Abstract
Cells (Chinese hamster ovary) in G1 phase were fused with cells in late S phase to determine if a cell in late S phase can induce DNA synthesis in the nucleus of a G1 cell and, if so, to determine if the DNA synthesis so induced in a G1 phase nucleus has an autoradiographic pattern characteristic of early or of late S phase synthesis. The results indicate (i) that 89% of the G1 nuclei in late-S/G1 binucleates synthesized DNA, while only 2% of the control unfused G1 cells synthesized DNA, and (ii) that in all late-S/G1 binucleates the G1 nucleus was induced to synthesize early S phase DNA. These results are compatible with the idea that a cytoplasmically transmissible factor initiates DNA synthesis but that an intranuclear mechanism defines the temporal order of replication.
Full text
PDF
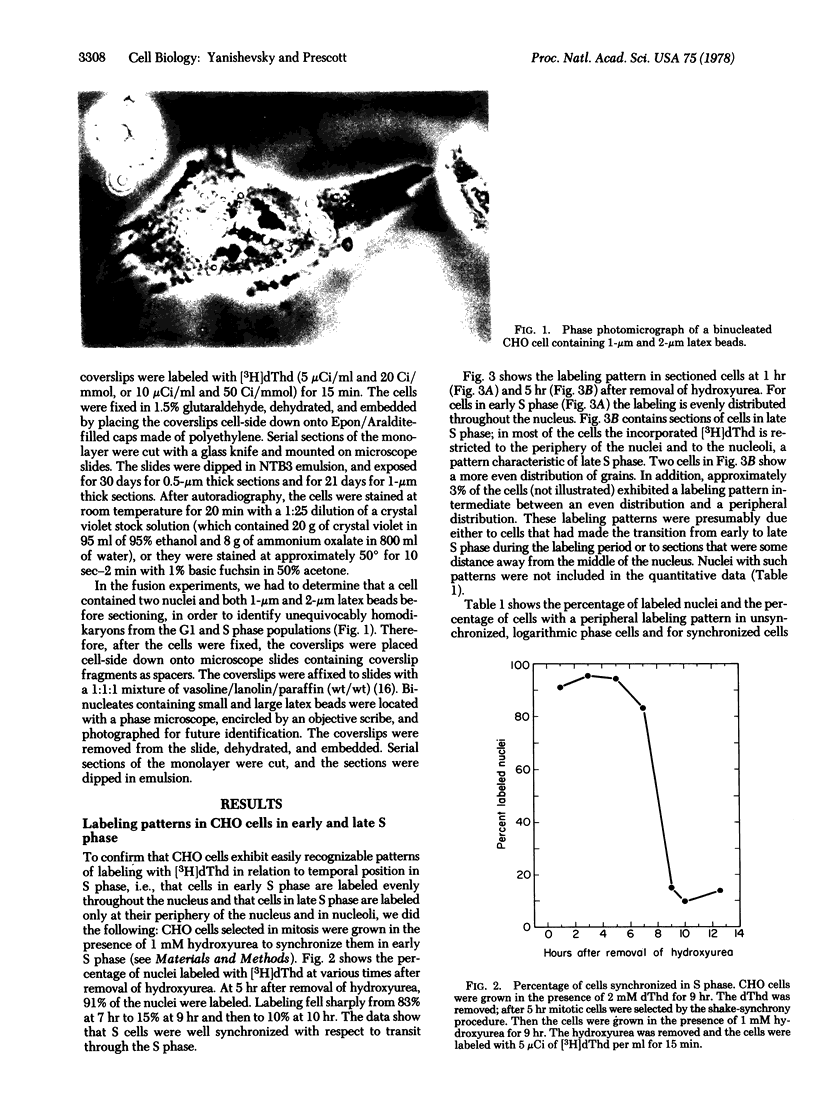


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOOTSMA D., BUDKE L., VOS O. STUDIES ON SYNCHRONOUS DIVISION OF TISSUE CULTURE CELLS INITIATED BY EXCESS THYMIDINE. Exp Cell Res. 1964 Jan;33:301–309. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4827(64)81035-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bostock C. J., Prescott D. M., Kirkpatrick J. B. An evaluation of the double thymidine block for synchronizing mammalian cells at the G1-S border. Exp Cell Res. 1971 Sep;68(1):163–168. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(71)90599-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun R., Mittermayer C., Rusch H. P. Sequential temporal replication of DNA in Physarum polycephalum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 May;53(5):924–931. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.5.924. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun R., Wili H. Time sequence of DNA replication in Physarum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Jan 21;174(1):246–252. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(69)90248-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S. W. Heterochromatin. Science. 1966 Jan 28;151(3709):417–425. doi: 10.1126/science.151.3709.417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon S., Cohn Z. Macrophage-melanoma cell heterokaryons. 3. The activation of macrophage DNA synthesis. Studies with inhibitors of protein synthesis and with synchronized melanoma cells. J Exp Med. 1971 Oct 1;134(4):935–946. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.4.935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goto S., Ringertz N. R. Preparation and characterization of chick erythrocyte nuclei from heterokaryons. Exp Cell Res. 1974 Mar 30;85(1):173–181. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(74)90228-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves J. A. Cell cycles and chromosome replication patterns in interspecific somatic hybrids. Exp Cell Res. 1972 Jul;73(1):81–94. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(72)90104-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves J. A. DNA synthesis in heterokaryons formed by fusion of mammalian cells from different species. Exp Cell Res. 1972 Jun;72(2):393–403. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(72)90007-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill R. N., Yunis J. J. Mammalian X-chromosomes: change in patterns of DNA replication during embryogenesis. Science. 1967 Mar 3;155(3766):1120–1121. doi: 10.1126/science.155.3766.1120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hori T. A., Lark K. G. Autoradiographic studies of the replication of satellite DNA in the kangaroo rat. Autoradiographs of satellite DNA. J Mol Biol. 1974 Sep 5;88(1):221–232. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90306-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. T., Mullinger A. M. The induction of DNA synthesis in the chick red cell nucleus in heterokaryons during the first cell cycle after fusion with HeLa cells. J Cell Sci. 1975 Aug;18(3):455–490. doi: 10.1242/jcs.18.3.455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin M. S., Davidson R. L. Replication of human chromosomes in human-mouse hybrids: evidence that the timing of DNA synthesis is determined independently in each human chromosome. Somatic Cell Genet. 1975 Jan;1(1):111–122. doi: 10.1007/BF01538735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liskay R. M. Genetic analysis of a Chinese hamster cell line lacking a G1 phase. Exp Cell Res. 1978 Jun;114(1):69–77. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(78)90037-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marin G., Colletta G. Patterns of late chromosomal DNA replication in unbalanced Chinese hamster-mouse somatic cell hybrids. Exp Cell Res. 1974 Dec;89(2):368–376. