Abstract
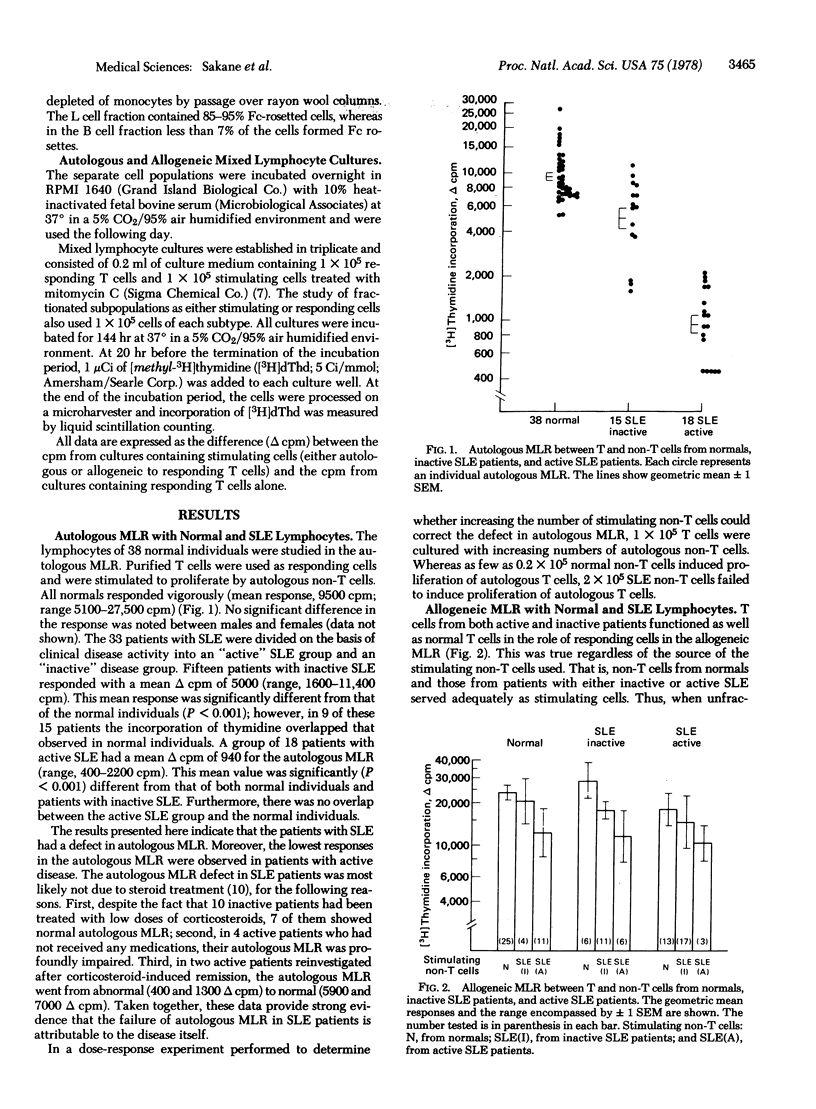
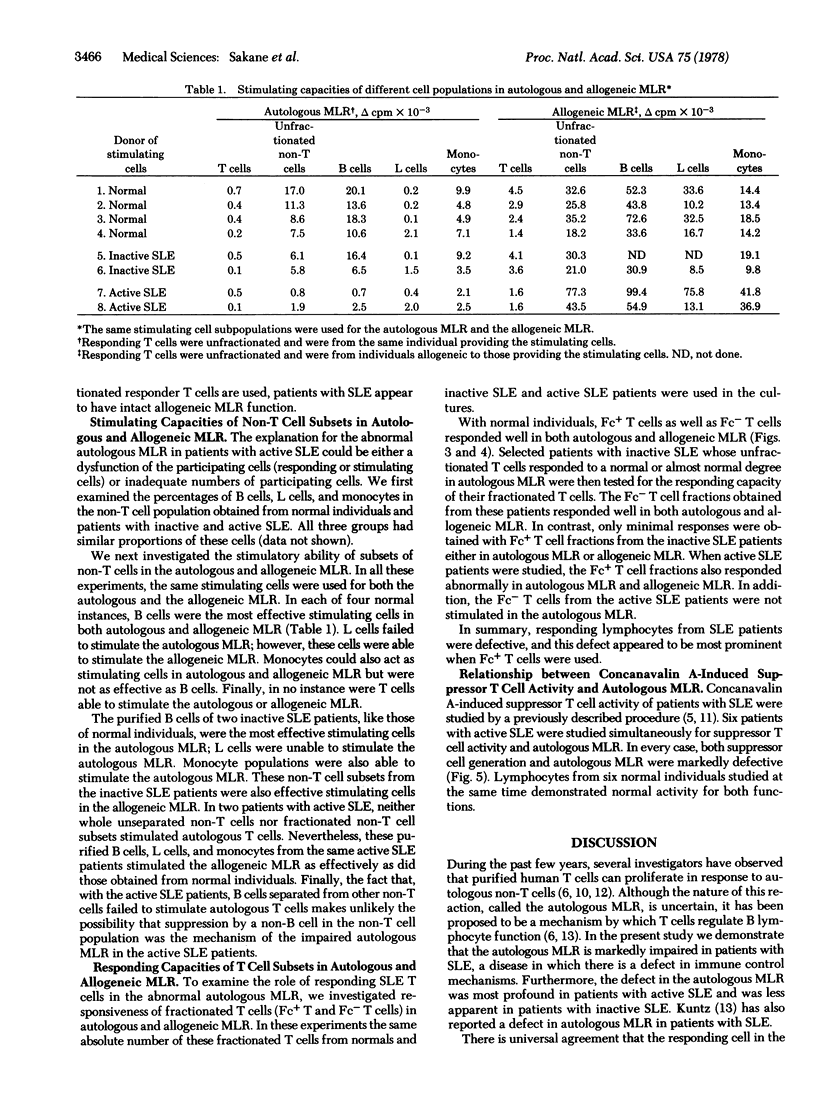
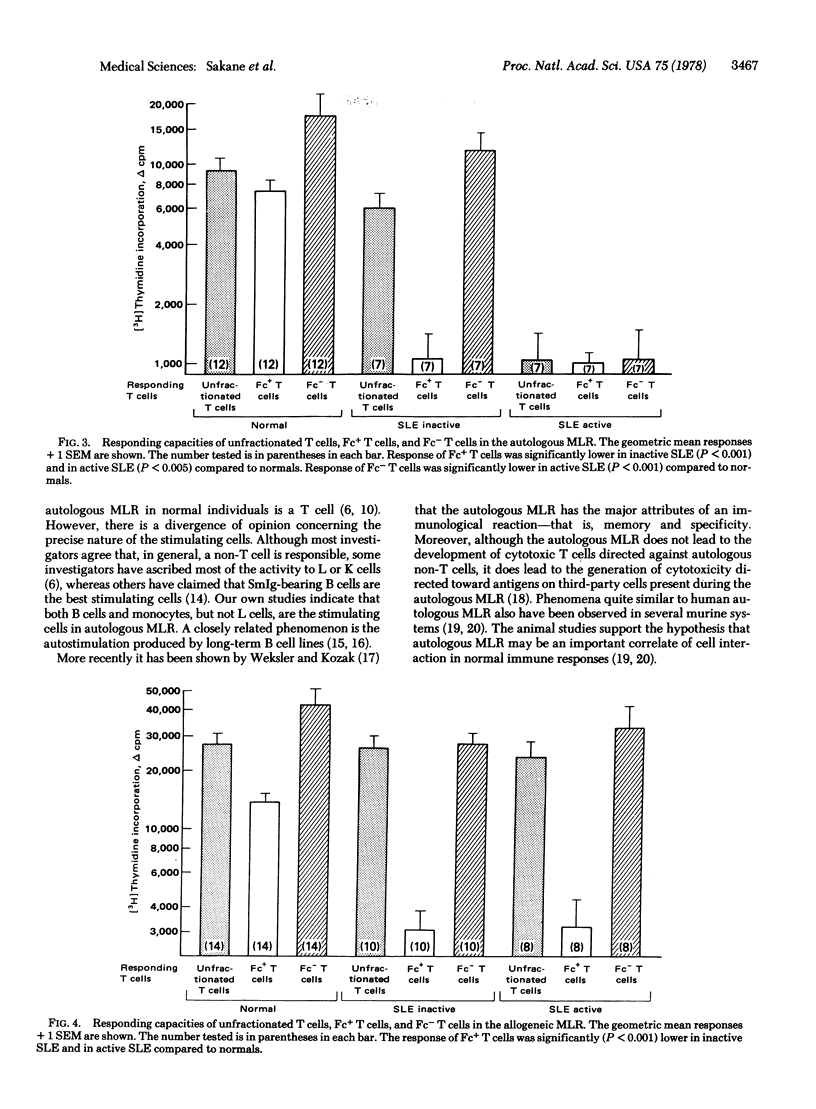
Normal human T cells proliferate vigorously when stimulated with autologous non-T cells. This autologous mixed lymphocyte reaction (MLR) between T and non-T cells was defective in patients with active systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). In contrast, T cells and non-T cells from active SLE patients behaved normally as responding and stimulating cells, respectively, in the allogeneic MLR. The etiology of the impaired autologous MLR was further examined by studying the functional capacity of subsets of stimulating or responding cells. B cells, L cells, and monocytes from active SLE patients failed to stimulate autologous T cells but these cells effectively stimulated allogeneic T cells. Fc(IgG)+ T cells from active patients were unable to respond in both the autologous and allogeneic MLR; their Fc(IgG)-T cells responded well in the allogeneic but not in the autologous MLR. The Fc(IgG)+ T cells, but not the Fc(IgG)- T cells, from inactive SLE patients also failed to respond in the both autologous and allogeneic MLR. These studies indicate that patients with SLE have functionally defective Fc(IgG)+ T cells and a defective autologous MLR, both of which may contribute to impaired regulation of immune functions.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bresnihan B., Jasin H. E. Suppressor function of peripheral blood mononuclear cells in normal individuals and in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest. 1977 Jan;59(1):106–116. doi: 10.1172/JCI108607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz S., Borcherding W., Moorthy A. V., Chesney R., Schulte-Wisserman H., Hong R. Induction of suppressor T cells in systemic lupus erythematosus by thymosin and cultured thymic epithelium. Science. 1977 Sep 2;197(4307):999–1001. doi: 10.1126/science.302032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz D. A., Garrett M. A. Distinctive functional properties of human blood L lymphocytes: a comparison with T lymphocytes, B lymphocytes, and monocytes. J Immunol. 