Abstract
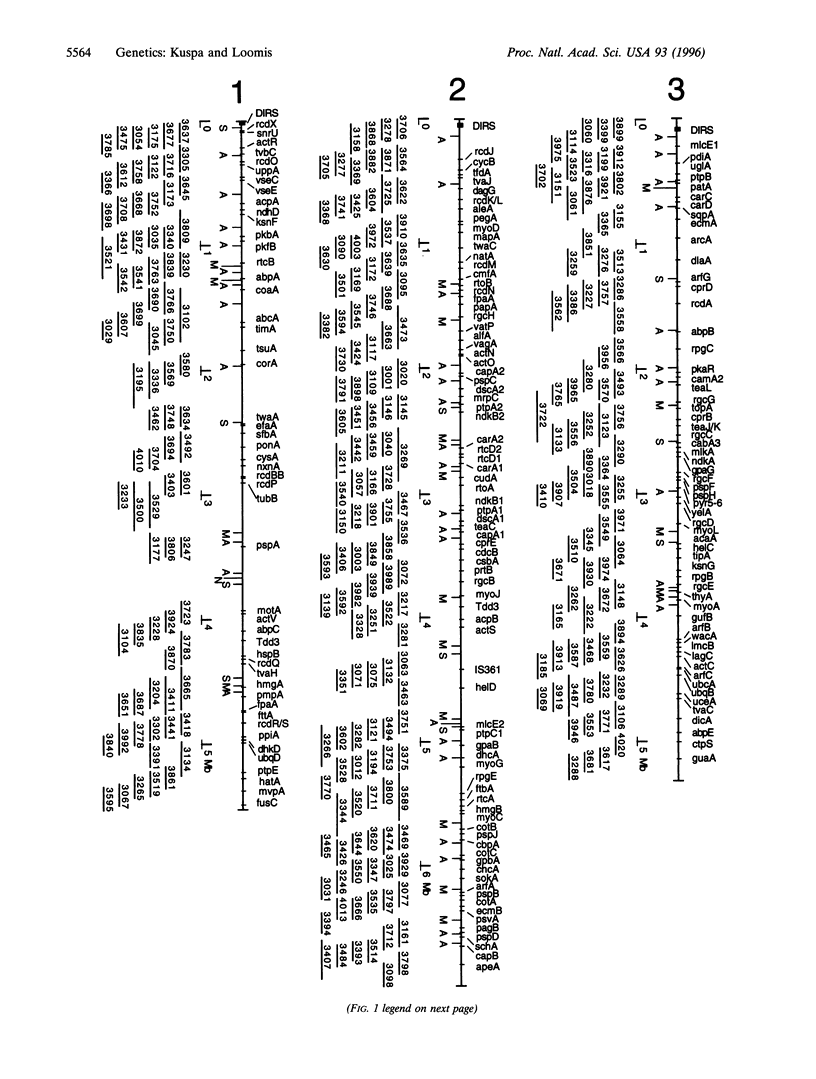
High resolution gene maps of the six chromosomes of Dictyostelium discoideum have been generated by a combination of physical mapping techniques. A set of yeast artificial chromosome clones has been ordered into overlapping arrays that cover >98% of the 34-magabase pair genome. Clones were grouped and ordered according to the genes they carried, as determined by hybridization analyses with DNA fragments from several hundred genes. Congruence of the gene order within each arrangement of clones with the gene order determined from whole genome restriction site mapping indicates that a high degree of confidence can be placed on the clone map. This clone-based description of the Dictyostelium chromosomes should be useful for the physical mapping and subcloning of new genes and should facilitate more detailed analyses of this genome. cost of silicon-based construction and in the efficient sample handling afforded by component integration.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barth A., Müller-Taubenberger A., Taranto P., Gerisch G. Replacement of the phospholipid-anchor in the contact site A glycoprotein of D. discoideum by a transmembrane region does not impede cell adhesion but reduces residence time on the cell surface. J Cell Biol. 1994 Jan;124(1-2):205–215. doi: 10.1083/jcb.124.1.205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corney A. J., Richards A. J., Phillpots T., Hames B. D. Developmental regulation of cell-type-enriched mRNAs in Dictyostelium discoideum. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Apr;4(4):613–623. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00630.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coukell B., Moniakis J., Grinberg A. Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of a cDNA encoding a developmentally regulated Ca(2+)-binding protein from Dictyostelium discoideum. FEBS Lett. 1995 Apr 10;362(3):342–346. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(95)00272-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel J., Bush J., Cardelli J., Spiegelman G. B., Weeks G. Isolation of two novel ras genes in Dictyostelium discoideum; evidence for a complex, developmentally regulated ras gene subfamily. Oncogene. 1994 Feb;9(2):501–508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demerec M., Adelberg E. A., Clark A. J., Hartman P. E. A proposal for a uniform nomenclature in bacterial genetics. Genetics. 1966 Jul;54(1):61–76. doi: 10.1093/genetics/54.1.61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingermann T., Amon E., Williams K. L., Welker D. L. Chromosomal mapping of tRNA genes from Dictyostelium discoideum. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Apr;207(1):176–187. doi: 10.1007/BF00331507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingermann T., Bertling W., Brechner T., Nerke K., Peffley D. M., Sogin M. L. Structure of two tRNA genes from Dictyostelium discoideum. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jan 24;14(2):1127–1127. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.2.1127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingermann T., Bertling W., Pistel F., Amon E. Characterisation of a Dictyostelium discoideum DNA fragment coding for a putative tRNAValGUU gene. Evidence for a single transcription unit consisting of two overlapping class III genes. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Jan 15;146(2):449–458. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08672.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giorda R., Ohmachi T., Ennis H. L. Organization of a gene family developmentally regulated during Dictyostelium discoideum spore germination. J Mol Biol. 1989 Jan 5;205(1):63–69. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90364-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldhagen H., Clarke M. Identification of the single gene for calmodulin in Dictyostelium discoideum. