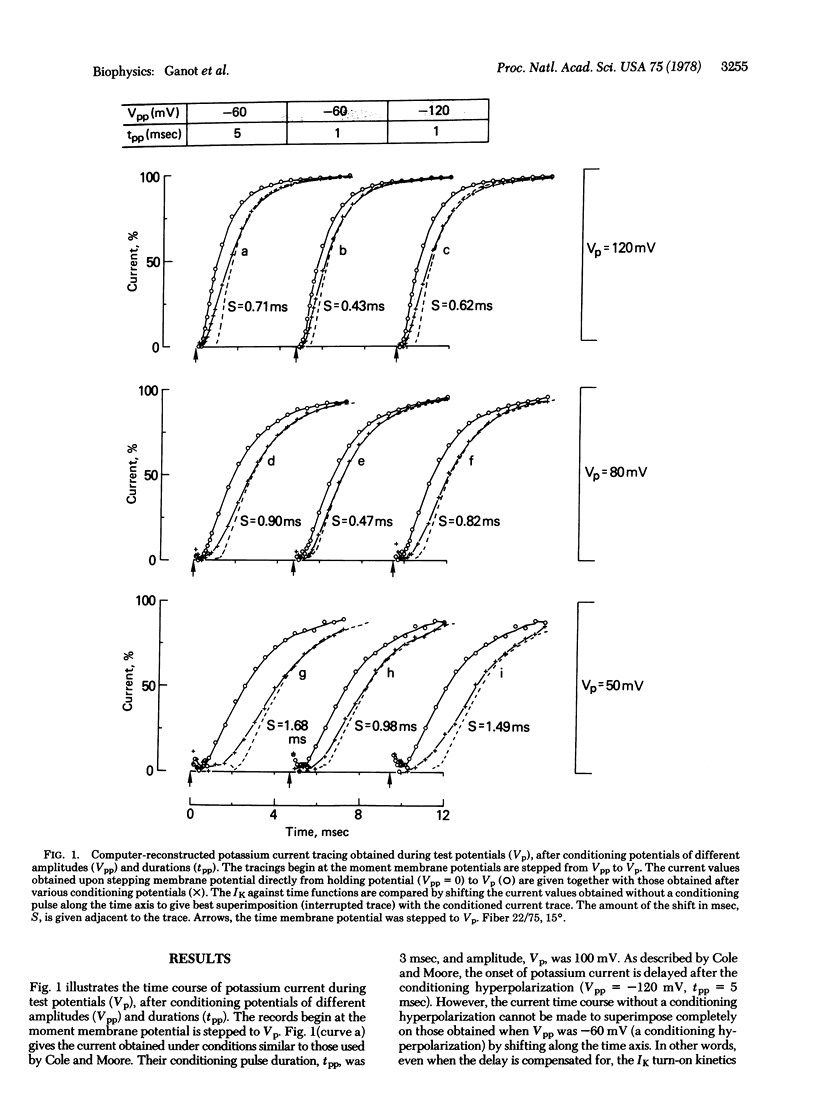
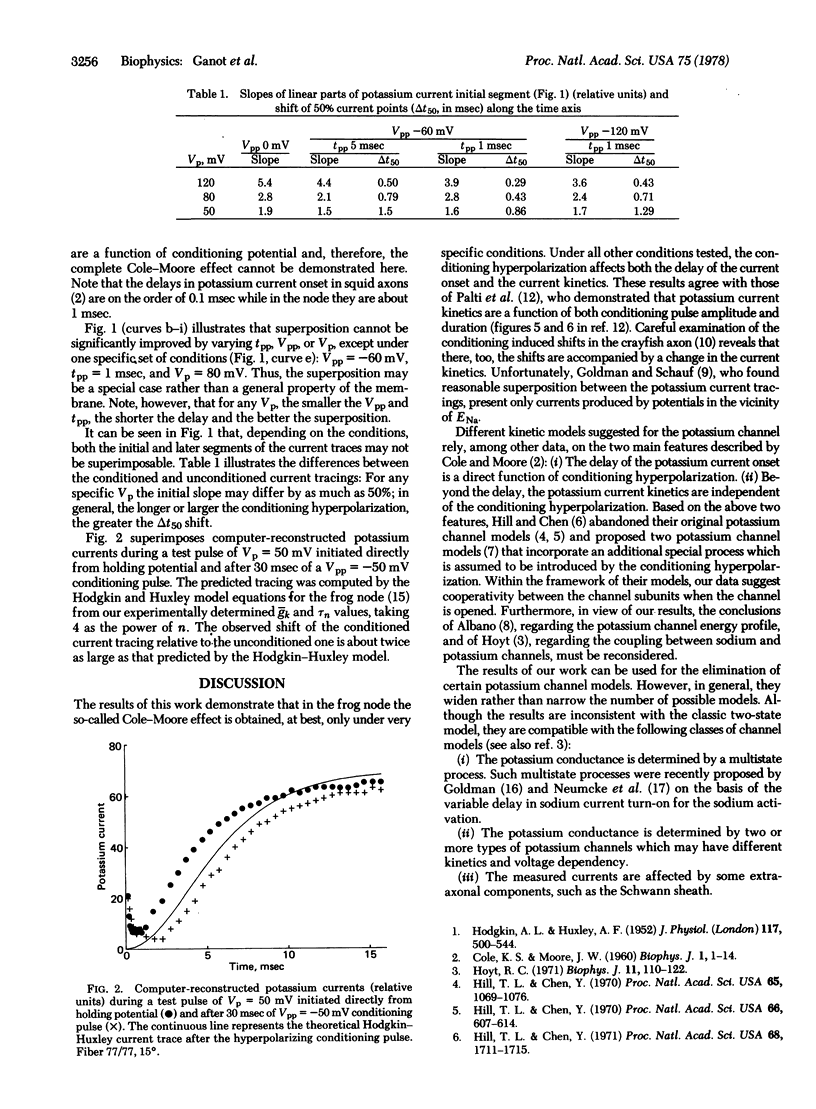
Potassium currents were recorded from the voltage-clamped frog node (Rana esculenta) during various test pulses that followed hyperpolarizing prepulses of different amplitudes and durations. Both the delay in potassium current onset and the shape of the current trace as a function of time were found to be a function of prepulse parameters. This finding is different from the current trace superposition described by Cole and Moore for a specific test pulse, sodium equilibrium potential in the squid giant axon. The Cole-Moore effect, which was found here only under a specific set of conditions, thus may be a special case rather than the general property of the membrane. The implication of these findings to the various excitable membrane potassium channel models, which are based on the Cole-Moore effect, is discussed.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albano A. M. Cole-Moore superposition and kinetic models for the potassium conductance of nerve fiber membranes. J Theor Biol. 1974 May;45(1):275–282. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(74)90055-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLE K. S., MOORE J. W. Potassium ion current in the squid giant axon: dynamic characteristic. Biophys J. 1960 Sep;1:1–14. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(60)86871-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman L. Kinetics of channel gating in excitable membranes. Q Rev Biophys. 1976 Nov;9(4):491–526. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500002651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman L., Schauf C. L. Quantitative description of sodium and potassium currents and computed action potentials in Myxicola giant axons. J Gen Physiol. 1973 Mar;61(3):361–384. doi: 10.1085/jgp.61.3.361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J Physiol. 1952 Aug;117(4):500–544. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill T. L., Chen Y. D. On the theory of ion transport across the nerve membrane. II. Potassium ion kinetics and cooperativity (with x = 4). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Aug;68(8):1711–1715. