Abstract
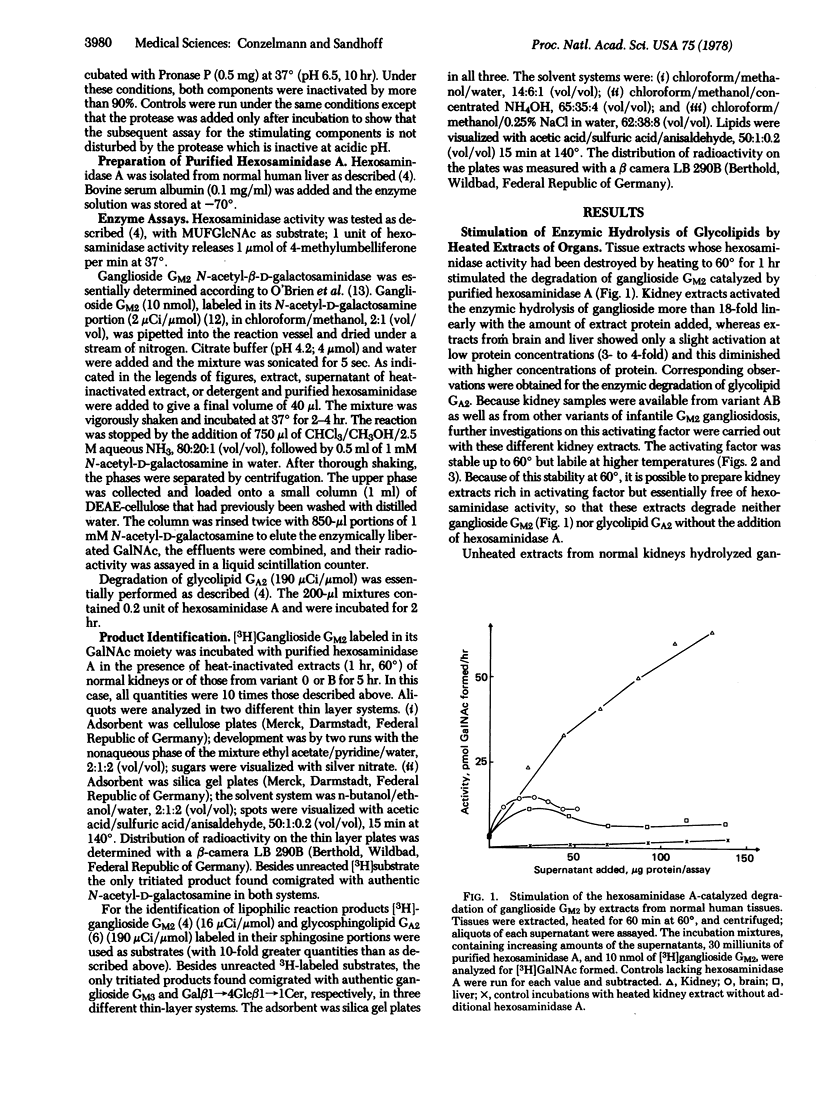
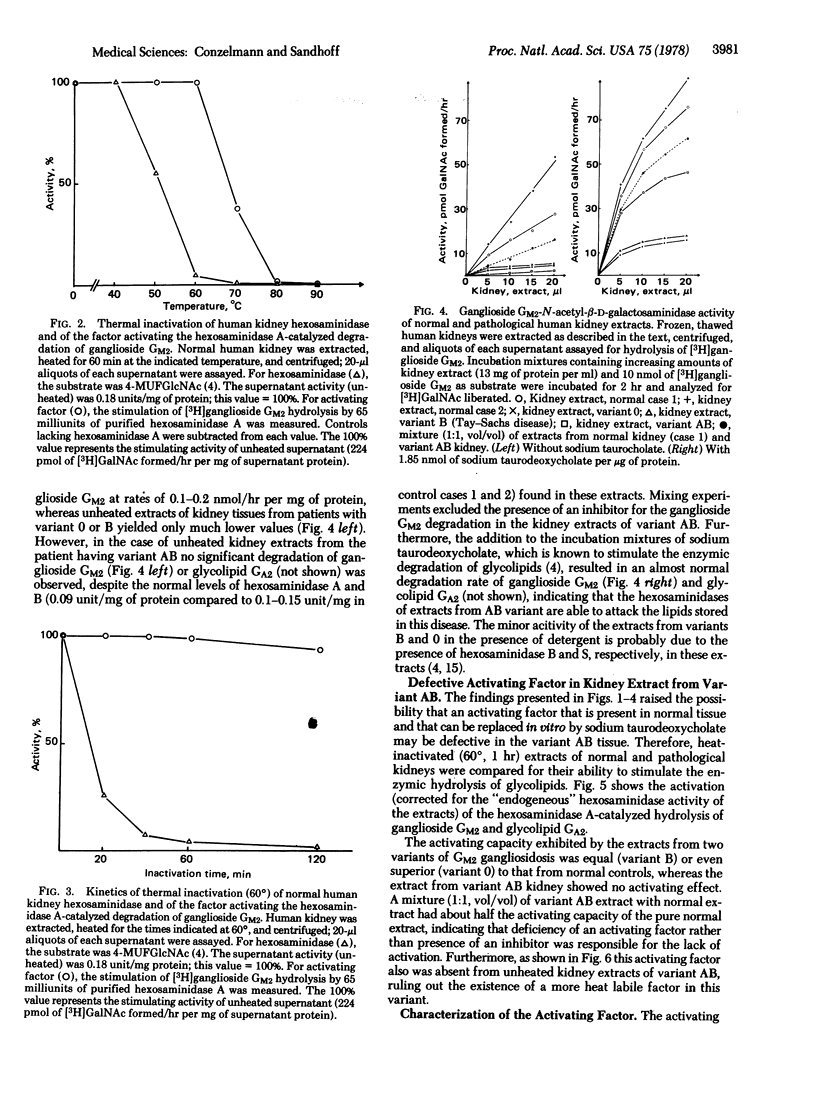
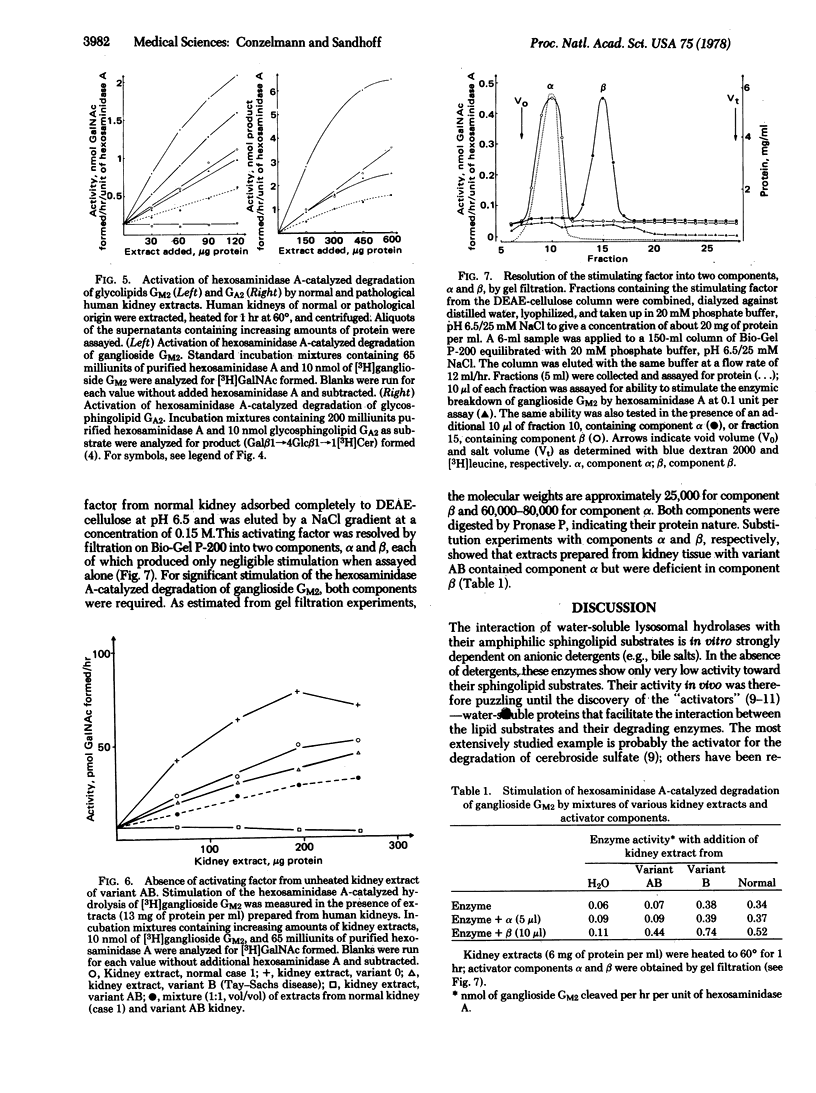
Human kidney extracts heated to 60 degrees and devoid of hexosaminidase activity (2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucoside acetamidodeoxyglucohydrolase EC 3.2.1.30) stimulate more than 20-fold the hexosaminidase A-catalyzed degradation of ganglioside GM2 and of glycolipid GA2, the neuronal storage compounds of GM2 gangliosidosis. The stimulating factor of this extract, which is labile at temperatures above 60 degrees, is also present in kidney extracts from patients with infantile GM2 gangliosidosis having a deficiency of hexosaminidase A (Tay-Sachs disease, variant B) and a deficiency of hexosaminidases A and B (variant 0). Evidence is presented that this factor is defective in the AB-variant of infantile GM2 gangliosidosis which is characterized by an accumulation of glycolipids GM2 and GA2 despite the fact that the degrading enzymes, hexosaminidases A and B, retain normal activity levels. Thus, variant AB is an example of a fatal lipid storage disease that is caused not by a defect of a degrading enzyme but rather by a defective factor necessary for the interaction of lipid substrates and the water-soluble hydrolase.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Conzelmann E., Sandhoff K., Nehrkorn H., Geiger B., Arnon R. Purification, biochemical and immunological characterisation of hexosaminidase A from variant AB of infantile GM2 gangliosidosis. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Mar;84(1):27–33. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12137.