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1851–1854. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haribabu B., Pavlovic J., Bodduluri S. R., Doody J. F., Ortiz B. D., Mullings S., Moon B., Dottin R. P. Signal transduction pathways involved in the expression of the uridine diphosphoglucose pyrophosphorylase gene of Dictyostelium discoideum. Dev Genet. 1991;12(1-2):35–44. doi: 10.1002/dvg.1020120108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haugwitz M., Noegel A. A., Rieger D., Lottspeich F., Schleicher M. Dictyostelium discoideum contains two profilin isoforms that differ in structure and function. J Cell Sci. 1991 Nov;100(Pt 3):481–489. doi: 10.1242/jcs.100.3.481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitt A. L., Lu T. H., Luna E. J. Ponticulin is an atypical membrane protein. J Cell Biol. 1994 Sep;126(6):1421–1431. doi: 10.1083/jcb.126.6.1421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard P. K., Sefton B. M., Firtel R. A. Analysis of a spatially regulated phosphotyrosine phosphatase identifies tyrosine phosphorylation as a key regulatory pathway in Dictyostelium. Cell. 1992 Nov 13;71(4):637–647. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90597-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessin R. H., Williams K. L., Newell P. C. Linkage analysis in Dictyostelium discoideum using temperature-sensitive growth mutants selected with bromodeoxyuridine. J Bacteriol. 1974 Sep;119(3):776–783. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.3.776-783.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knecht D. A., Cohen S. M., Loomis W. F., Lodish H. F. Developmental regulation of Dictyostelium discoideum actin gene fusions carried on low-copy and high-copy transformation vectors. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):3973–3983. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.3973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozarov E., van der Wel H., Field M., Gritzali M., Brown R. D., Jr, West C. M. Characterization of FP21, a cytosolic glycoprotein from Dictyostelium. J Biol Chem. 1995 Feb 17;270(7):3022–3030. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.7.3022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreitmeier M., Gerisch G., Heizer C., Müller-Taubenberger A. A talin homologue of Dictyostelium rapidly assembles at the leading edge of cells in response to chemoattractant. J Cell Biol. 1995 Apr;129(1):179–188. doi: 10.1083/jcb.129.1.179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuspa A., Loomis W. F. REMI-RFLP mapping in the Dictyostelium genome. Genetics. 1994 Nov;138(3):665–674. doi: 10.1093/genetics/138.3.665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuspa A., Loomis W. F. Tagging developmental genes in Dictyostelium by restriction enzyme-mediated integration of plasmid DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 15;89(18):8803–8807. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.18.8803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuspa A., Maghakian D., Bergesch P., Loomis W. F. Physical mapping of genes to specific chromosomes in Dictyostelium discoideum. Genomics. 1992 May;13(1):49–61. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90201-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loomis W. F., Welker D., Hughes J., Maghakian D., Kuspa A. Integrated maps of the chromosomes in Dictyostelium discoideum. Genetics. 1995 Sep;141(1):147–157. doi: 10.1093/genetics/141.1.147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaelis C., Weeks G. The isolation from a unicellular organism, Dictyostelium discoideum, of a highly-related cdc2 gene with characteristics of the PCTAIRE subfamily. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Nov 7;1179(2):117–124. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(93)90132-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Taubenberger A., Graack H. R., Grohmann L., Schleicher M., Gerisch G. An extended ubiquitin of Dictyostelium is located in the small ribosomal subunit. