Abstract
Various lipids extracted from bovine thyroid glands were tested for their ability to affect the binding of 125I-labeled thyrotropin to bovine thyroid membranes. The most potent inhibitors were the acidic phospholipids in the order cardiolipin greater than phosphatidylglycerol greater than phosphatidylinositol greater than phosphatidylserine. Other phospholipids, neutral lipids, and neutral glycolipids were ineffective. As reported previously [mullin, B. R., Pacuszka, T., Lee, G., Kohn, L. D., Brady, R. O. & Fishman, P. H. (1978) Science 199, 77--79], thyroid gangliosides also inhibited thyrotropin binding but not as effectively as phospholipids. In addition, the mode of action of these two classes of acidic lipids was different. When thyroid membranes were preincubated with the phospholipids and then separated by centrifugation, their ability to bind thyrotropin was still diminished. In contrast, gangliosides appear to interact with the hormone and not with the membranes. The effect of phospholipids on thyroid membranes was further examined by incubating the membranes with phospholipase A. The treated membranes now bound more labeled hormone. These results suggest that certain acidic phospholipids, which are present in only small amounts in thyroid membranes, influence the state of the thyrotropin receptor and its ability to bind thyrotropin.
Full text
PDF
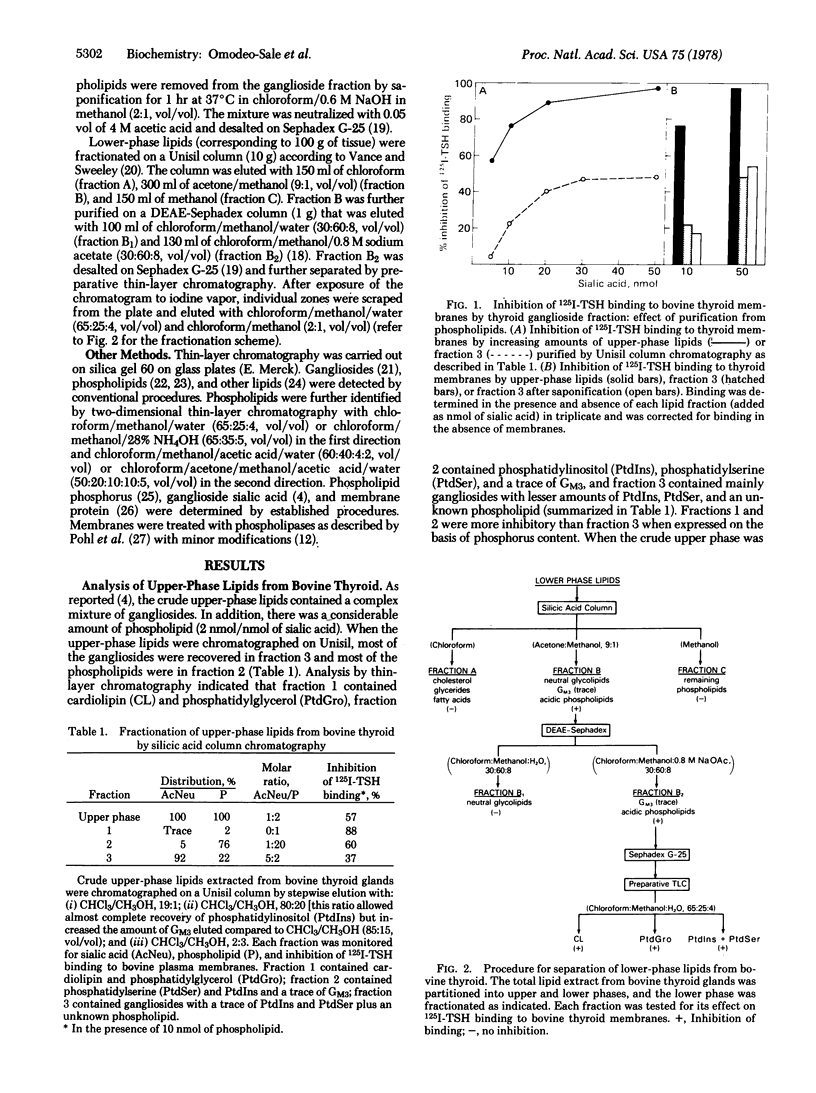


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aloj S. M., Kohn L. D., Lee G., Meldolesi M. F. The binding of thyrotropin to liposomes containing gangliosides. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Feb 7;74(3):1053–1059. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91624-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amir S. M., Goldfine I. D., Ingbar S. H. Properties of the interaction between bovine thyrotropin and bovine thyroid plasma membranes. J Biol Chem. 1976 Aug 10;251(15):4693–4699. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borochov H., Shinitzky M. Vertical displacement of membrane proteins mediated by changes in microviscosity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Dec;73(12):4526–4530. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.12.4526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishman P. H., Aloj S. M., Kohn L. D., Brady R. O. Relationship of gangliosides to the structure and function of thyrotropin receptors: their absence on plasma membranes of a thyroid tumor defective in thyrotropin receptor activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):4060–4064. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.4060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishman P. H., Bradley R. M., Henneberry R. C. Butyrate-induced glycolipid biosynthesis in HeLa cells: properties of the induced sialyltransferase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 Feb;172(2):618–626. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90116-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishman P. H., Brady R. O. Biosynthesis and function of gangliosides. Science. 1976 Nov 26;194(4268):906–915. doi: 10.1126/science.185697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishman P. H., Moss J., Osborne J. C., Jr Interaction of choleragen with the oligosaccharide of ganglioside GM1: evidence for multiple oligosaccharide binding sites. Biochemistry. 1978 Feb 21;17(4):711–716. doi: 10.1021/bi00597a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haye B., Jacquemin Cl. Interaction de la thyreostimuline avec ses recepteurs cellulaires: Effet de la phospholipase C sur la fixation et l'activité biologique. FEBS Lett. 1971 Oct 15;18(1):47–52. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80403-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurosky A., Markel D. E., Peterson J. W., Fitch W. M. Primary structure of cholera toxin beta-chain: a glycoprotein hormone analog? Science. 1977 Jan 21;195(4275):299–301. doi: 10.1126/science.831277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledley F. D., Mullin B. R., Lee G., Aloj S. M., Fishman P. H., Hunt L. T., Dayhoff M. O., Kohn L. D. Sequence similarity between cholera toxin and glycoprotein hormones: implications for structure activity relationship and mechanism of action. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Apr 19;69(4):852–859. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90452-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levey G. S., Fletcher M. A., Klein I. Glucagon and adenylate cyclase: binding studies and requirements for activation. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1975;5:53–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levis G. M., Karli J. N., Malamos B. The phospholipids of the thyroid gland. Clin Chim Acta. 1972 Oct;41:335–345. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(72)90529-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARINETTI G. V., ERBLAND J., STOTZ E. Phosphatides of pig heart cell fractions. J Biol Chem. 1958 Sep;233(3):562–565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macchia V., Tamburrini O., Pastan I. Role of lecithin in the mechanism of TSH action. Endocrinology. 