Abstract
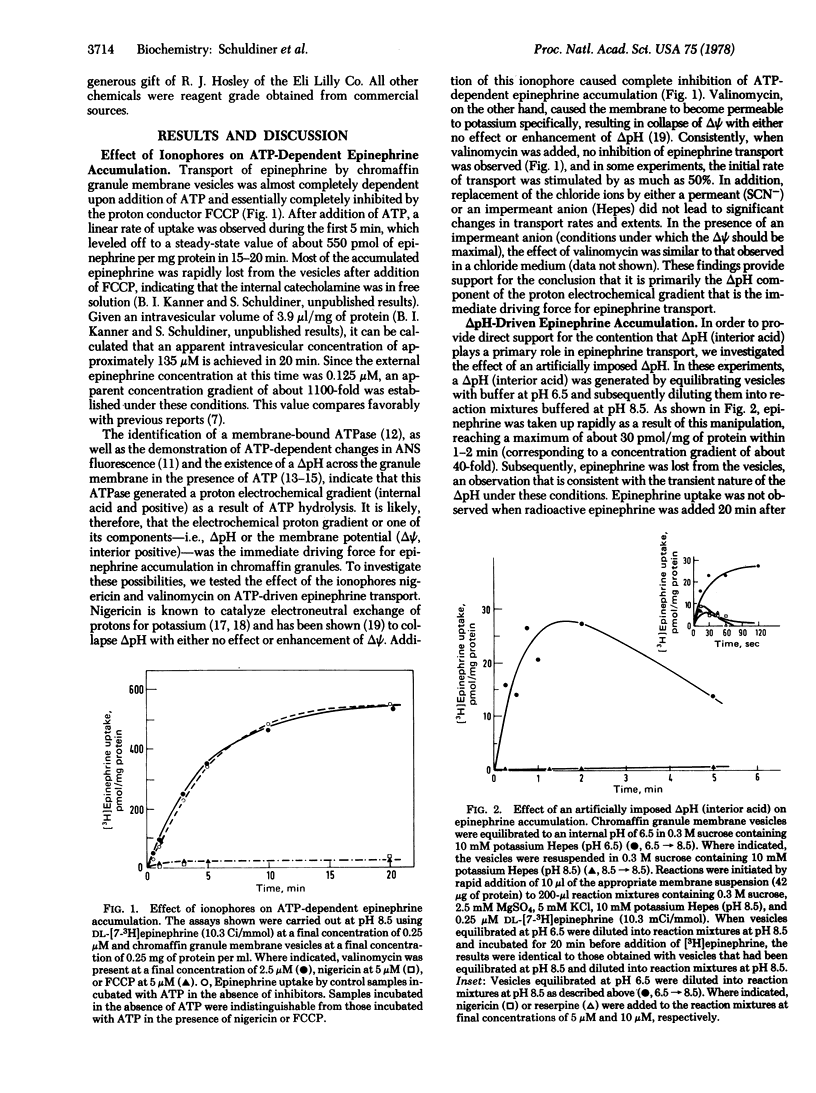
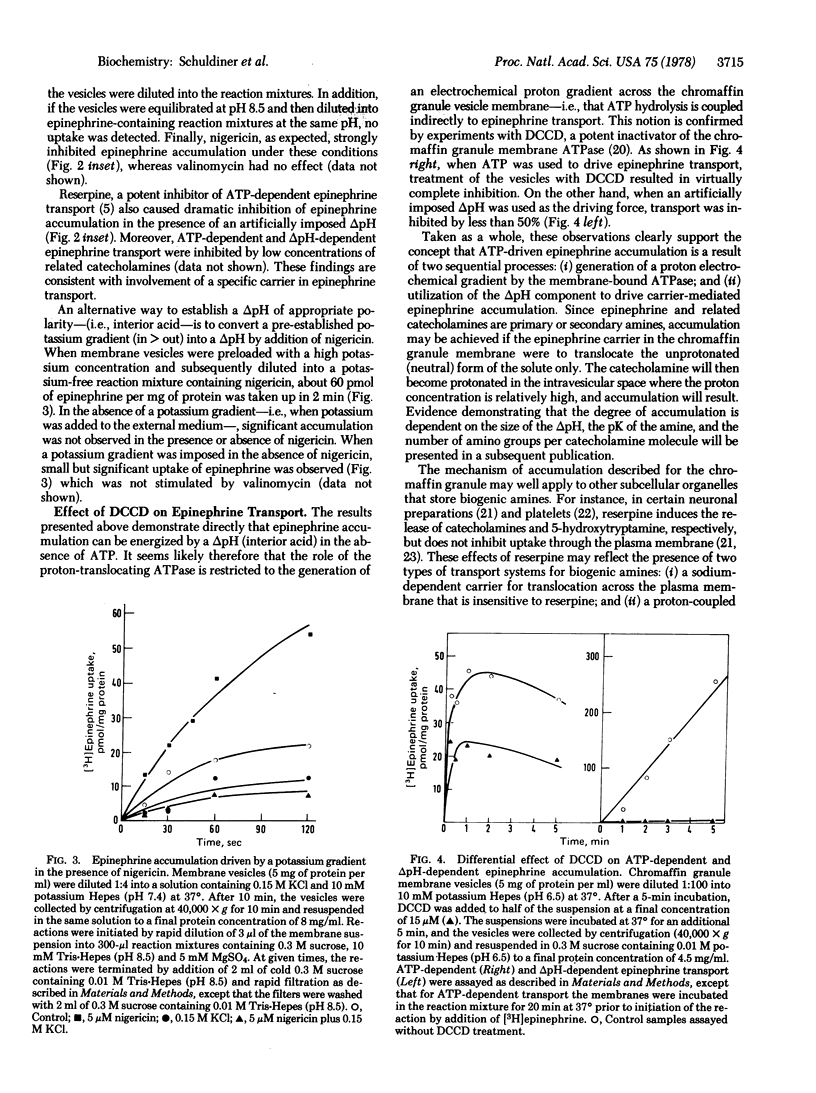
ATP-driven transport and accumulation of epinephrine in chromaffin granule membrane vesicles isolated from bovine adrenal medulla is inhibited by the proton ionophores carbonylcyanide p-trifluoromethoxyphenylhydrazone and nigericin, but not by valinomycin. Moreover, an artificially imposed pH gradient (interior acid) is able to drive this reserpine-sensitive transport system in the absence of ATP. Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide, an inactivator of the chromaffin granule membrane-bound ATPase, completely inhibits ATP-dependent epinephrine accumulation, but has much less effect when an imposed pH gradient is the driving force for epinephrine transport. The findings provide a strong indication that a pH gradient (interior acid) is the immediate driving force for epinephrine uptake in these storage granules and suggest that ATP-driven epinephrine transport is the result of two processes: (i) generation of a proton electrochemical gradient (interior acid and positive) by the membrane-bound, proton-translocating ATPase; and (ii) pH gradient-driven accumulation of the catecholamine.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BANKS P. THE ADENOSINE-TRIPHOSPHATASE ACTIVITY OF ADRENAL CHROMAFFIN GRANULES. Biochem J. 1965 May;95:490–496. doi: 10.1042/bj0950490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bashford C. L., Casey R. P., Radda G. K., Ritchie G. A. Energy-coupling in adrenal chromaffin granules. Neuroscience. 1976;1(5):399–412. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(76)90133-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bashford C. L., Casey R. P., Radda G. K., Ritchie G. A. The effect of uncouplers on catecholamine incorporation by vesicles of chromaffin granules. Biochem J. 1975 Apr;148(1):153–155. doi: 10.1042/bj1480153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bashford C. L., Radda G. K., Ritchie G. A. Energy-linked activities of the chromaffin granule membrane. FEBS Lett. 1975 Jan 15;50(1):21–24. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)81031-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casey R. P., Njus D., Radda G. K., Sehr P. A. Active proton uptake by chromaffin granules: observation by amine distribution and phosphorus-31 nuclear magnetic resonance techniques. Biochemistry. 