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5319–5322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noegel A. A., Gerisch G., Lottspeich F., Schleicher M. A protein with homology to the C-terminal repeat sequence of Octopus rhodopsin and synaptophysin is a member of a multigene family in Dictyostelium discoideum. FEBS Lett. 1990 Jun 18;266(1-2):118–122. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81521-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohmachi T., Giorda R., Shaw D. R., Ennis H. L. Molecular organization of developmentally regulated Dictyostelium discoideum ubiquitin cDNAs. Biochemistry. 1989 Jun 13;28(12):5226–5231. doi: 10.1021/bi00438a046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peffley D. M., Sogin M. L. A putative tRNATrp gene cloned from Dictyostelium discoideum: its nucleotide sequence and association with repetitive deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochemistry. 1981 Jul 7;20(14):4015–4021. doi: 10.1021/bi00517a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutherford C. L., Peery R. B., Sucic J. F., Yin Y. Z., Rogers P. V., Luo S., Selmin O. Cloning, structural analysis, and expression of the glycogen phosphorylase-2 gene in Dictyostelium. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 5;267(4):2294–2302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schauer T. M., Nesper M., Kehl M., Lottspeich F., Müller-Taubenberger A., Gerisch G., Baumeister W. Proteasomes from Dictyostelium discoideum: characterization of structure and function. J Struct Biol. 1993 Sep-Oct;111(2):135–147. doi: 10.1006/jsbi.1993.1044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singleton C. K., Manning S. S., Feng Y. Effect of protein synthesis inhibition on gene expression during early development of Dictyostelium discoideum. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):10–16. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singleton C. K., Manning S. S., Ken R. Primary structure and regulation of vegetative specific genes of Dictyostelium discoideum. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Dec 11;17(23):9679–9692. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.23.9679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tafuri S. R., Rushforth A. M., Kuczmarski E. R., Chisholm R. L. Dictyostelium discoideum myosin: isolation and characterization of cDNAs encoding the regulatory light chain. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;9(7):3073–3080. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.7.3073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Titus M. A., Kuspa A., Loomis W. F. Discovery of myosin genes by physical mapping in Dictyostelium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Sep 27;91(20):9446–9450. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.20.9446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Triviños-Lagos L., Ohmachi T., Albrightson C., Burns R. G., Ennis H. L., Chisholm R. L. The highly divergent alpha- and beta-tubulins from Dictyostelium discoideum are encoded by single genes. J Cell Sci. 1993 Aug;105(Pt 4):903–911. doi: 10.1242/jcs.105.4.903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Hostos E. L., Bradtke B., Lottspeich F., Gerisch G. Coactosin, a 17 kDa F-actin binding protein from Dictyostelium discoideum. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1993;26(3):181–191. doi: 10.1002/cm.970260302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Hostos E. L., Bradtke B., Lottspeich F., Guggenheim R., Gerisch G. Coronin, an actin binding protein of Dictyostelium discoideum localized to cell surface projections, has sequence similarities to G protein beta subunits. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(13):4097–4104. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04986.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



