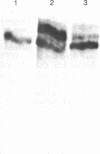
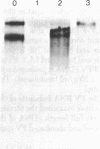
Abstract
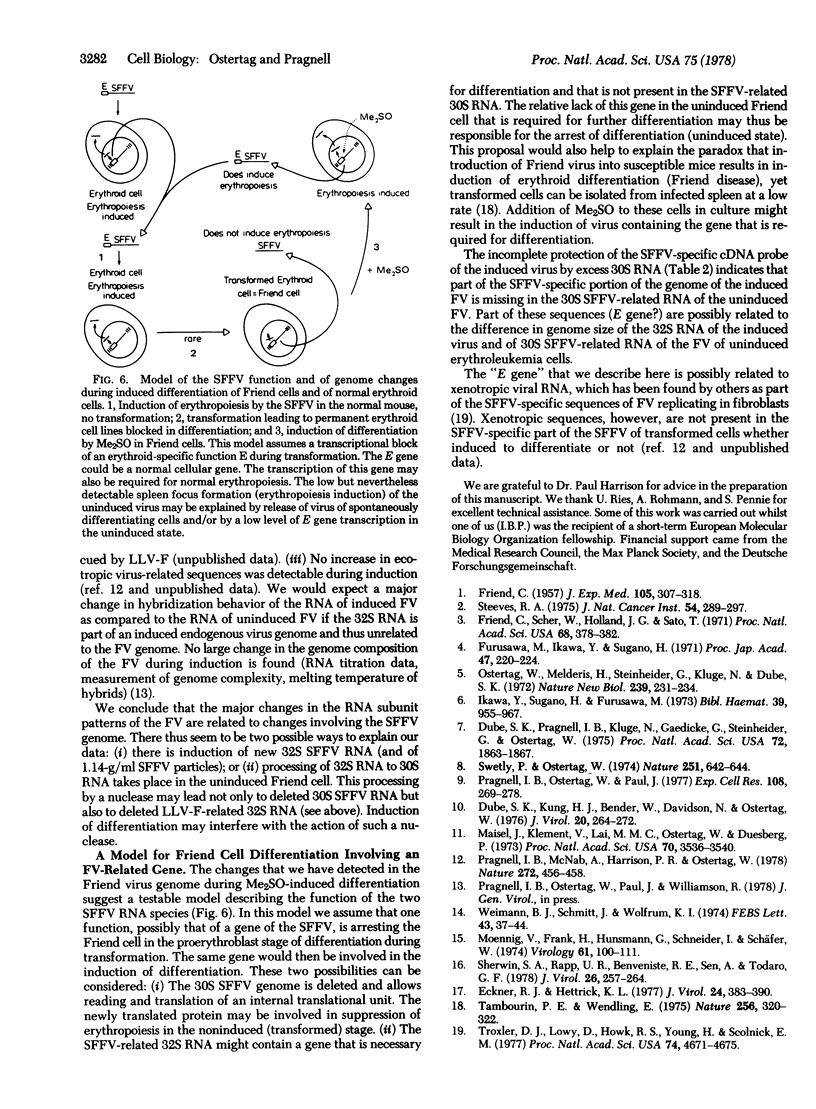
The Friend spleen focus-forming virus (SFFV) complex released by Friend virus-transformed erythroid cells has been analyzed with respect to changes in the genome composition that may occur during induction of erythropoiesis with dimethyl sulfoxide. It is shown that: (a) There are three types of virus particles, one with buoyant density 1.20 g/ml, one with density 1.17 g/ml (the density of the cloned lymphatic leukemia virus helper component of the complex), and a major fraction that has a density of 1.14 g/ml. (b) Three RNA subunits-35S, 32S, and 30S-have previously been shown to be detectable in the Friend virus complex. The 1.20-g/ml particles contain only 30S RNA, whilst the 1.14- to 1.17-g/ml particles contain a mixture consisting of predominantly 30S and 32S RNA and about 5-10% 35S RNA. (c) Induction of differentiation results in an increase in the 1.14-g/ml particles and 32S RNA. The amount of 30S RNA does not change. (d) Hybridization of the different genomic viral RNAs with full-length virus cDNA shows that the 30S RNA (of induced and uninduced Friend virus) is more closely related to the 32S RNA of the induced Friend virus than to the 32S RNA of the constitutively released Friend virus. (e) The 30S RNA contains SFFV-specific sequences. (f) A hypothesis is presented in which the induction of the new 32S RNA species is related to the increase of SFFV activity and to a specific function of the SFFV during induction of erythropoiesis.
