Abstract
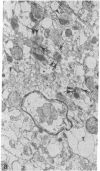
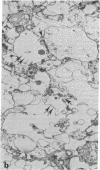
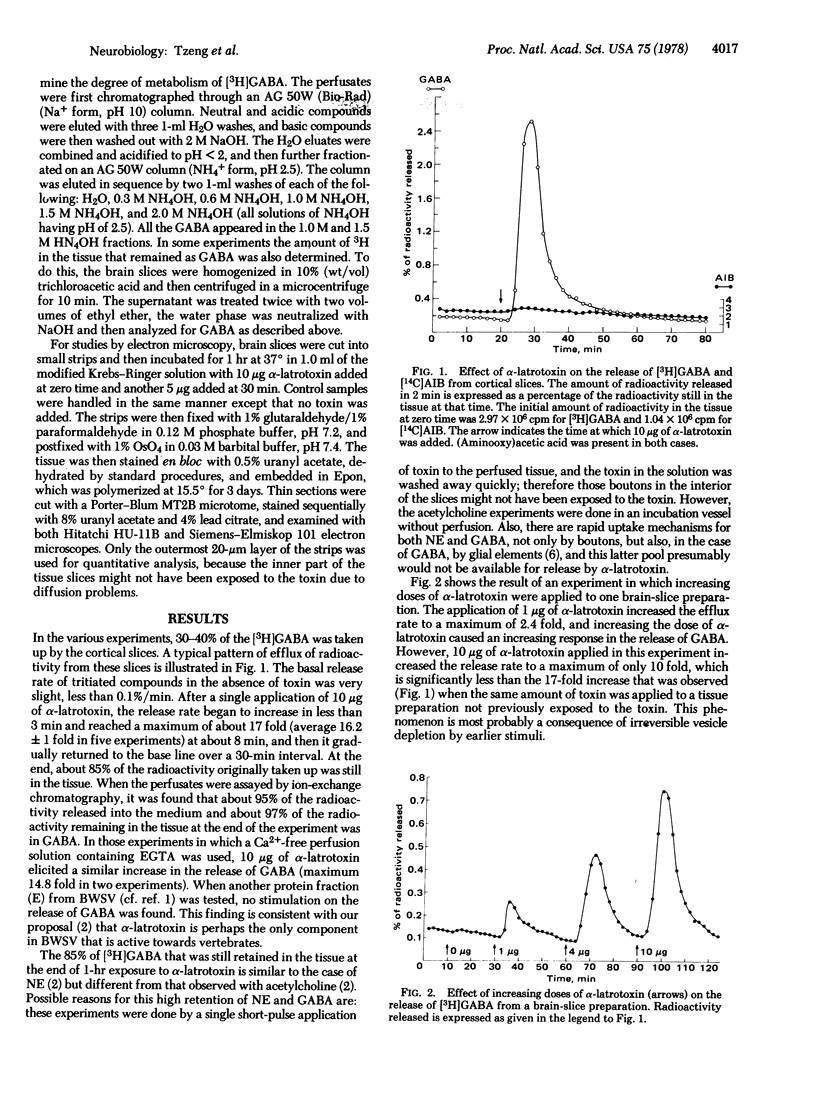
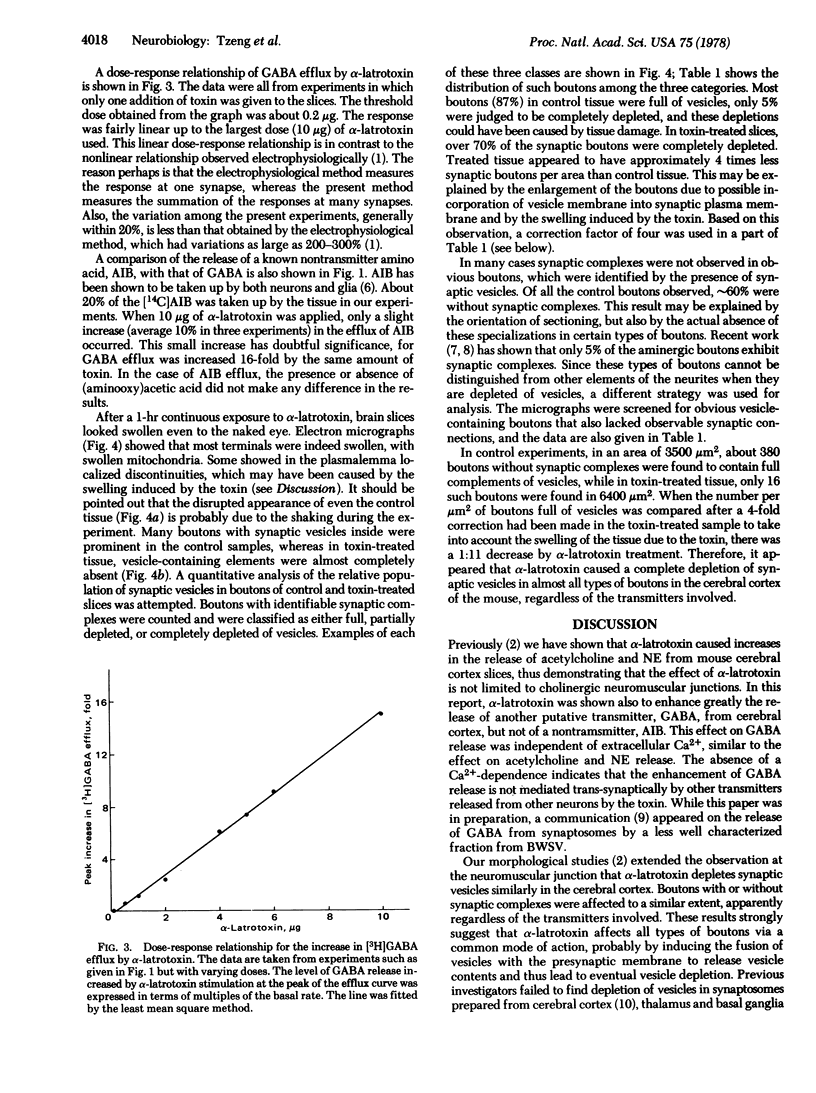
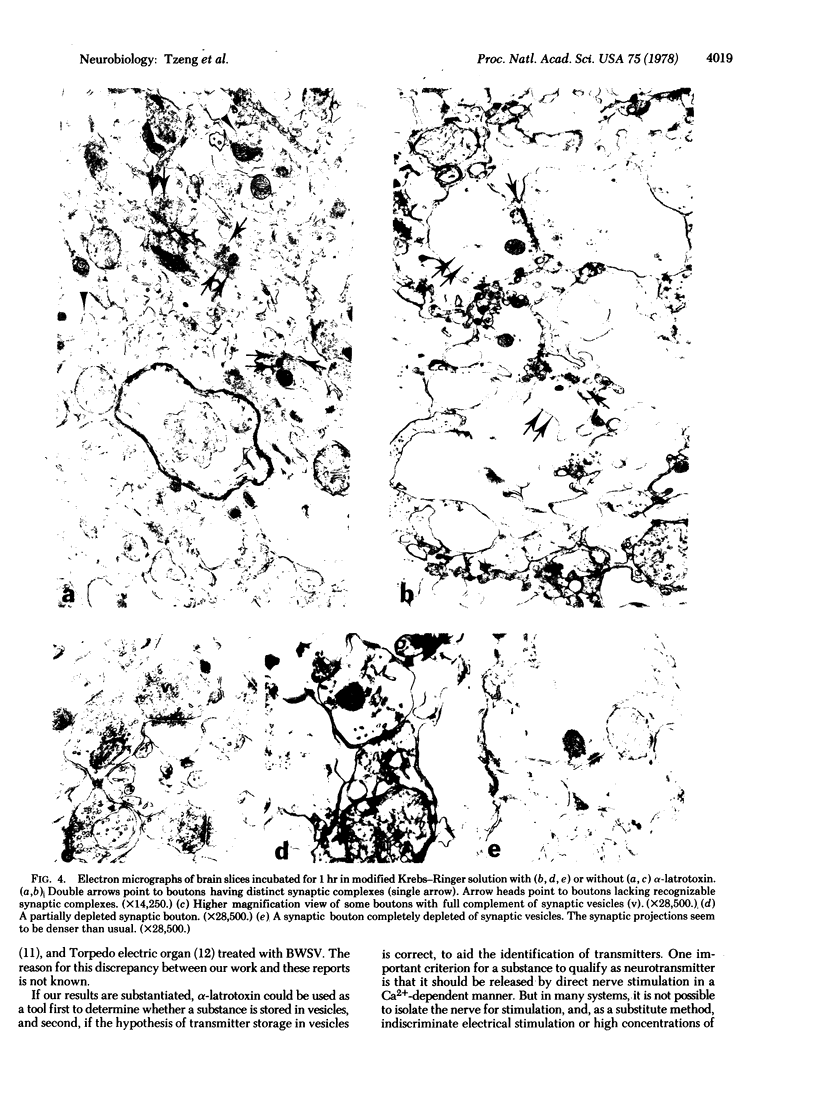
The effect of alpha-latrotoxin on cerebral cortex slices was studied by both biochemical and morphological methods. This toxin greatly stimulates the release of preloaded gamma-amino[3H]butyric acid from cortex slices. The response increases linearly with dose. The release is not dependent on the presence of extracellular Ca2+, and therefore it is not mediated by the release of other transmitters from other types of neurons. In contrast, no significant increase in the release of a nontransmitter substance alpha-amino[14C]isobutyric acid is observed. Since previously we have shown that alpha-latrotoxin stimulated the release of acetylcholine and norepinephrine from cortex slices, it appears that the toxin probably selectively releases all neurotransmitters. The toxin also profoundly depletes the synaptic vesicle population in boutons in the cortex slices. The results suggest that the release of neurotransmitter and the depletion of synaptic vesicle in boutons are manifestations of a single action of the toxin. Therefore, alpha-latrotoxin can be used as a good tool for the identification of neurotransmitters and in studies on the mechanism of neurotransmitter release.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baba A., Sen I., Cooper J. R. The action of black widow spider venom on cholinergic mechanisms in synaptosomal preparations of rat brain cortices. Life Sci. 1977 Mar 1;20(5):833–841. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(77)90035-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark A. W., Hurlbut W. P., Mauro A. Changes in the fine structure of the neuromuscular junction of the frog caused by black widow spider venom. J Cell Biol. 1972 Jan;52(1):1–14. doi: 10.1083/jcb.52.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark A. W., Mauro A., Longenecker H. E., Jr, Hurlbut W. P. Effects of black widow spider venom on the frog neuromuscular junction. Effects on the fine structure of the frog neuromuscular junction. Nature. 1970 Feb 21;225(5234):703–705. doi: 10.1038/225703a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Descarries L., Beaudet A., Watkins K. C. Serotonin nerve terminals in adult rat neocortex. Brain Res. 1975 Dec 26;100(3):563–588. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90158-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Descarries L., Watkins K. C., Lapierre Y. Noradrenergic axon terminals in the cerebral cortex of rat. III. Topometric ultrastructural analysis. Brain Res. 1977 Sep 16;133(2):197–222. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90759-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FINKELSTEIN A., Rubin L. L., Tzeng M. C. Black widow spider venom: effect of purified toxin on lipid bilayer membranes. Science. 1976 Sep 10;193(4257):1009–1011. doi: 10.1126/science.948756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frontali N., Ceccarelli B., Gorio A., Mauro A., Siekevitz P., Tzeng M. C., Hurlbut W. P. Purification from black widow spider venom of a protein factor causing the depletion of synaptic vesicles at neuromuscular junctions. J Cell Biol. 1976 Mar;68(3):462–479. doi: 10.1083/jcb.68.3.462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorio A., Rubin L. L., Mauro A. Double mode of action of black widow spider venom on frog neuromuscular junction. J Neurocytol. 1978 Apr;7(2):193–202. doi: 10.1007/BF01217918. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granata F., Traina M. E., Frontali N., Bertolini B. Effects of black widow spider venom on acetylcholine release from Torpedo electric tissue slices and subcellular fractions in vitro. Comp Biochem Physiol A Comp Physiol. 1974 May 1;48(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/0300-9629(74)90846-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grasso A., Rufini S., Senni I. Concanavalin A blocks black widow spider toxin stimulation of transmitter release from synaptosomes. FEBS Lett. 1978 Jan 15;85(2):241–244. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80464-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamberger A. Amino acid uptake in neuronal and glial cell fractions from rabbit cerebral cortex. Brain Res. 1971 Aug 7;31(1):169–178. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(71)90641-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopkin J., Neal M. J. Effect of electrical stimulation and high potassium concentrations on the effux of (14C) glycine from slices of spinal cord. Br J Pharmacol. 1971 Jun;42(2):215–223. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1971.tb07102.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longenecker H. E., Jr, Hurlbut W. P., Mauro A., Clark A. W. Effects of black widow spider venom on the frog neuromuscular junction. Effects on end-plate potential, miniature end-plate potential and nerve terminal spike. Nature. 