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(74)90802-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin R. G., Chou J. Y., Avila J., Saral R. The semiautonomous replicon: a molecular model for the oncogenicity of SV40. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 1):17–24. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller G. C., Kajiwara K. Early- and late-replicating deoxyribonucleic acid complexes in HeLa nuclei. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Jan 18;114(1):108–115. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(66)90258-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muldoon J. J., Evans T. E., Nygaard O. F., Evans H. H. Control of DNA replication by protein synthesis at defined times during the S period in Physarum polycephalum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Oct 14;247(2):310–321. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(71)90679-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ockey C. H., Allen T. D. Distribution of DNA or DNA synthesis in mammalian cells following inhibition with hydroxyurea and 5-fluorodeoxyuridine. Exp Cell Res. 1975 Jul;93(2):275–282. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(75)90451-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plaut W. On ordered DNA replication in polytene chromosomes. Genetics. 1969;61(1 Suppl):239–244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao P. N., Johnson R. T. Mammalian cell fusion: studies on the regulation of DNA synthesis and mitosis. Nature. 1970 Jan 10;225(5228):159–164. doi: 10.1038/225159a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid W., Leppert M. F. Rates of DNA synthesis in heterochromatic and euchromatic segments of the chromosome complements of two rodents. Cytogenetics. 1969;8(2):125–135. doi: 10.1159/000130029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinclair W. K. Hydroxyurea: differential lethal effects on cultured mammalian cells during the cell cycle. Science. 1965 Dec 24;150(3704):1729–1731. doi: 10.1126/science.150.3704.1729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder J. A., McIntosh J. R. Initiation and growth of microtubules from mitotic centers in lysed mammalian cells. J Cell Biol. 1975 Dec;67(3):744–760. doi: 10.1083/jcb.67.3.744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonnenschein C. Somatic cell hybridization: pattern of chromosome replication in viable Chinese hamster x Armenian hamster hybrids. Exp Cell Res. 1970 Nov;63(1):195–199. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(70)90349-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAYLOR J. H. Asynchronous duplication of chromosomes in cultured cells of Chinese hamster. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1960 Jun;7:455–464. doi: 10.1083/jcb.7.3.455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TERASIMA T., TOLMACH L. J. Growth and nucleic acid synthesis in synchronously dividing populations of HeLa cells. Exp Cell Res. 1963 Apr;30:344–362. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(63)90306-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veomett G., Prescott D. M., Shay J., Porter K. R. Reconstruction of mammalian cells from nuclear and cytoplasmic components separated by treatment with cytochalasin B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 May;71(5):1999–2002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.5.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walters R. A., Tobey R. A., Hildebrand C. E. Hydroxyurea does not prevent synchronized G1 chinese hamster cells from entering the DNA synthetic period. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Mar 8;69(1):212–217. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(76)80294-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wille J. J., Jr, Kauffman S. A. Premature replication of late S period DNA regions in early S nuclei transferred to late S cytoplasm by fusion in Physarum polycephalum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Oct 1;407(2):158–173. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(75)90282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams C. A., Ockey C. H. Distribution of DNA replicator sites in mammalian nuclei after different methods of cell synchronization. Exp Cell Res. 1970 Dec;63(2):365–372. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(70)90224-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- XEROS N. Deoxyriboside control and synchronization of mitosis. Nature. 1962 May 19;194:682–683. doi: 10.1038/194682a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]