Keywords: Friend cells, spleen focus-forming virus, erythropoiesis, erythroid transformation
Full text
PDF
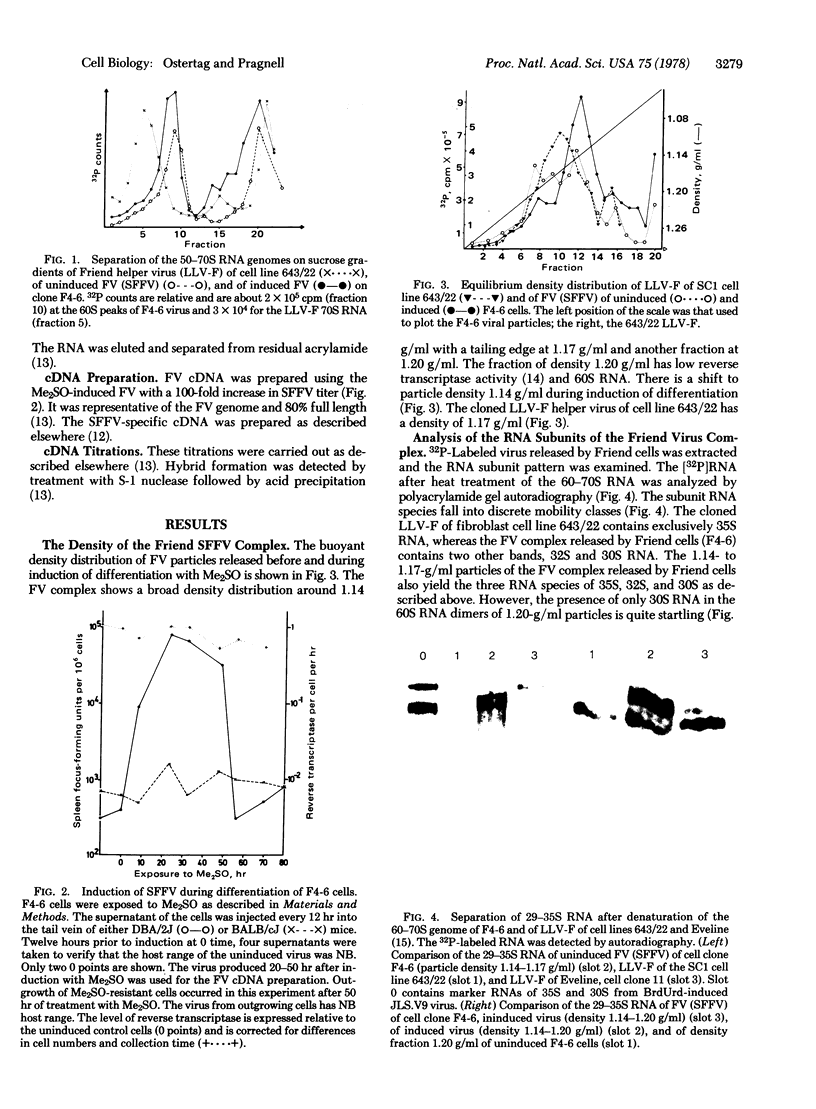

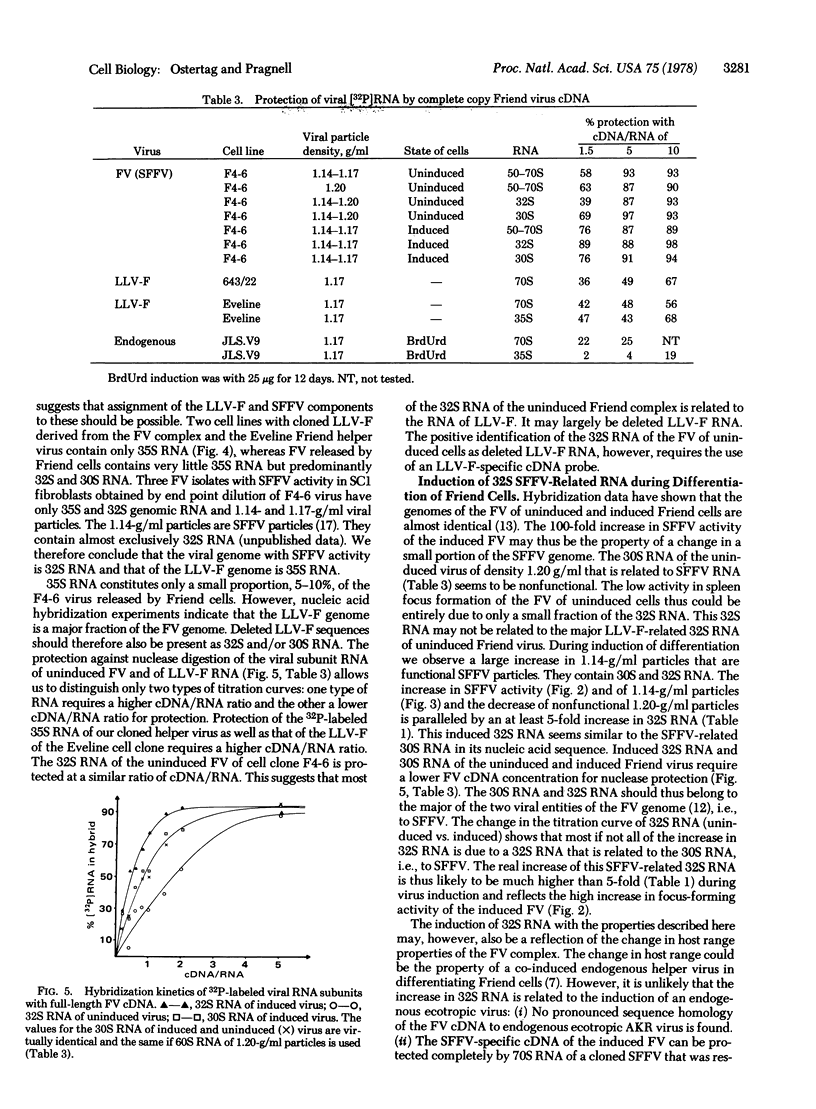
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dube S. K., Pragnell I. B., Kluge N., Gaedicke G., Steinheider G., Ostertag W. Induction of endogenous and of spleen focus-forming viruses during dimethylsulfoxide-induced differentiation of mouse erythroleukemia cells transformed by spleen focus-forming virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 May;72(5):1863–1867. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.5.1863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dube S., Kung H. J., Bender W., Davidson N., Ostertag W. Size, subunit composition, and secondary structure of the Friend virus genome. J Virol. 1976 Oct;20(1):264–272. doi: 10.1128/jvi.20.1.264-272.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckner R. J., Hettrick K. L. Defective Friend spleen focus-forming virus: interfering properties and isolation free from standard leukemia-inducing helper virus. J Virol. 1977 Oct;24(1):383–396. doi: 10.1128/jvi.24.1.383-396.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRIEND C. Cell-free transmission in adult Swiss mice of a disease having the character of a leukemia. J Exp Med. 1957 Apr 1;105(4):307–318. doi: 10.1084/jem.105.4.307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friend C., Scher W., Holland J. G., Sato T. Hemoglobin synthesis in murine virus-induced leukemic cells in vitro: stimulation of erythroid differentiation by dimethyl sulfoxide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Feb;68(2):378–382. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.2.378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikawa Y., Furusawa M., Sugano H. Erythrocyte membrane-specific antigens in Friend virus-induced leukemia cells. Bibl Haematol. 1973;39:955–967. doi: 10.1159/000427928. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maisel J., Klement V., Lai M. M., Ostertag W., Duesberg P. Ribonucleic acid components of murine sarcoma and leukemia viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3536–3540. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moennig V., Frank H., Hunsmann G., Schneider I., Schafer W. Properties of mouse leukemia viruses. VII. The major viral glycoprotein of friend leukemia virus. Isolation and physicochemical properties. Virology. 1974 Sep;61(1):100–111. