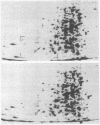
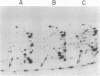
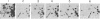Abstract
A component of high-affinity histidine transport in Salmonella typhimurium has been identified. It is a basic (pI about 9.0) membrane-bound protein, the P protein. It is shown to be coded for by the distal half of the previously described hisP gene by analysis of numerous hisP mutants, two of which exhibit P proteins with altered electrophoretic mobilities. Upon separation of the cytoplasmic (inner) from the outer membrane, it can be shown that the P protein is located in the cytoplasmic membrane. The P protein is under the same regulatory controls as histidine transport--i.e., transport operon promoter dhuA and nitrogen regulation. A wild-type cell contains about 200 molecules of P protein. As a result of this work we now divide the hisP gene into two genes: the hisP gene proper and the hisQ gene, which codes for another essential component of histidine transport, the Q protein. The P protein was shown previously by genetic analysis to interact with the periplasmic histidine-binding protein J, another essential component of histidine transport. Possible mechanism for the interaction of the J, P, and Q components in histidine transport, and of P and Q in lysine/arginine/ornithine transport, are discussed.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMES G. F. UPTAKE OF AMINO ACIDS BY SALMONELLA TYPHIMURIUM. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1964 Jan;104:1–18. doi: 10.1016/s0003-9861(64)80028-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ames G. F., Lever J. Components of histidine transport: histidine-binding proteins and hisP protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Aug;66(4):1096–1103. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.4.1096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ames G. F., Nikaido K. Two-dimensional gel electrophoresis of membrane proteins. Biochemistry. 1976 Feb 10;15(3):616–623. doi: 10.1021/bi00648a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ames G. F., Noel K. D., Taber H., Spudich E. N., Nikaido K., Afong J. Fine-structure map of the histidine transport genes in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1977 Mar;129(3):1289–1297. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.3.1289-1297.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ames G. F. Resolution of bacterial proteins by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis on slabs. Membrane, soluble, and periplasmic fractions. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jan 25;249(2):634–644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ames G. F., Spudich E. N., Nikaido H. Protein composition of the outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium: effect of lipopolysaccharide mutations. J Bacteriol. 1974 Feb;117(2):406–416. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.2.406-416.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ames G. F., Spurich E. N. Protein-protein interaction in transport: periplasmic histidine-binding protein J interacts with P protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jun;73(6):1877–1881. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.6.1877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boos W. Bacterial transport. Annu Rev Biochem. 1974;43(0):123–146. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.43.070174.001011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox C. F., Carter J. R., Kennedy E. P. GENETIC CONTROL OF THE MEMBRANE PROTEIN COMPONENT OF THE LACTOSE TRANSPORT SYSTEM OF Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Mar;57(3):698–705. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.3.698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata H., Sone N., Yoshida M., Kagawa Y. Isolation of the alanine carrier from the membranes of a thermophilic bacterium and its reconstitution into vesicles capable of transport. J Supramol Struct. 1977;6(1):77–84. doi: 10.1002/jss.400060106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy E. P., Rumley M. K., Armstrong J. B. Dierect measurement of the binding of labeled sugars to the lactose permease M protein. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jan 10;249(1):33–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kustu S. G., Ames G. F. The hisP protein, a known histidine transport component in Salmonella typhimurium, is also an arginine transport component. J Bacteriol. 1973 Oct;116(1):107–113. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.1.107-113.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kustu S. G., Ames G. F. The histidine-binding protein J, a histidine transport component, has two different functional sites. J Biol Chem. 1974 Nov 10;249(21):6976–6983. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lever J. E. Purification and properties of a component of histidine transport in Salmonella typhimurium. The histidine-binding protein J. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jul 10;247(13):4317–4326. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo T. C. The molecular mechanism of dicarboxylic acid transport in Escherichia coli K 12. J Supramol Struct. 1977;7(3-4):463–480. doi: 10.1002/jss.400070316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. Z., Goodman H. M., O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of basic as well as acidic proteins. Cell. 1977 Dec;12(4):1133–1141. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90176-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson K. E., Hartman P. E. Linkage map of Salmonella typhimurium, edition V. Microbiol Rev. 1978 Jun;42(2):471–519. doi: 10.1128/mr.42.2.471-519.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer S. J. The molecular organization of membranes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1974;43(0):805–833. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.43.070174.004105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smit J., Kamio Y., Nikaido H. Outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium: chemical analysis and freeze-fracture studies with lipopolysaccharide mutants. J Bacteriol. 1975 Nov;124(2):942–958. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.2.942-958.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strange P. G., Koshland D. E., Jr Receptor interactions in a signalling system: competition between ribose receptor and galactose receptor in the chemotaxis response. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Mar;73(3):762–766. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.3.762. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teather R. M., Müller-Hill B., Abrutsch U., Aichele G., Overath P. Amplification of the lactose carrier protein in Escherichia coli using a plasmid vector. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 Feb 27;159(3):239–248. doi: 10.1007/BF00268260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willis R. C., Furlong C. E. Purification and properties of a periplasmic glutamate-aspartate binding protein from Escherichia coli K12 strain W3092. J Biol Chem. 1975 Apr 10;250(7):2574–2580. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittenberg J. B. Myoglobin-facilitated oxygen diffusion: role of myoglobin in oxygen entry into muscle. Physiol Rev. 1970 Oct;50(4):559–636. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1970.50.4.559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]