1977 May;118(5):1712–1721. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ilfeld D. N., Krakauer R. S., Blaese R. M. Suppression of the human autologous mixed lymphocyte reaction by physiologic concentrations of hydrocortisone. J Immunol. 1977 Aug;119(2):428–434. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuntz M. M., Innes J. B., Weksler M. E. Lymphocyte transformation induced by autologous cells. IV. Human T-lymphocyte proliferation induced by autologous or allogeneic non-T lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1976 May 1;143(5):1042–1054. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.5.1042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobo P. I., Horwitz D. A. An appraisal of Fc receptors on human peripheral blood B and L lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1976 Sep;117(3):939–943. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moretta L., Webb S. R., Grossi C. E., Lydyard P. M., Cooper M. D. Functional analysis of two human T-cell subpopulations: help and suppression of B-cell responses by T cells bearing receptors for IgM or IgG. J Exp Med. 1977 Jul 1;146(1):184–200. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.1.184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Opelz G., Kiuchi M., Takasugi M., Terasaki P. I. Autologous stimulation of human lymphocyte subpopulation. J Exp Med. 1975 Nov 1;142(5):1327–1333. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.5.1327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponzio N. M., Finke J. H., Battisto J. R. Adult murine lymph node cells respond blastogenically to a new differentiation antigen on isologous and autologous B lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1975 Mar;114(3):971–975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakane T., Green I. Human suppressor T cells induced by concanavalin A: suppressor T cells belong to distinctive T cell subclasses. J Immunol. 