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer G., Jatzkewitz H. The activator of cerebroside sulphatase. Purification from human liver and identification as a protein. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1975 May;356(5):605–613. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1975.356.1.605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiger B., Arnon R. Chemical characterization and subunit structure of human N-acetylhexosaminidases A and B. Biochemistry. 1976 Aug 10;15(16):3484–3493. doi: 10.1021/bi00661a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiger B., Arnon R., Sandhoff K. Immunochemical and biochemical investigation of hexosaminidase S. Am J Hum Genet. 1977 Sep;29(5):508–522. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hechtman P. Characterization of an activating factor required for hydrolysis of Gm2 ganglioside catalyzed by hexosaminidase A. Can J Biochem. 1977 Apr;55(4):315–324. doi: 10.1139/o77-044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hechtman P., LeBlanc D. Purification and properties of the hexosaminidase A-activating protein from human liver. Biochem J. 1977 Dec 1;167(3):693–701. doi: 10.1042/bj1670693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho M. W., O'Brien J. S. Gaucher's disease: deficiency of 'acid' -glucosidase and reconstitution of enzyme activity in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Nov;68(11):2810–2813. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.11.2810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien J. S., Norden G. W., Miller A. L., Frost R. G., Kelly T. E. Ganglioside GM2 N-acetyl-beta-D-galactosaminidase and asialo GM2 (GA2) N-acetyl-beta-D-galactosaminidase; studies in human skin fibroblasts. Clin Genet. 1977 Mar;11(3):171–183. