Abstract
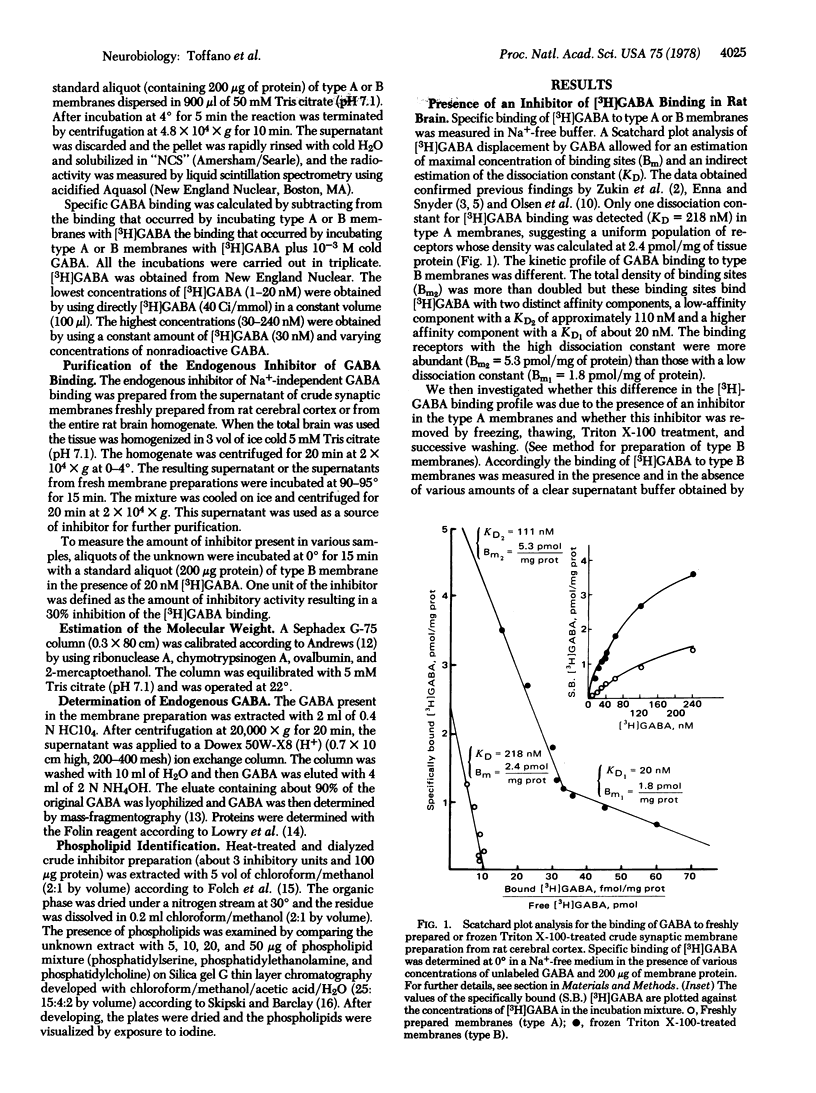
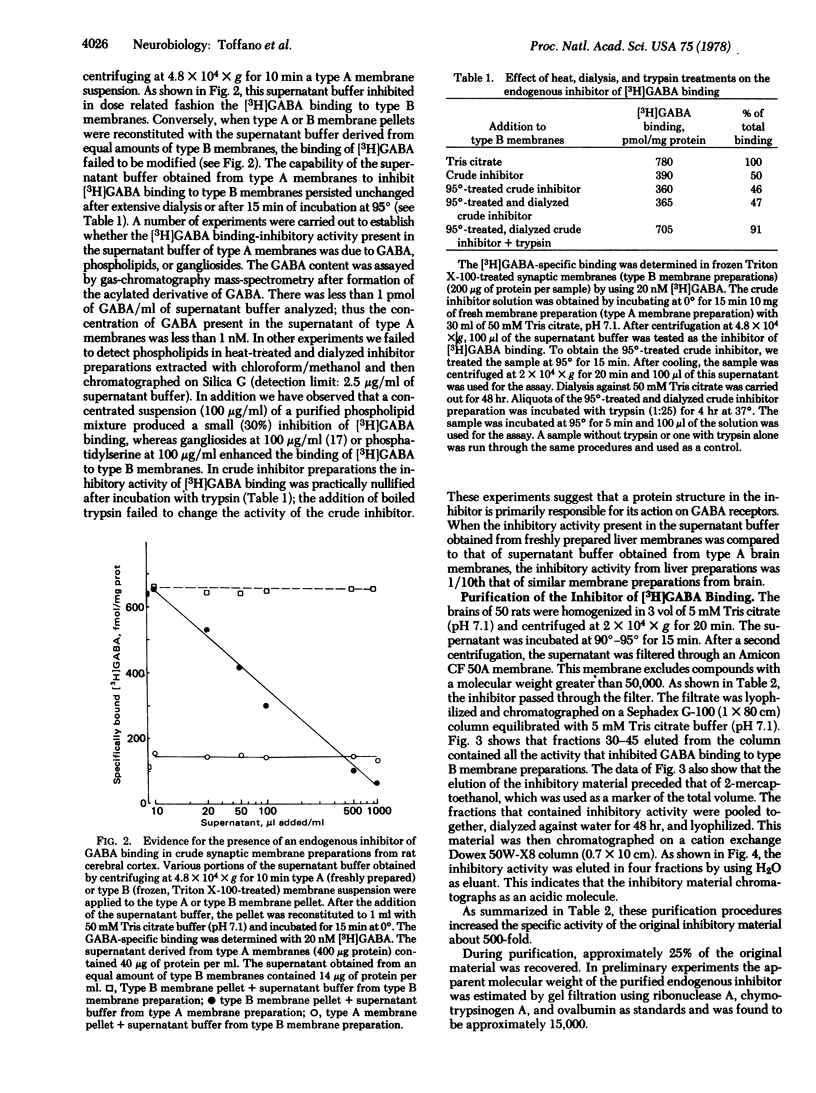
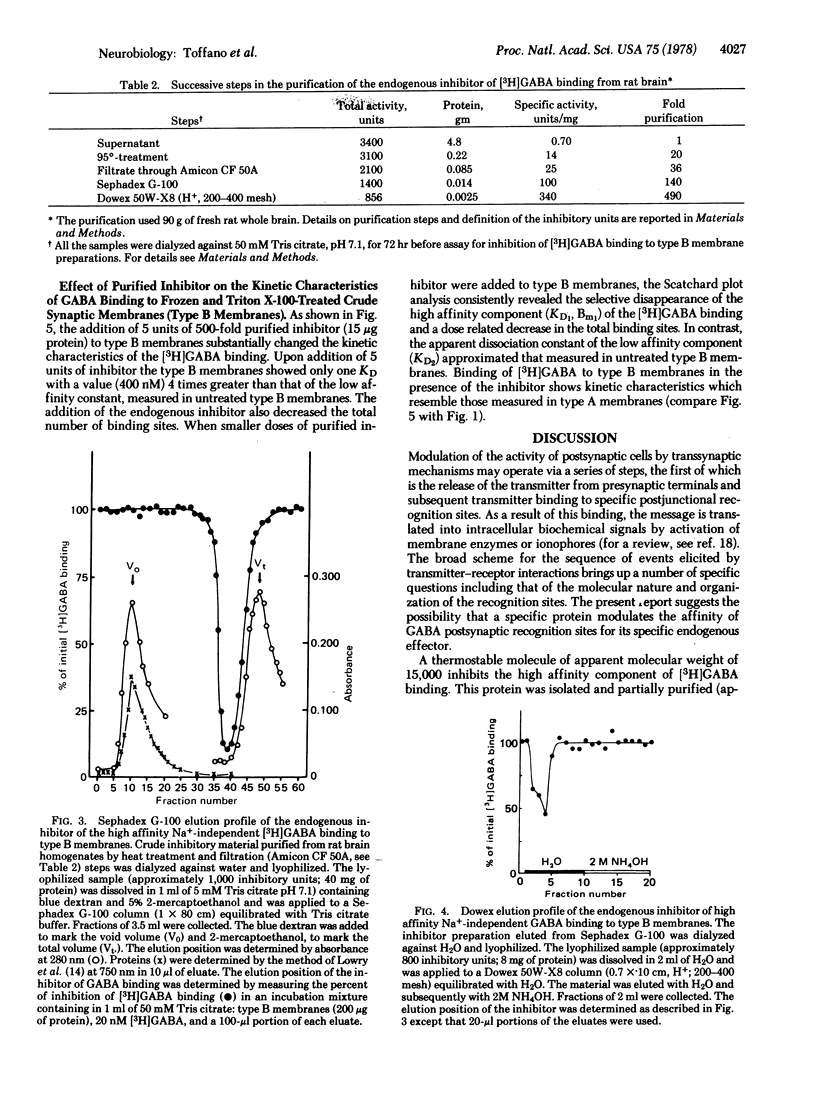
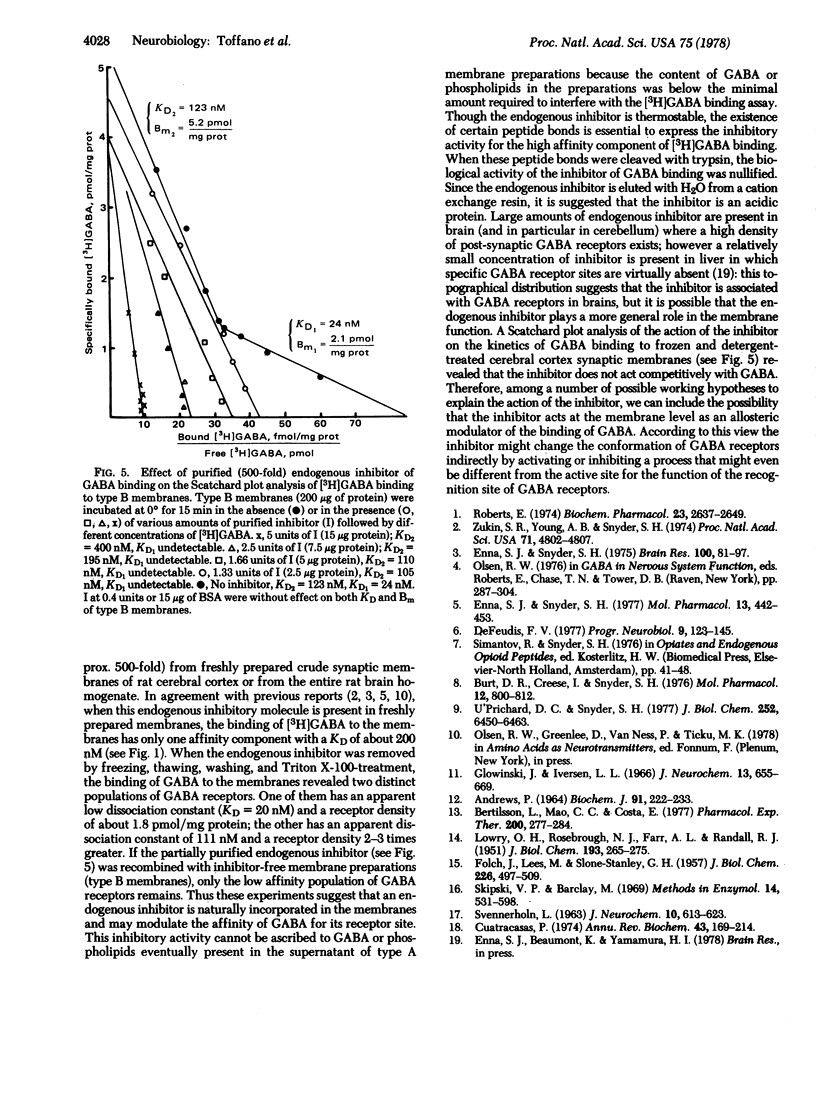
In a medium without Na+, gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) binds at 0 degrees to freshly prepared crude synaptic membranes from rat cerebral cortex with an apparent dissociation constant of 218 nM. An endogenous inhibitor of the Na+-independent GABA binding was removed from these membranes by freezing and thawing and by repeated washing with Tris citrate buffer (50 mM, pH 7.1) containing 0.01% Triton X-100. As a result, the crude synaptic membranes bind GABA at 0 degrees with two dissociation constants, 20 nM and 111 nM. The endogenous inhibitor is a thermostable (95 degrees for 15 min) acidic protein of approximately 1.5 X 10(4) daltons. It was purified (about 500-fold) with a series of procedures including gel chromatography on Sephadex G-100 and ion exchange chromatography on Dowex 50W-X8 (H+). Recombination of the purified endogenous inhibitor with crude synaptic membrane preparations deprived of the endogenous inhibitor showed that the purified inhibitor blocked noncompetitively the sites for high-affinity GABA binding. A role of this endogenous regulator in the functional of GABA-ergic synapses is discussed.