1970 Apr;86(4):787–792. doi: 10.1210/endo-86-4-787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mashiter K., Mashiter G. D., Hauger R. L., Field J. B. Effects of cholera and E. coli enterotoxins on cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate levels and intermediary metabolism in the thyroid. Endocrinology. 1973 Feb;92(2):541–549. doi: 10.1210/endo-92-2-541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore W. V., Wolff J. Thyroid-stimulating hormone binding to beef thyroid membranes. Relation to adenylate cyclase activity. J Biol Chem. 1974 Oct 10;249(19):6255–6263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullin B. R., Aloj S. M., Fishman P. H., Lee G., Kohn L. D., Brady R. O. Cholera toxin interactions with thyrotropin receptors on thyroid plasma membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 May;73(5):1679–1683. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.5.1679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullin B. R., Fishman P. H., Lee G., Aloj S. M., Ledley F. D., Winand R. J., Kohn L. D., Brady R. O. Thyrotropin-ganglioside interactions and their relationship to the structure and function of thyrotropin receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Mar;73(3):842–846. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.3.842. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullin B. R., Pacuszka T., Lee G., Kohn L. D., Brady R. O., Fishman P. H. Thyroid gangliosides with high affinity for thyrotropin: potential role in thyroid regulation. Science. 1978 Jan 6;199(4324):77–79. doi: 10.1126/science.199.4324.77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pacuszka T., Osborne J. C., Jr, Brady R. O., Fishman P. H. Interaction of human chorionic gonadotropin with membrane components of rat testes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Feb;75(2):764–768. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.2.764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pohl S. L., Birnbaumer L., Rodbell M. The glucagon-sensitive adenyl cyclase system in plasma membranes of rat liver. I. Properties. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 25;246(6):1849–1856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pohl S. L., Krans H. M., Kozyreff V., Birnbaumer L., Rodbell M. The glucagon-sensitive adenyl cyclase system in plasma membranes of rat liver. VI. Evidence for a role of membrane lipids. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jul 25;246(14):4447–4454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubalcava B., Rodbell M. The role of acidic phospholipids in glucagon action on rat liver adenylate cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jun 10;248(11):3831–3837. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SVENNERHOLM L. Quantitative estimation of sialic acids. II. A colorimetric resorcinol-hydrochloric acid method. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1957 Jun;24(3):604–611. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(57)90254-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satyaswaroop P. G. Lipids of bovine thyroid. Lipids. 1971 Sep;6(9):661–665. doi: 10.1007/BF02531526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharom F. J., Grant C. W. A model for ganglioside behaviour in cell membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Feb 21;507(2):280–293. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90423-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skipski V. P., Peterson R. F., Barclay M. Quantitative analysis of phospholipids by thin-layer chromatography. Biochem J. 1964 Feb;90(2):374–378. doi: 10.1042/bj0900374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vance D. E., Sweeley C. C. Quantitative determination of the neutral glycosyl ceramides in human blood. J Lipid Res. 1967 Nov;8(6):621–630. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaskovsky V. E., Svetashev V. I. Phospholipid spray reagents. J Chromatogr. 1972 Feb 23;65(2):451–453. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)92571-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff J., Jones A. B. The purification of bovine thyroid plasma membranes and the properties of membrane-bound adenyl cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jun 25;246(12):3939–3947. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita K., Bloom G., Rainard B., Zor U., Field J. B. Effects of chlorpromazine, propranolol and phospholipase C on thyrotropin and prostaglandin stimulation of adenyl cyclase-cyclic AMP system in dog thyroid slices. Metabolism. 1970 Dec;19(12):1109–1118. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(70)90036-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita K., Field J. B. The role of phospholipids in TSH stimulation of adenylate cyclase in thyroid plasma membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 May 28;304(3):686–692. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(73)90213-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu R. K., Ledeen R. W. Gangliosides of human, bovine, and rabbit plasma. J Lipid Res. 1972 Sep;13(5):680–686. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]