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.8.1711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill T. L., Chen Y. D. On the theory of ion transport across the nerve membrane. V. Two models for the Cole-Moore K + hyperpolarization delay. Biophys J. 1972 Aug;12(8):960–976. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(72)86137-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill T. L., Chen Y. Cooperative effects in models of steady-state transport across membranes. 3. Simulation of potassium ion transport in nerve. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jul;66(3):607–614. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.3.607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill T. L., Chen Y. Cooperative effects in models of steady-state transport across membranes. I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Apr;65(4):1069–1076. doi: 10.1073/pnas.65.4.1069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyt R. C. Independence of the sodium and potassium conductance channels. A kinetic argument. Biophys J. 1971 Jan;11(1):110–122. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(71)86199-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore L. E. Effect of temperature and calcium ions on rate constants of myelinated nerve. Am J Physiol. 1971 Jul;221(1):131–137. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.221.1.131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neumcke B., Nonner W., Stämpfli R. Asymmetrical displacement current and its relation with the activation of sodium current in the membrane of frog myelinated nerve. Pflugers Arch. 1976 Jun 22;363(3):193–203. doi: 10.1007/BF00594601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonner W., Rojas E., Stämpfli H. Displacement currents in the node of Ranvier. Voltage and time dependence. Pflugers Arch. 1975;354(1):1–18. doi: 10.1007/BF00584499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palti Y., Ganot G., Stämpfli R. Effect of conditioning potential on potassium current kinetics in the frog node. Biophys J. 1976 Mar;16(3):261–273. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(76)85686-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shrager P. Ionic conductance changes in voltage clamped crayfish axons at low pH. J Gen Physiol. 1974 Dec;64(6):666–690. doi: 10.1085/jgp.64.6.666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