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews P. Estimation of the molecular weights of proteins by Sephadex gel-filtration. Biochem J. 1964 May;91(2):222–233. doi: 10.1042/bj0910222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertilsson L., Mao C. C., Costa E. Application of principles of steady-state kinetics to the estimation of gamma-aminobutyric acid turnover rate in nuclei of rat brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1977 Feb;200(2):277–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burt D. R., Creese I., Snyder S. H. Properties of [3H]haloperidol and [3H]dopamine binding associated with dopamine receptors in calf brain membranes. Mol Pharmacol. 1976 Sep;12(5):800–812. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enna S. J., Snyder S. H. Influences ions, enzymes, and detergents on gamma-aminobutyric acid-receptor binding in synaptic membranes of rat brain. Mol Pharmacol. 1977 May;13(3):442–453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enna S. J., Snyder S. H. Properties of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) receptor binding in rat brain synaptic membrane fractions. Brain Res. 1975 Dec 12;100(1):81–97. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90243-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., LEES M., SLOANE STANLEY G. H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glowinski J., Iversen L. L. Regional studies of catecholamines in the rat brain. I. The disposition of [3H]norepinephrine, [3H]dopamine and [3H]dopa in various regions of the brain. J Neurochem. 1966 Aug;13(8):655–669. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1966.tb09873.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts E. Gamma-aminobutyric acid and nervous system function--a perspective. Biochem Pharmacol. 1974 Oct 1;23(19):2637–2649. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(74)90033-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SVENNERHOLM L. CHROMATOGRAPHIC SEPARATION OF HUMAN BRAIN GANGLIOSIDES. J Neurochem. 1963 Sep;10:613–623. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1963.tb08933.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- U'Prichard D. C., Snyder S. H. Binding of 3H-catecholamines to alpha-noradrenergic receptor sites in calf brain. J Biol Chem. 1977 Sep 25;252(18):6450–6463. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zukin S. R., Young A. B., Snyder S. H. Gamma-aminobutyric acid binding to receptor sites in the rat central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Dec;71(12):4802–4807. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.12.4802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