1970 Feb 21;225(5234):701–703. doi: 10.1038/225701a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadler J. V., Cooper J. R. Metabolism of the aspartyl moiety of N-acetyl-L-aspartic acid in the rat brain. J Neurochem. 1972 Sep;19(9):2091–2105. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1972.tb05119.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orrego F., Miranda R. Electrically induced release of (3H)GABA from neocortical thin slices. Effects of stimulus waveform and of amino-oxyacetic acid. J Neurochem. 1976 May;26(5):1033–1038. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1976.tb06489.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts P. J. The release of amino acids with proposed neurotransmitter function from the cuneate and gracile nuclei of the rat in vivo. Brain Res. 1974 Mar 8;67(3):419–428. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)90491-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sellström A., Hamberger A. Potassium-stimulated gamma-aminobutyric acid release from neurons and glia. Brain Res. 1977 Jan 1;119(1):189–198. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90099-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. E., Clark A. W., Kuster T. A. Suppression by elevated calcium of black widow spider venom activity at frog neuromuscular junctions. J Neurocytol. 1977 Oct;6(5):519–539. doi: 10.1007/BF01205217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzeng M. C., Siekevitz P. The effect of the purified major protein factor (alpha-latrotoxin) of black widow spider venom on the release of acetylcholine and norepinephrine from mouse cerebral cortex slices. Brain Res. 1978 Jan 6;139(1):190–196. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90073-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Gelder N. M. The effect of aminooxyacetic acid on the metabolism of gamma-aminobutyric acid in brain. Biochem Pharmacol. 1966 May;15(5):533–539. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(66)90019-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vargas O., Orrego F. Elevated extracellular potassium as a stimulus for releasing [EH] norepinephrine and [14C] alpha-amino isobutyrate from neocortical slice. Specificity and calcium dependency of the process. J Neurochem. 1976 Jan;26(1):31–34. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1976.tb04431.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wernicke J. F., Vanker A. D., Howard B. D. The mechanism of action of beta-bungarotoxin. J Neurochem. 1975 Oct;25(4):483–496. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1975.tb04354.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]