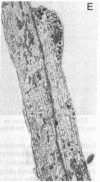
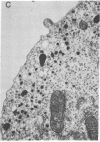
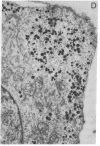
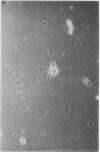
Abstract
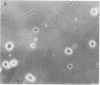
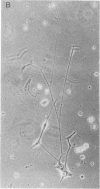
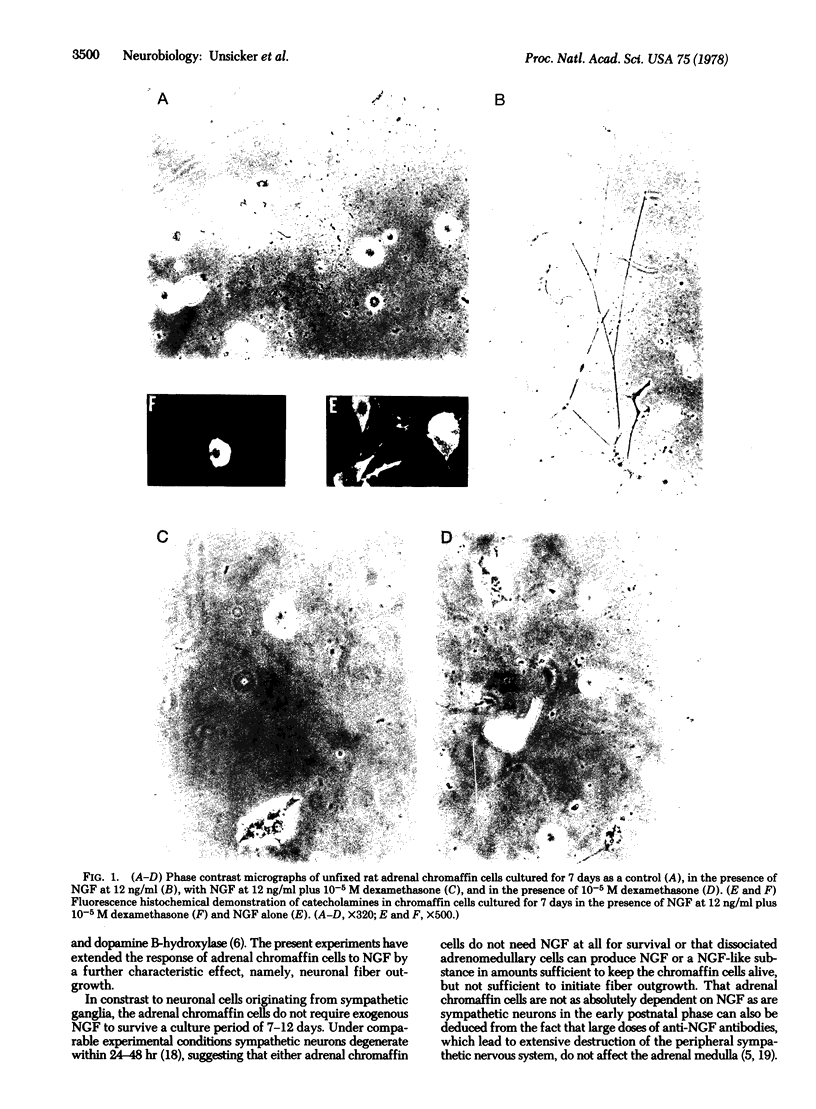
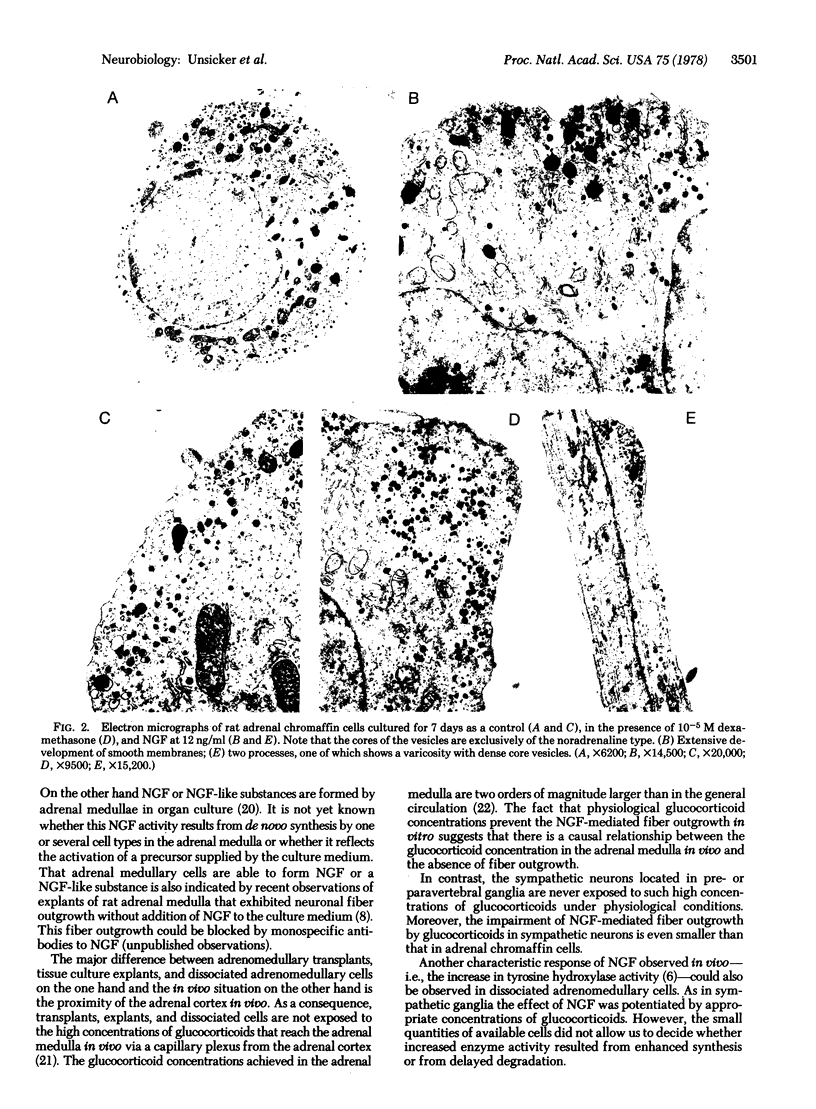
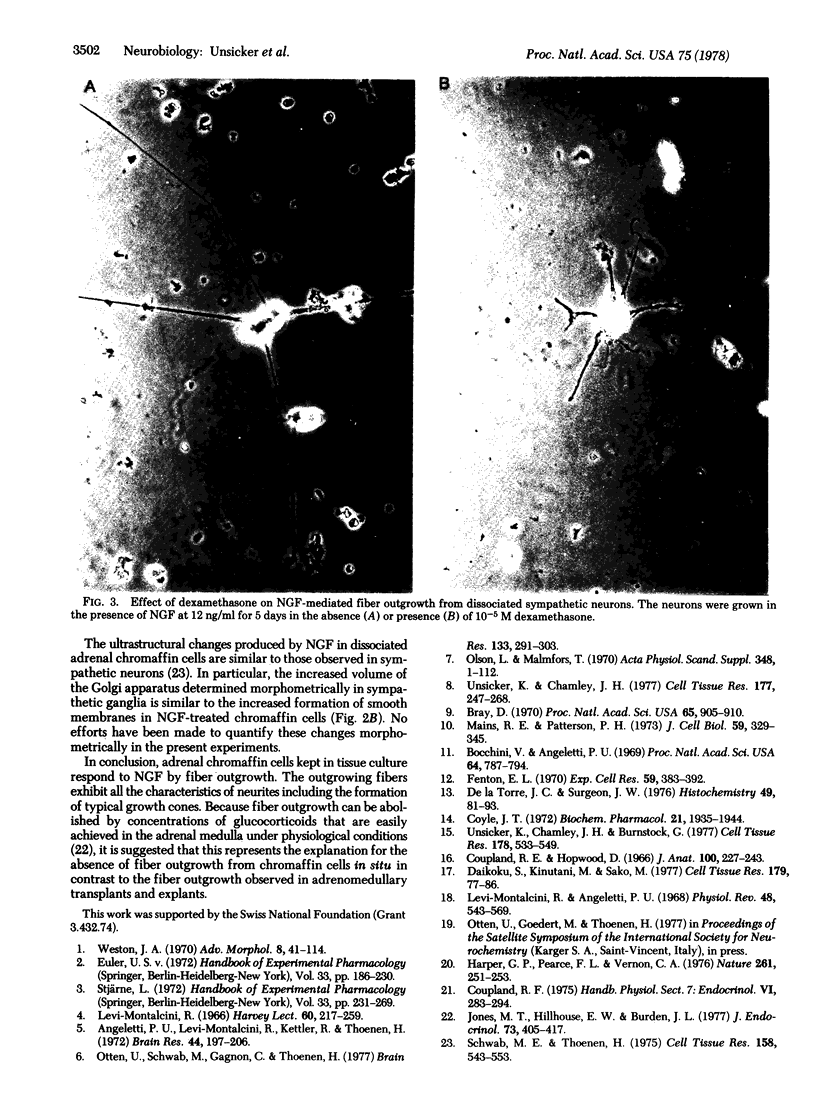
Addition of nerve growth factor to cultures of dissociated rat adrenal medullary cells caused fiber outgrowth from chromaffin cells. These fibers exhibited all the characteristics of neurites, particularly the formation of typical growth cones exhibiting intense catecholamine-specific fluorescence. Because this nerve growth factor-mediated neurite outgrowth could be abolished by physiological concentrations of glucocorticoids, it is concluded that the high glucocorticoid concentrations normally present in the adrenal medulla prevent the fiber outgrowth from medullary chromaffin cells in vivo. In dissociated sympathetic neurons the same concentrations of glucocorticoids markedly reduce but do not completely abolish neuronal fiber outgrowth.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angeletti P. U., Levi-Montalcini R., Kettler R., Thoenen H. Comparative studies on the effect of the nerve growth factor on sympathetic ganglia and adrenal medulla in newborn rats. Brain Res. 1972 Sep 15;44(1):197–206. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(72)90375-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bocchini V., Angeletti P. U. The nerve growth factor: purification as a 30,000-molecular-weight protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Oct;64(2):787–794. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.2.787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bray D. Surface movements during the growth of single explanted neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Apr;65(4):905–910. doi: 10.1073/pnas.65.4.905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coupland R. E., Hopwood D. The mechanism of the differential staining reaction for adrenaline-and noreadrenaline-storing granules in tissues fixed in glutaraldehyde. J Anat. 1966 Apr;100(Pt 2):227–243. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coyle J. T. Tyrosine hydroxylase in rat brain--cofactor requirements, regional and subcellular distribution. Biochem Pharmacol. 1972 Jul 15;21(14):1935–1944. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(72)90006-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daikoku S., Kinutani M., Sako M. Development of the adrenal medullary cells in rats with reference to synaptogenesis. Cell Tissue Res. 1977 Mar 30;179(1):77–86. doi: 10.1007/BF00278463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenton E. L. Tissue culture assay of nerve growth factor and of the specific antiserum. Exp Cell Res. 1970 Mar;59(3):383–392. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(70)90645-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper G. P., Pearce F. L., Vernon C. A. Production of nerve growth factor by the mouse adrenal medulla. Nature. 1976 May 20;261(5557):251–253. doi: 10.1038/261251a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones M. T., Hillhouse E. W., Burden J. L. Dynamics and mechanics of corticosteroid feedback at the hypothalamus and anterior pituitary gland. J Endocrinol. 1977 Jun;73(3):405–417. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0730405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi-Montalcini R., Angeletti P. U. Nerve growth factor. Physiol Rev. 1968 Jul;48(3):534–569. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1968.48.3.534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi-Montalcini R. The nerve growth factor: its mode of action on sensory and sympathetic nerve cells. Harvey Lect. 1966;60:217–259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mains R. E., Patterson P. H. Primary cultures of dissociated sympathetic neurons. I. Establishment of long-term growth in culture and studies of differentiated properties. J Cell Biol. 1973 Nov;59(2 Pt 1):329–345. doi: 10.1083/jcb.59.2.329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson L., Malmfors T. Growth characteristics of adrenergic nerves in the adult rat. Fluorescence histochemical and 3H-noradrenaline uptake studies using tissue transplantations to the anterior chamber of the eye. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1970;348:1–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otten U., Schwab M., Gagnon C., Thoenen H. Selective induction of tyrosine hydroxylase and dopamine beta-hydroxylase by nerve growth factor: comparison between adrenal medulla and sympathetic ganglia of adult and newborn rats. Brain Res. 1977 Sep 16;133(2):291–303. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90765-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwab M. E., Thoenen H. Early effects of nerve growth factor on adrenergic neurons: an electron microscopic morphometric study of the rat superior cervical ganglion. Cell Tissue Res. 1975 May 20;158(4):543–553. doi: 10.1007/BF00220218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torre J. C., Surgeon J. W. A methodological approach to rapid and sensitive monoamine histofluorescence using a modified glyoxylic acid technique: the SPG method. Histochemistry. 1976 Oct 22;49(2):81–93. doi: 10.1007/BF00495672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unsicker K., Chamley J. H., Burnstock G. Studies on the interactions between nerve fibres from para- and orthosympathetic ganglia and adreno-cortical and -medullary cells in joint culture. Cell Tissue Res. 1977 Mar 24;178(4):533–549. doi: 10.1007/BF00219573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unsicker K., Chamley J. H. Growth characteristics of postnatal rat adrenal medulla in culture. A study correlating phase contrast, microcinematographic, histochemical, and electron microscopical observations. Cell Tissue Res. 1977 Feb 9;177(2):247–268. doi: 10.1007/BF00221086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weston J. A. The migration and differentiation of neural crest cells. Adv Morphog. 1970;8:41–114. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-028608-9.50006-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]