1977 Mar 8;16(5):972–977. doi: 10.1021/bi00624a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Da Prada M., Pletscher A., Tranzer J. P., Knuchel H. Action of reserpine on subcellular 5-hydroxytryptamine organelles of blood platelets. Life Sci. 1968 May 1;7(9):477–480. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(68)90050-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flatmark T., Ingebretsen O. C. ATP-dependent proton translocation in resealed chromaffin granule ghosts. FEBS Lett. 1977;78(1):53–56. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80271-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harold F. M. Conservation and transformation of energy by bacterial membranes. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Jun;36(2):172–230. doi: 10.1128/br.36.2.172-230.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasselbach W., Taugner G. The effect of a cross-bridging thiol reagent on the catecholamine fluxes of adrenal medulla vesicles. Biochem J. 1970 Sep;119(2):265–271. doi: 10.1042/bj1190265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. G., Scarpa A. Internal pH of isolated chromaffin vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1976 Apr 10;251(7):2189–2191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIRSHNER N. Uptake of catecholamines by a particulate fraction of the adrenal medulla. J Biol Chem. 1962 Jul;237:2311–2317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard H. B., Zinder O., Hoffman P. G., Nikodejevic O. Regulation of the transmembrane potential of isolated chromaffin granules by ATP, ATP analogs, and external pH. J Biol Chem. 1976 Aug 10;251(15):4544–4550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramos S., Schuldiner S., Kaback H. R. The electrochemical gradient of protons and its relationship to active transport in Escherichia coli membrane vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jun;73(6):1892–1896. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.6.1892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudnick G. Active transport of 5-hydroxytryptamine by plasma membrane vesicles isolated from human blood platelets. J Biol Chem. 1977 Apr 10;252(7):2170–2174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