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90245-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostertag W., Melderis H., Steinheider G., Kluge N., Dube S. Synthesis of mouse haemoglobin and globin mRNA in leukaemic cell cultures. Nat New Biol. 1972 Oct 25;239(95):231–234. doi: 10.1038/newbio239231a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pragnell I. B., McNab A., Harrison P. R., Osterag W. Are spleen focus-forming virus sequences related to xenotropic viruses and expressed specifically in normal erythroid cells? Nature. 1978 Mar 30;272(5652):456–458. doi: 10.1038/272456a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pragnell I. B., Ostertag W., Paul J. The expression of viral and globin genes during differentiation of the Friend cell. Exp Cell Res. 1977 Sep;108(2):269–278. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4827(77)80034-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherwin S. A., Rapp U. R., Benveniste R. E., Sen A., Todaro G. J. Rescue of endogenous 30S retroviral sequences from mouse cells by baboon type C virus. J Virol. 1978 May;26(2):257–264. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.2.257-264.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steeves R. A. Editorial: Spleen focus-forming virus in Friend and Rauscher leukemia virus preparations. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1975 Feb;54(2):289–297. doi: 10.1093/jnci/54.2.289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swetly P., Ostertag W. Friend virus release and induction of haemoglobin synthesis in erythroleukaemic cells respond differently to interferon. Nature. 1974 Oct 18;251(5476):642–644. doi: 10.1038/251642a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tambourin P. E., Wendling F. Target cell for oncogenic action of polycythaemia-inducing Friend virus. Nature. 1975 Jul 24;256(5515):320–322. doi: 10.1038/256320a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troxler D. H., Lowy D., Howk R., Young H., Scolnick E. M. Friend strain of spleen focus-forming virus is a recombinant between ecotropic murine type C virus and the env gene region of xenotropic type C virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4671–4675. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weimann B. J., Schmidt J., Wolfrum D. I. RNA-dependent DNA polymerase and ribonuclease H from Friend virions. FEBS Lett. 1974 Jul 1;43(1):37–44. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)81100-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]