Abstract
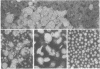
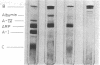
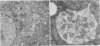
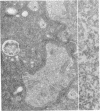
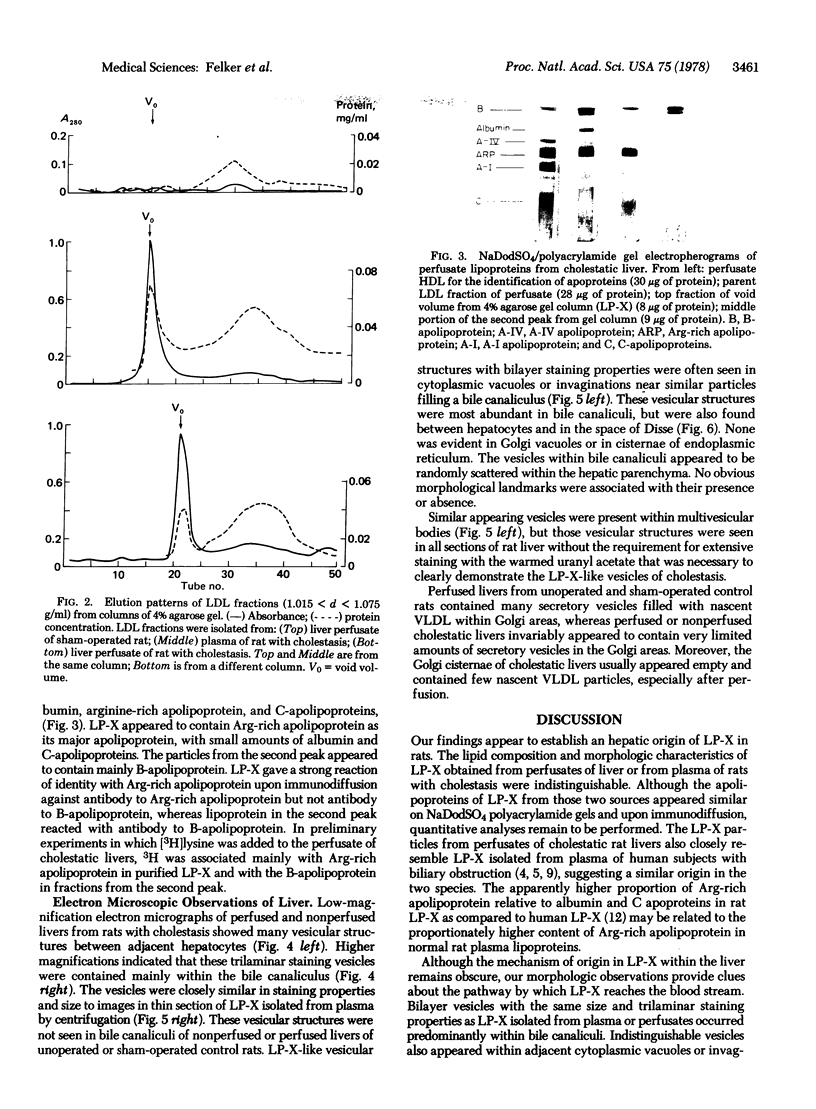
The major abnormal plasma lipoprotein of cholestasis (LP-X) was isolated from blood plasma and from perfusates of isolated livers of rats with biliary obstruction. In both cases LP-X was composed mainly of about equimolar parts of phospholipids and unesterified cholesterol; the small protein component was primarily the arginine-rich apolipoprotein. By electron microscopy, LP-X appeared as a unilamellar liposome (690 A mean diameter, range 400-1000 A) with the trilaminar staining image typical of phospholipid bilayers. Extensive block staining of cholestatic livers for 48 hr with warmed uranyl acetate (37 degrees) permitted the visualization of vesicles indistinguishable from LP-X within hepatic parenchyma. These trilaminar-staining vesicles occurred predominantly within bile canaliculi. They also were seen in nearby cytoplasmic vacuoles or invaginations between hepatocytes and in the space of Disse. Similar vesicles were not seen in the endoplasmic reticulum or Golgi cisternae. These observations raise the possibility that the vesicles are formed within bile canaliculi and are transported from the canaliculi to the space of Disse within pinocytotic vacuoles.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AHRENS E. H., Jr, KUNKEL H. G. The relationship between serum lipids and skin xanthomata in 18 patients with primary biliary cirrhosis. J Clin Invest. 1949 Nov;28(6 Pt 2):1565–1574. doi: 10.1172/JCI102222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blomhoff J. P. High density lipoproteins in cholestasis. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1974;9(6):591–596. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calandra S., Montaguti M., Cartoni V., Pasquali-Ronchetti I. Plasma lipoproteins in rats with experimental biliary obstruction. I. A chemical study. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Oct 21;409(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(75)90075-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danielsson B., Ekman R., Petersson B. G. An abnormal high density lipoprotein in cholestatic plasma isolated by zonal ultracentrifugation. FEBS Lett. 1975 Feb 1;50(2):180–184. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80484-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDER H. A., RUSS E. M., PRITCHETT R. A. R., WILBER M. M., BARR D. P. Protein-lipid relationships in human plasma: in biliary cirrhosis, obstructive jaundice, and acute hepatitis. J Clin Invest. 1955 Jul;34(7 Pt 1):1147–1162. doi: 10.1172/JCI103163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faergeman O., Havel R. J. Metabolism of cholesteryl esters of rat very low density lipoproteins. J Clin Invest. 1975 Jun;55(6):1210–1218. doi: 10.1172/JCI108039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fainaru M., Felker T. E., Hamilton R. L., Havel R. J. Evidence that a separate particle containing B-apoprotein is present in high-density lipoproteins from perfused rat liver. Metabolism. 1977 Sep;26(9):999–1004. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(77)90017-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fainaru M., Havel R. J., Felker T. E. Radioimmunoassay of apolipoprotein A-I of rat serum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Sep 28;446(1):56–68. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(76)90097-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fainaru M., Havel R. J., Imaizumi K. Radioimmunoassay of arginine-rich apolipoprotein of rat serum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Jan 25;490(1):144–155. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(77)90114-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felker T. E., Fainaru M., Hamilton R. L., Havel R. J. Secretion of the arginine-rich and A-I apolipoproteins by the isolated perfused rat liver. J Lipid Res. 1977 Jul;18(4):465–473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton R. L., Berry M. N., Williams M. C., Severinghaus E. M. A simple and inexpensive membrane "lung" for small organ perfusion. J Lipid Res. 1974 Mar;15(2):182–186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton R. L., Havel R. J., Kane J. P., Blaurock A. E., Sata T. Cholestasis: lamellar structure of the abnormal human serum lipoprotein. Science. 