Abstract
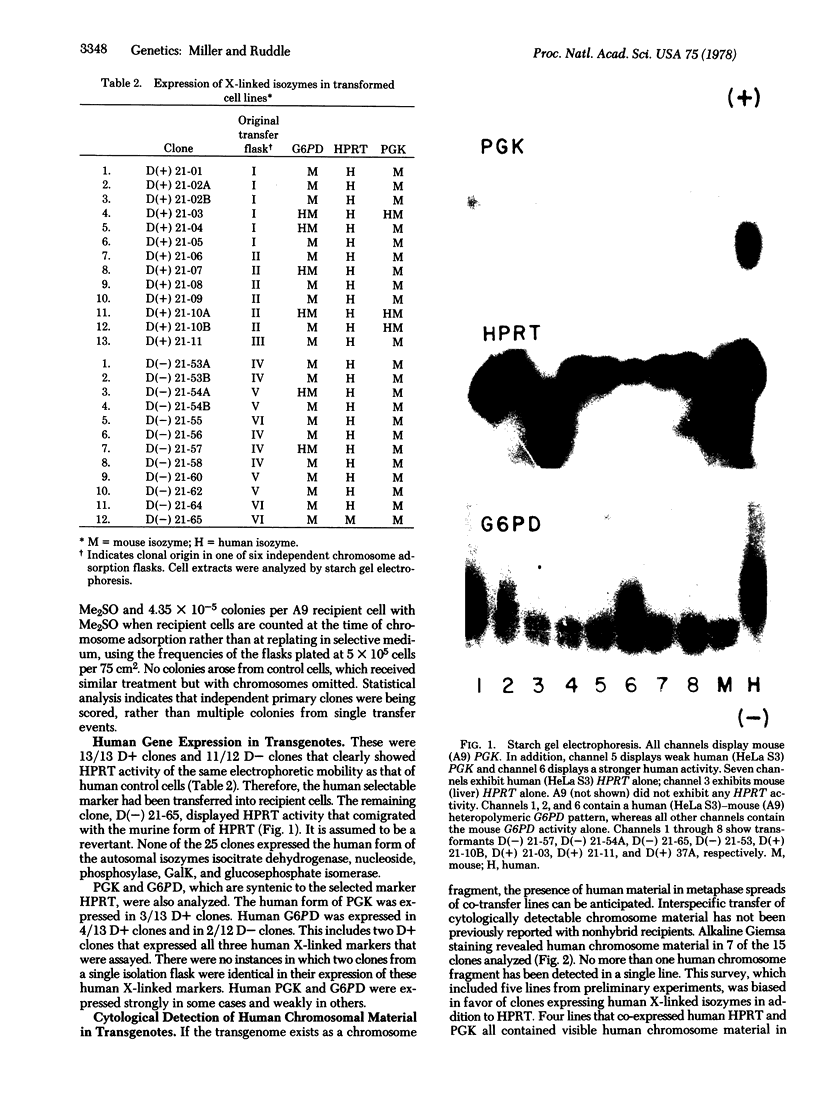
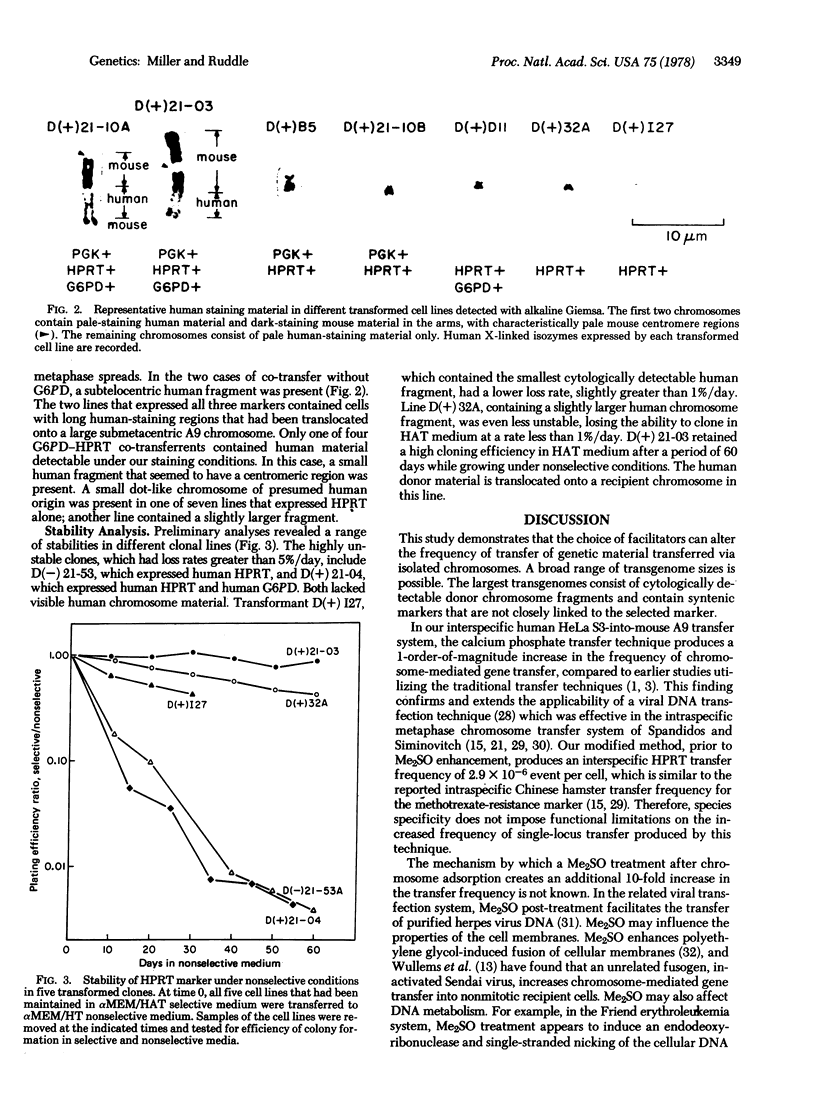
Transformation frequencies of 4 × 10-5 were obtained in chromosome-mediated gene transfer experiments using human cell line HeLa S3 as donor and mouse cell line A9 as recipient. This high frequency of interspecific transformation was achieved by treating the recipient cells with dimethylsulfoxide in addition to other facilitators. The high frequency of transformation correlated positively with transgenome size on the basis of both co-transfer of linked markers and chromosome analysis. The syntenic human markers glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (D-glucose-6-phosphate:NADP+ 1-oxidoreductase, EC 1.1.1.49) and phosphoglycerate kinase (ATP:3-phospho-D-glycerate 1-phosphotransferase, EC 2.7.2.3) were sometimes transferred together with the selected X-linked prototrophic marker hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase (IMP: pyrophosphate phosphoribosyltransferase, EC 2.4.2.8) into murine somatic cells. Donor human chromosome material could be demonstrated cytologically in some of the transformed cell lines. Transformants exhibited various rates of loss of the human hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase marker when grown under nonselective conditions. These results reveal a broader range of possible interspecific transgenome sizes than has been recognized in the past. The largest transgenomes consist of cytologically detectable donor fragments and contain syntenic markers that are not closely linked to the selected marker.
Keywords: gene transfer, dimethyl sulfoxide, somatic cell genetics, gene mapping
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Athwal R. S., McBride O. W. Serial transfer of a human gene to rodent cells by sequential chromosome-mediated gene transfer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):2943–2947. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.2943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burch J. W., McBride O. W. Human gene expression in rodent cells after uptake of isolated metaphase chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 May;72(5):1797–1801. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.5.1797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Degnen G. E., Miller I. L., Eisenstadt J. M., Adelberg E. A. Chromosome-mediated gene transfer between closely realted strains of cultured mouse cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Aug;73(8):2838–2842. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.8.2838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fournier R. E., Ruddle F. H. Stable association of the human transgenome and host murine chromosomes demonstrated with trispecific microcell hybrids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3937–3941. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friend K. K., Dorman B. P., Kucherlapati R. S., Ruddle F. H. Detection of interspecific translocations in mouse-human hybrids by alkaline Giemsa staining. Exp Cell Res. 1976 Apr;99(1):31–36. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(76)90676-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goss S. J., Harris H. Gene transfer by means of cell fusion I. Statistical mapping of the human X-chromosome by analysis of radiation-induced gene segregation. J Cell Sci. 1977 Jun;25:17–37. doi: 10.1242/jcs.25.1.17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goss S. J., Harris H. New method for mapping genes in human chromosomes. Nature. 