1977 Sep;119(3):1169–1178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakane T., Green I. Protein A from Staphylococcus aureus-a mitogen for human T lymphocytes and B lymphocytes but not L lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1978 Jan;120(1):302–311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakane T., Steinberg A. D., Green I. Studies of immune functions of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. I. Dysfunction of suppressor T-cell activity related to impaired generation of, rather than response to, suppressor cells. Arthritis Rheum. 1978 Jul-Aug;21(6):657–664. doi: 10.1002/art.1780210608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg A. D., Klassen L. W. Role of suppressor T cells in lymphopoietic disorders. Clin Haematol. 1977 Jun;6(2):439–478. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stobo J. D., Loehnen C. P. Immunoregulation and autoimmunity. Mayo Clin Proc. 1976 Aug;51(8):479–483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vande Stouwe R. A., Kunkel H. G., Halper J. P., Weksler M. E. Autologous mixed lymphocyte culture reactions and generation of cytotoxic T cells. J Exp Med. 1977 Dec 1;146(6):1809–1814. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.6.1809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Von Boehmer H. Selective stimulation by B lymphocytes in the syngeneic mixed lymphocyte reaction. Eur J Immunol. 1974 Feb;4(2):105–110. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830040209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weksler M. E., Kozak R. Lymphocyte transformation induced by autologous cells. V. Generation of immunologic memory and specificity during the autologous mixed lymphocyte reaction. J Exp Med. 1977 Dec 1;146(6):1833–1838. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.6.1833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weksler M. E. Lymphocyte transformation induced by autologous cells. III. Lymphoblast-induced lymphocyte to stimulation does not correlate with EB viral antigen expression or immunity. J Immunol. 1976 Feb;116(2):310–314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