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1977.tb01296.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada S., O'Brien J. S. Tay-Sachs disease: generalized absence of a beta-D-N-acetylhexosaminidase component. Science. 1969 Aug 15;165(3894):698–700. doi: 10.1126/science.165.3894.698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandhoff K., Andreae U., Jatzkewitz H. Deficient hexosaminidase activity in an exceptional case of Tay-Sachs disease with additional storage of kidney globoside in visceral organs. Pathol Eur. 1968;3(2):278–285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandhoff K., Conzelmann E., Nehrkorn H. Specificity of human liver hexosaminidases A and B against glycosphingolipids GM2 and GA2. Purification of the enzymes by affinity chromatography employing specific elution. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1977 Jul;358(7):779–787. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1977.358.2.779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandhoff K., Harzer K., Wässle W., Jatzkewitz H. Enzyme alterations and lipid storage in three variants of Tay-Sachs disease. J Neurochem. 1971 Dec;18(12):2469–2489. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1971.tb00204.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandhoff K. The biochemistry of sphingolipid storage diseases. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 1977 May;16(5):273–285. doi: 10.1002/anie.197702733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandhoff K. Variation of beta-N-acetylhexosaminidase-pattern in Tay-Sachs disease. FEBS Lett. 1969 Aug;4(4):351–354. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(69)80274-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