1975 Jun 26;255(5511):680–684. doi: 10.1038/255680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LITTLEFIELD J. W. SELECTION OF HYBRIDS FROM MATINGS OF FIBROBLASTS IN VITRO AND THEIR PRESUMED RECOMBINANTS. Science. 1964 Aug 14;145(3633):709–710. doi: 10.1126/science.145.3633.709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Littlefield J. W. The use of drug-resistant markers to study the hybridization of mouse fibroblasts. Exp Cell Res. 1966 Jan;41(1):190–196. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(66)90558-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBride O. W., Athwal R. S. Genetic analysis by chromosome-mediated gene transfer. In Vitro. 1976 Nov;12(11):777–786. doi: 10.1007/BF02835452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBride O. W., Burch J. W., Ruddle F. H. Cotransfer of thymidine kinase and galactokinase genes by chromosome-mediated gene transfer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Feb;75(2):914–918. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.2.914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBride O. W., Ozer H. L. Transfer of genetic information by purified metaphase chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Apr;70(4):1258–1262. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.4.1258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBride O., Athwal R. S. Chromosome-mediated gene transfer with resultant expression and integration of the transferred genes in eukaryotic cells. Brookhaven Symp Biol. 1977 May 12;(29):116–126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKusick V. A., Ruddle F. H. The status of the gene map of the human chromosomes. Science. 1977 Apr 22;196(4288):390–405. doi: 10.1126/science.850784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols E. A., Ruddle F. H. A review of enzyme polymorphism, linkage and electrophoretic conditions for mouse and somatic cell hybrids in starch gels. J Histochem Cytochem. 1973 Dec;21(12):1066–1081. doi: 10.1177/21.12.1066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norwood T. H., Zeigler C. J., Martin G. M. Dimethyl sulfoxide enhances polyethylene glycol-mediated somatic cell fusion. Somatic Cell Genet. 1976 May;2(3):263–270. doi: 10.1007/BF01538964. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puck T. T., Marcus P. I. A RAPID METHOD FOR VIABLE CELL TITRATION AND CLONE PRODUCTION WITH HELA CELLS IN TISSUE CULTURE: THE USE OF X-IRRADIATED CELLS TO SUPPLY CONDITIONING FACTORS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1955 Jul 15;41(7):432–437. doi: 10.1073/pnas.41.7.432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruddle F. H., Fournier R. E. Somatic cell genetic analysis of gene transfer in mammalian cells. Brookhaven Symp Biol. 1977 May 12;(29):96–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scher W., Friend C. Breakage of DNA and alterations in folded genomes by inducers of differentiation in Friend erythroleukemic cells. Cancer Res. 1978 Mar;38(3):841–849. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shin S., Caneva R., Schildkraut C. L., Klinger H. P., Siniscalco M. Cells with phosphoribosyl transferase activity recovered from mouse cells resistant to 8-azaguanine. Nat New Biol. 1973 Feb 14;241(111):194–196. doi: 10.1038/newbio241194a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spandidos D. A., Siminovitch L. Genetic analysis by chromosome-mediated gene transfer in hamster cells. Brookhaven Symp Biol. 1977 May 12;(29):127–134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spandidos D. A., Siminovitch L. Linkage of markers controlling consecutive biochemical steps in CHO cells as demonstrated by chromosome transfer. Cell. 1977 Sep;12(1):235–242. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90201-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spandidos D. A., Siminovitch L. Transfer of anchorage independence by isolated metaphase chromosomes in hamster cells. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):675–682. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90267-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spandidos D. A., Siminovitch L. Transfer of codominant markers by isolated metaphase chromosomes in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3480–3484. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spandios D. A., Siminovitch L. Transfer of the marker for morphologically transformed phenotype by isolated metaphase chromosomes in hamster cells. Nature. 1978 Jan 19;271(5642):259–261. doi: 10.1038/271259a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stow N. D., Wilkie N. M. An improved technique for obtaining enhanced infectivity with herpes simplex virus type 1 DNA. J Gen Virol. 1976 Dec;33(3):447–458. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-33-3-447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terada M., Nudel U., Fibach E., Rifkind R. A., Marks P. A. Changes in DNA associated with induction of erythroid differentiation by dimethyl sulfoxide in murine erythroleukemia cells. Cancer Res. 1978 Mar;38(3):835–840. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tischfield J. A., Bernhard H. P., Ruddle F. H. A new electrophoretic-autoradiographic method for the visual detection of phosphotransferases. Anal Biochem. 1973 Jun;53(2):545–554. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90105-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willecke K., Lange R., Krüger A., Reber T. Cotransfer of two linked human genes into cultured mouse cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Apr;73(4):1274–1278. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.4.1274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willecke K., Ruddle F. H. Transfer of the human gene for hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase via isolated human metaphase chromosomes into mouse L-cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 May;72(5):1792–1796. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.5.1792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wullems G. J., van der Horst J., Bootsma D. Incorporation of isolated chromosomes and induction of hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase in Chinese hamster cells. Somatic Cell Genet. 1975 Apr;1(2):137–151. doi: 10.1007/BF01538544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wullems G. J., van der Horst J., Bootsma D. Transfer of the human X chromosome to human--Chinese hamster cell hybrids via isolated HeLa metaphase chromosomes. Somatic Cell Genet. 1976 Jul;2(4):359–371. doi: 10.1007/BF01538840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wullems G. J., van der Horst J., Bootsma D. Transfer of the human genes coding for thymidine kinase and galactokinase to Chinese hamster cells and human-Chinese hamster cell hybrids. Somatic Cell Genet. 1977 May;3(3):281–293. doi: 10.1007/BF01538746. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]