1971 Apr 30;172(3982):475–478. doi: 10.1126/science.172.3982.475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton R. L., Williams M. C., Fielding C. J., Havel R. J. Discoidal bilayer structure of nascent high density lipoproteins from perfused rat liver. J Clin Invest. 1976 Sep;58(3):667–680. doi: 10.1172/JCI108513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones A. L., Schmucker D. L., Mooney J. S., Adler R. D., Ockner R. K. Morphometric analysis of rat hepatocytes after total billary obstruction. Gastroenterology. 1976 Dec;71(6):1050–1060. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostner G. M., Laggner P., Prexl H. J., Holasek A. Investigation of the abnormal low-density lipoproteins occurring in patients with obstructive jaundice. Biochem J. 1976 Aug 1;157(2):401–407. doi: 10.1042/bj1570401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUFT J. H. Improvements in epoxy resin embedding methods. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Feb;9:409–414. doi: 10.1083/jcb.9.2.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laggner P., Glatter O., Müller K., Kratky O., Kostner G., Holasek A. The lipid bilayer structure of the abnormal human plasma lipoprotein X. An X-ray small-angle-scattering study. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Jul 1;77(1):165–171. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11654.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manzato E., Fellin R., Baggio G., Walch S., Neubeck W., Seidel D. Formation of lipoprotein-X. Its relationship to bile compounds. J Clin Invest. 1976 May;57(5):1248–1260. doi: 10.1172/JCI108393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntyre N., Harry D. S., Pearson A. J. The hypercholesterolaemia of obstructive jaundice. Gut. 1975 May;16(5):379–391. doi: 10.1136/gut.16.5.379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mjos O. D., Faergeman O., Hamilton R. L., Havel R. J. Characterization of remnants produced during the metabolism of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins of blood plasma and intestinal lymph in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1975 Sep;56(3):603–615. doi: 10.1172/JCI108130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller P., Felin R., Lambrecht J., Agostini B., Wieland H., Rost W., Seidel D. Hypertriglyceridaemia secondary to liver disease. Eur J Clin Invest. 1974 Dec 5;4(6):419–428. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1974.tb00415.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PALADE G. E. A study of fixation for electron microscopy. J Exp Med. 1952 Mar;95(3):285–298. doi: 10.1084/jem.95.3.285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sata T., Havel R. J., Jones A. L. Characterization of subfractions of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins separated by gel chromatography from blood plasma of normolipemic and hyperlipemic humans. J Lipid Res. 1972 Nov;13(6):757–768. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidel D., Agostini B., Müller P. Sturucture of an abnormal plasma lipoprotein (LP-X) characterizing obstructive jaundice. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jan 27;260(1):146–152. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(72)90082-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidel D., Alaupovic P., Furman R. H. A lipoprotein characterizing obstructive jaundice. I. Method for quantitative separation and identification of lipoproteins in jaundiced subjects. J Clin Invest. 1969 Jul;48(7):1211–1223. doi: 10.1172/JCI106085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidel D., Alaupovic P., Furman R. H., McConathy W. J. A lipoprotein characterizing obstructive jaundice. II. Isolation and partial characterization of the protein moieties of low density lipoproteins. J Clin Invest. 1970 Dec;49(12):2396–2407. doi: 10.1172/JCI106459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidel D., Büff H. U., Fauser U., Bleyl U. On the metabolism of lipoprotein-X (LP-X). Clin Chim Acta. 1976 Jan 16;66(2):195–207. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(76)90057-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein O., Alkan M., Stein Y. Obstructive jaundice lipoprotein particles studied in ultrathin sections of livers of bile duct-ligated mice. Lab Invest. 1973 Aug;29(2):166–172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swaney J. B., Reese H., Eder H. A. Polypeptide composition of rat high density lipoprotein: characterization by SDS-gel electrophoresis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Jul 24;59(2):513–519. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80010-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]